Fibroids in Pregnancy
-
Upload
pruthvish-patel -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
0
Transcript of Fibroids in Pregnancy
-
8/13/2019 Fibroids in Pregnancy
1/29
Uterine Leiomyomata in
Pregnancy
Ruth Stefanski, PGY-1
January 12, 2010
-
8/13/2019 Fibroids in Pregnancy
2/29
Objectives
Discuss case of patient in labor withfibroids
Review clinical manifestations Discuss possible complications of
fibroids during labor and delivery
Review management of fibroids inpregnancy
-
8/13/2019 Fibroids in Pregnancy
3/29
Case
27 y/o G2P0010 presented at 41weeks 1 dayby LMP 3/14/09 c/w 7 wk Sono. EDD12/19/09. Pt presented for post-dates IOL.+FM, -VB/LOF/ctx.
PNI: 1. Subserosal myoma, anterior leftuterus. On 6/18/09 U/S: 17x15x14cm. On12/10/09 U/S: 12.4x12.9x13cm 2. Multiple UTIs, on suppression therapy
3. GBS bacteruria
4. Anemia, on Iron supplements
-
8/13/2019 Fibroids in Pregnancy
4/29
Case, Continued
OB Hx: 2008 TOP at 8wks
GYN Hx: 13/regular/3-5. No STIs. No cysts.
+fibroids as above. H/o ASCUS pap. PMH: fibroid as above, anemia
PSH: D&C x1
Meds: PNV, Iron
All: NKDA
FH: MGM with DM, No HTN/cancer
SH: lives with 2 sisters, no h/o
DV/Depression/Anxiety. No toxic habits.
-
8/13/2019 Fibroids in Pregnancy
5/29
Case, Continued
PE: 114/70 P:101
Gen: NAD CV: RRR, S1S2 Pulm: CTAB
Abd: gravid, large palpable fibroid left fundalregion Extrem: no edema B/L
FHT: B/l 150, moderate variability, +accels,no decels
SVE: 2/50/-3
Toco: no ctx Sono: vertex
EFW: 3900gm
Labs: WBC: 10 H/H: 11.4/33.1 Plt: 214
-
8/13/2019 Fibroids in Pregnancy
6/29
Case, Continued
A/P: 27 y/o G2P0010 at 41weeks 1 dayadmitted for post-dates IOL.
1. Admit to L&D, NPO, IVF, check labs 2. Labor: Pts cervix unfavorable, placed
Cytotec 25mg PV for ripening. ConsiderPitocin for augmentation of ctx as needed.
3. Fetus: Category 1 EFM
4. Analgesia per patient request
5. GBS+: PCN prophylaxis in active labor
6. Anemia: f/u CBC, continue Iron
7. Myoma: ..
-
8/13/2019 Fibroids in Pregnancy
7/29
Patient was concerned about how thiswould effect her labor and delivery
Reported pain at site of fibroid with fetalmovement and with contractions
What do we need to know to care for
this patient?
-
8/13/2019 Fibroids in Pregnancy
8/29
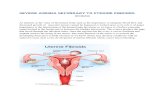
Definitions
Uterine leiomyomata= benign smooth muscletumors of the uterus
Described based on location in the uterus: Intramural: develop from within uterine wall, do not
distort uterine cavity, 50% protrudes out of serosal surface
Cervical: located in the cervix, rather than uterinecorpus
-
8/13/2019 Fibroids in Pregnancy
9/29
-
8/13/2019 Fibroids in Pregnancy
10/29
Clinical Manifestations
Abnormal uterine bleeding
Menorrhagia
submucosal
NOT intermenstrual bleeding
Pelvic pressure and pain
-
8/13/2019 Fibroids in Pregnancy
11/29
Clinical, Continued
Reproductive difficulty: infertility andloss
Obstruction of implantation Impaired placental growth at myoma site
Increased uterine contractility
Location, location, location Submucosal or intramural that protrudes into
cavity
-
8/13/2019 Fibroids in Pregnancy
12/29
Complications during
Pregnancy Pregnancy loss
Preterm labor and
birth Placental abruption
Placenta previa
Pain
PPH
Dysfunctional labor
Malpresentation Malposition
Cesarean delivery
-
8/13/2019 Fibroids in Pregnancy
13/29
Preterm Labor and Birth
Evidence not consistent across the literature
Increased risk if placenta is adjacent to or
overlies a fibroid Decreased oxytocinase activityhigher
oxytocin levelspremature contractions (?)
Fibroid uteri are less distensible, once uterusgrows to a certain pointcontractions (?)
-
8/13/2019 Fibroids in Pregnancy
14/29
Placental Abruption
Conflicting evidence
Submucosal, retroplacental
Abnormal placental perfusion:decreased blood flow to endometriumoverlying fibroidplacental ischemia,
decidual necrosisabruption (?)
-
8/13/2019 Fibroids in Pregnancy
15/29
Placenta previa
Most studies haveshown no association(adjusting for maternal
age and prior uterinesurgery)
One study by Qidwai etal. reported increased
rate (also adjusted forprior C/S andmyomectomy)
-
8/13/2019 Fibroids in Pregnancy
16/29
Pain
Reduced perfusion
with rapid growth offibroid
Ischemia, necrosis,release of
prostaglandins
-
8/13/2019 Fibroids in Pregnancy
17/29
Postpartum Hemorrhage
Greater risk: retroplacental or cesareandelivery
Decreased force and coordination ofcontractionsuterine atony
Be prepared: PPH precautions
-
8/13/2019 Fibroids in Pregnancy
18/29
Dysfunctional Labor
Varying evidence
Decreased force of contractions
Asymmetric wave of contractile forceacross uterus
-
8/13/2019 Fibroids in Pregnancy
19/29
Malpresentation, Malposition
Consistentevidence
Distorted shape ofuterine cavity
-
8/13/2019 Fibroids in Pregnancy
20/29
Cesarean Delivery
Consistent evidence
Location in lower
uterine segment Due to higher risk of
malpresentation,dysfunctional labor,
abruption
-
8/13/2019 Fibroids in Pregnancy
21/29
Evidence
2006 Qidwai GI, Caughey AB, Jacoby AF: Retrospective cohort study comparing pregnancy
outcomes in women with and without fibroids who
underwent a routine 2nd trimester sonogram anddelivered viable infants
Presence of fibroids associated with increased riskof:
Cesarean delivery, breech presentation, malposition,preterm delivery, placenta previa, severe PPH
No association between fibroids and: PROM, operative vaginal delivery, chorioamnionitis,
endomyometritis
-
8/13/2019 Fibroids in Pregnancy
22/29
Management during
pregnancy, labor & delivery1. Keep in mind complications above
Counsel patient on risks of loss, preterm
labor, PPH, C/S, dysfunctional labor, pain,etc.
Ultrasonography: size & location offibroids, fetal presentation, placentalposition
Monitor labor curve
-
8/13/2019 Fibroids in Pregnancy
23/29
Management, Continued
2. Pain Management Primary intervention: supportive care and
Acetaminophen Secondary: narcotics or NSAIDs
Indomethacin 25mg PO q6h x 48hours(studied by Dildy et al.) Limited to 48 hours, weekly sonos forassessment of these findings is recommended; ifpresent, d/c or reduce to 25mg q12h
-
8/13/2019 Fibroids in Pregnancy
24/29
Management, Continued
3. Myomectomy
Preconception: inadequate data to support
Antepartum: pregnancy is contraindication tomyomectomy; however some case series havesuggested it may be safe in 1st and 2nd trimesters
Intractable pain
Largest series showed lower rates ofspontaneous abortions, preterm birth, andpuerperal hysterectomy; but higher rate ofcesarean section for those who underwentantepartum myomectomy
-
8/13/2019 Fibroids in Pregnancy
25/29
Myomectomy, Continued
Intrapartum: due to the increased risk ofhemorrhage, elective myomectomy at time
of cesarean is strongly discouraged only indication = if the presence of the fibroid
makes adequate closure of the uterine incisionimpossible
-
8/13/2019 Fibroids in Pregnancy
26/29
Case Re-visited
Patient made adequate cervical change withCytotec
Received epidural for pain management,started on Pitocin
AROM at 5am, clear fluid
Around 8am, started having variable decels
At 10:45am, recurrent decels, Pitocinstopped, pt allowed to labor down
-
8/13/2019 Fibroids in Pregnancy
27/29
Case Re-visited, Continued
NSVD with compoundpresentation of righthand and midline
episiotomy to facilitatedelivery
Peri-urethral lacerationand episiotomy repaired
without complications EBL 400cc, no PPH
recorded in chart
Postpartum course
uncomplicated
-
8/13/2019 Fibroids in Pregnancy
28/29
Summary
Overall, good maternal and neonataloutcomes are expected in pregnant womenwith uterine fibroids
Several obstetric complications may be morecommon in pregnancies with fibroids, but thereis conflicting evidence on many of these
More research is needed
-
8/13/2019 Fibroids in Pregnancy
29/29
References
Bajekal N, Li TC. Fibroids, infertility, and pregnancy wastage.Human Reproduction Update 2000 Nov-Dec; 6 (6): 614-20.
Coronado GD, Marshall LM, Schwartz SM. Complications inPregnancy. Labor, and Delivery with Uterine Leiomyomas: A
Population-Based Study. Obstetrics and Gynecology 2000; 95: 764-9. Dilby GA et al. Indomethacin for the treatment of symptomatic
leiomyoma uteri during pregnancy. American Journal of Perinatology
1992; 9:185. Klatsky PC, Tran MD, Caughey AB, Fujimoto VY. Fibroids and
reproductive outcomes: a systematic literature review from conception
to delivery. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2008;
198: 357-66. Qidwai GI, Caughey AB, Jacoby AF. Obstetric outcomes in women
with sonographically identified uterine leiomyomata. Obstetrics andGynecology. 2006 February; 107 (2): 376-82.