Gear Train
description
Transcript of Gear Train

Gear Train

Three-Speed Transmission

Synchronizers cone clutch f
Before the teeth can engage, the cone clutch engages first, which brings the selector and gear to the same speed using friction.

First Gear

Second Gear

Third Gear (Direct Gear)

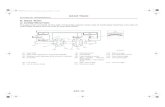
Shown below is a three- speed transmission. Gears 4,5 and 6 are free to spin about their shaft, while gears 3,7,8,9,10 and 11 are keyed to their respective shafts. Gear 10 is an idler gear whose centre is not in line with those of gears 6 and 11. C1 and C2 are synchronizers that fix one gear to the shaft each time, so power is transmitted from the input shaft to the output shaft.
Idler gear 10: reverses the direction of rotation without changing the gear ratio

Assume the following parameters:All gears have a diametral pitch
p=12center –to –center distance between
input shaft and counter shaft C=4 inapproximate speed ratios first gear e1=0.2, second gear
e2=0.51, third gear e3=1, reverse er=-0.22
idler gear: number of teeth =16, pitch diameterD10= D6/3, centre- to centre distance C10/11=2 in
drive
driven
wew
1in


Questions:
(1)Calculate the gears’ teeth number
(2)Calculate the gears’ diameters

Solution:Because all gears are to have the
same module and meshing gears must share a common center –to –center distance,
3 7 4 8 5 9C r r r r r r
3 7 4 8 5 9
2 2 2d d d d d d
C
r is pitch radiusd is pitch diameter

We know that the relationship between the number of teeth and the pitch diameter is
Ndp
where P is the diametral pitch.
3 7 4 8 5 92 2*12*4 96pC N N N N N N
3 7
4 8
5 9
969696
N NN NN N
3 9 7 51
7 5 7 5
(96 )(96 )0.2
N N N Ne
N N N N
The first gear speed ration is (1)drive
driven
wew

The second gear speed ration is 3 8 7 4
27 4 7 4
(96 )(96 ) 0.51N N N NeN N N N
(2)
The reverse gear speed ration is
3 10 7 1111
7 10 6 7 6
(96 )* * 0.22revN N N NNeN N N N N
(3)

From (1), (2), (3),we can get:
27
57 7
96 960.2 96
NN
N N
27
47 7
96 960.51 96
NNN N
11
76 11
960.22
NNN N
10 6
1010 10 6
66
13
13
D D
Nd N NpNdp
10 16N
6 3*16 48N
10 11 10 1110/11 10 11 2 2
d d N NC r rp
Nd
p
11 10/11 102 48 16 32( )N pC N teeth

117
6 11
27
57 7
27
47 7
96 72.18 720.22
96 96 600.2 96
96 96 37.9 380.51 96
NN teethN N
NNN N
NN teethN N
3 7
4 8
5 9
969696
N NN NN N
3 7
8 4
9 5
96 96 72 2496 96 38 5896 96 60 36
N N teethN N teethN N teeth
3 7 4 8 5 92 2*12*4 96pC N N N N N N

Ndp
Calculate gear diameters
33
44
55
66
77
24 21238 3.1671260 51248 41272 612
Nd inpNd inpNd inpN
d inpN
d inp
88
99
10 6
1111
58 4.8331236 312
1 4 1.333 3
32 2.66712
Nd in
pN
d inp
d d in
Nd inp