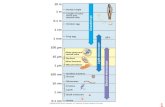
Fig. 6-2 10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm 1 mm 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm 1 nm 0.1 nm Atoms Small...
-
Upload
estella-york -
Category
Documents
-
view
236 -
download
2
Transcript of Fig. 6-2 10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm 1 mm 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm 1 nm 0.1 nm Atoms Small...
Fig. 6-210 m
1 m
0.1 m
1 cm
1 mm
100 µm
10 µm
1 µm
100 nm
10 nm
1 nm
0.1 nm Atoms
Small molecules
Lipids
Proteins
Ribosomes
Viruses
Smallest bacteria
Mitochondrion
Nucleus
Most bacteria
Most plant and animal cells
Frog egg
Chicken egg
Length of some nerve and muscle cells
Human height
Un
aid
ed e
ye
Lig
ht
mic
rosc
op
e
Ele
ctro
n m
icro
sco
pe
Fig. 6-8Surface area increases while
total volume remains constant
5
11
6 150 750
125 1251
6 61.2
Total surface area
[Sum of the surface areas
(height width) of all
boxes
sides number of boxes]Total volume
[height width length number of boxes]
Surface-to-volume
(S-to-V) ratio
[surface area ÷ volume]
Fig. 6-6
Fimbriae
Nucleoid
Ribosomes
Plasma membrane
Cell wall
Capsule
Flagella
Bacterialchromosome
(a) A typical rod-shaped bacterium
(b) A thin section through the bacterium Bacillus coagulans (TEM)
0.5 µm
Fig. 6-9a
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ER)
Smooth ERRough ERFlagellum
Centrosome
CYTOSKELETON:
Microfilaments
Intermediatefilaments
Microtubules
Microvilli
Peroxisome
MitochondrionLysosome
Golgiapparatus
Ribosomes
Plasma membrane
Nuclearenvelope
Nucleolus
Chromatin
NUCLEUS
Fig. 6-9b
NUCLEUS
Nuclear envelopeNucleolus
Chromatin
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Ribosomes
Central vacuole
Microfilaments
Intermediate filaments
Microtubules
CYTO-SKELETON
Chloroplast
PlasmodesmataWall of adjacent cell
Cell wall
Plasma membrane
Peroxisome
Mitochondrion
Golgiapparatus
Table 6-1
10 µm 10 µm 10 µm
Column of tubulin dimers
Tubulin dimer
Actin subunit
25 nm
7 nm
Keratin proteins
Fibrous subunit (keratins coiled together)
8–12 nm
Fig. 6-32
Tight junction
0.5 µm
1 µmDesmosome
Gap junction
Extracellularmatrix
0.1 µm
Plasma membranesof adjacent cells
Spacebetweencells
Gapjunctions
Desmosome
Intermediatefilaments
Tight junction
Tight junctions preventfluid from movingacross a layer of cells
Fig. 6-3ab
(a) Brightfield (unstained specimen)
(b) Brightfield (stained specimen)
TECHNIQUE RESULTS
50 µm
Fig. 6-4
(a) Scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
TECHNIQUE RESULTS
(b) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM)
Cilia
Longitudinalsection ofcilium
Cross sectionof cilium
1 µm
1 µm
Fig. 6-9a
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ER)
Smooth ERRough ERFlagellum
Centrosome
CYTOSKELETON:
Microfilaments
Intermediatefilaments
Microtubules
Microvilli
Peroxisome
MitochondrionLysosome
Golgiapparatus
Ribosomes
Plasma membrane
Nuclearenvelope
Nucleolus
Chromatin
NUCLEUS
Fig. 6-10
NucleolusNucleus
Rough ER
Nuclear lamina (TEM)
Close-up of nuclear envelope
1 µm
1 µm
0.25 µm
Ribosome
Pore complex
Nuclear pore
Outer membraneInner membraneNuclear envelope:
Chromatin
Surface ofnuclear envelope
Pore complexes (TEM)
Fig. 6-12Smooth ER
Rough ER Nuclear envelope
Transitional ER
Rough ERSmooth ERTransport vesicle
RibosomesCisternaeER lumen
200 nm
Fig. 6-11
Cytosol
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
Free ribosomes
Bound ribosomes
Large subunit
Small subunit
Diagram of a ribosomeTEM showing ER and ribosomes
0.5 µm
Fig. 6-12Smooth ER
Rough ER Nuclear envelope
Transitional ER
Rough ERSmooth ERTransport vesicle
RibosomesCisternaeER lumen
200 nm
Fig. 6-13
cis face(“receiving” side of Golgi apparatus) Cisternae
trans face(“shipping” side of Golgi apparatus)
TEM of Golgi apparatus
0.1 µm
Fig. 6-14
Nucleus 1 µm
Lysosome
Digestiveenzymes
Lysosome
Plasmamembrane
Food vacuole
(a) Phagocytosis
Digestion
(b) Autophagy
Peroxisome
Vesicle
Lysosome
Mitochondrion
Peroxisomefragment
Mitochondrionfragment
Vesicle containingtwo damaged organelles
1 µm
Digestion
Fig. 6-14
Nucleus 1 µm
Lysosome
Digestiveenzymes
Lysosome
Plasmamembrane
Food vacuole
(a) Phagocytosis
Digestion
(b) Autophagy
Peroxisome
Vesicle
Lysosome
Mitochondrion
Peroxisomefragment
Mitochondrionfragment
Vesicle containingtwo damaged organelles
1 µm
Digestion
Fig. 6-9b
NUCLEUS
Nuclear envelopeNucleolus
Chromatin
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Ribosomes
Central vacuole
Microfilaments
Intermediate filaments
Microtubules
CYTO-SKELETON
Chloroplast
PlasmodesmataWall of adjacent cell
Cell wall
Plasma membrane
Peroxisome
Mitochondrion
Golgiapparatus
Fig. 6-9a
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ER)
Smooth ERRough ERFlagellum
Centrosome
CYTOSKELETON:
Microfilaments
Intermediatefilaments
Microtubules
Microvilli
Peroxisome
MitochondrionLysosome
Golgiapparatus
Ribosomes
Plasma membrane
Nuclearenvelope
Nucleolus
Chromatin
NUCLEUS
Fig. 6-17
Free ribosomesin the mitochondrial matrix
Intermembrane space
Outer membrane
Inner membraneCristae
Matrix
0.1 µm
Fig. 6-9b
NUCLEUS
Nuclear envelopeNucleolus
Chromatin
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Ribosomes
Central vacuole
Microfilaments
Intermediate filaments
Microtubules
CYTO-SKELETON
Chloroplast
PlasmodesmataWall of adjacent cell
Cell wall
Plasma membrane
Peroxisome
Mitochondrion
Golgiapparatus
Fig. 6-28
Secondary cell wall
Primary cell wall
Middle lamella
Central vacuoleCytosol
Plasma membrane
Plant cell walls
Plasmodesmata
1 µm
Fig. 6-24
0.1 µm
Triplet
(c) Cross section of basal body
(a) Longitudinal section of cilium
0.5 µm
Plasma membrane
Basal body
Microtubules
(b) Cross section of cilium
Plasma membrane
Outer microtubule doublet
Dynein proteins
Central microtubuleRadial spoke
Protein cross-linking outer doublets
0.1 µm
Fig. 6-25Microtubuledoublets
Dyneinprotein
ATP
ATP
(a) Effect of unrestrained dynein movement
Cross-linking proteinsinside outer doublets
Anchoragein cell
(b) Effect of cross-linking proteins
1 3
2
(c) Wavelike motion
Fig. 6-23
5 µm
Direction of swimming
(a) Motion of flagella
Direction of organism’s movement
Power stroke Recovery stroke
(b) Motion of cilia15 µm