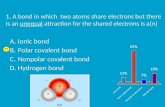
HONORS BIOLOGY. What is an ionic bond? How does a hydrogen bond form? Organize the following in the...
-
Upload
katrina-sims -
Category
Documents
-
view
212 -
download
0
Transcript of HONORS BIOLOGY. What is an ionic bond? How does a hydrogen bond form? Organize the following in the...

MIDTERM REVIEW QUESTIONSHONORS BIOLOGY

What is an ionic bond?How does a hydrogen bond form?Organize the following in the correct level of
organization by increasing size:CellMacromoleculeEcosystemPopulationAtomCommunityTissueOrgan system

Describe the causes and biological relevance of the following properties of water:High surface tensionHigh heat capacityIce is less dense than waterHigh cohesion and adhesion
Draw 4 connected water molecules and label their bonds.
Give an example of a biological process that produces water.
Give an example of a biological process that uses water.

Describe the characteristics of acidsWhat is an indicator? Give an example.Define what an organic substance is.What is a monomer? What are the monomers
of the following:CarbohydratesSimple lipidsPhospholipidsProteinsNucleic acids
What are the functions of the following:MonosaccharidesStarchPhospholipids
Define what an enzyme is.

What is denaturation? What causes it?What are the benefits and disadvantages of
light microscopes?What are the functions of the following
organelles:MicrofilamentRough ERSmooth ERGolgi apparatus
Draw the cell membrane and label its parts.What kind of transport would be used for:
Moving a Mg ion from high to low concentration through a protein
Moving a sucrose from low to high concentration

Compare and contrast plant cells and animal cell
Compare and contrast mitochondria and chloroplasts
List five functions of proteins.Describe the primary and secondary
structures of proteinsDraw and label the parts of the cell
membraneDefine passive transport and list its types.Describe through an example how active
transport takes place.What type of transport would a cell use to
engulf a bacterium?State the first law of thermodynamics

What part of the microscope would be used to:Hold the slide glass and cover slipProvide the highest possible magnificationTo control the amount of light that hits the
specimenTo hold the slide glass on the microscope
State the purpose, location and parts of cellular respiration.
Explain why a H+ concentration difference is significant in cellular respiration and photosynthesis.
If a poison stops the enzyme that normally binds CO2 to RuBP during the Calvin cycle. What are the consequences of this change?