ECEN 301Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods1 DateDayClass No. TitleChaptersHW Due date Lab Due...
-
Upload
kelly-terence-pierce -
Category
Documents
-
view
241 -
download
0
Transcript of ECEN 301Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods1 DateDayClass No. TitleChaptersHW Due date Lab Due...

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 1
Date Day ClassNo.
Title Chapters HWDue date
LabDue date
Exam
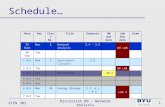
24 Sept Wed 7 Network Analysis 3.1 – 3.3
25 Sept Thu LAB 2
26 Sept Fri Recitation HW 3
27 Sept Sat
28 Sept Sun
29 Sept Mon 8 Network Analysis 3.4 – 3.5
NO LAB
30 Sept Tue
1 Oct Wed 9 Equivalent Circuits 3.6
Schedule…

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 2
Learning is good only when humble2 Nephi 9: 28-2928 O that cunning plan of the evil one! O the vainness,
and the frailties, and the foolishness of men! When they are learned they think they are wise, and they hearken not unto the counsel of God, for they set it aside, supposing they know of themselves, wherefore, their wisdom is foolishness and it profiteth them not. And they shall perish.
29 But to be learned is good if they hearken unto the counsels of God.

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 3
Lecture 7 – Network Analysis
Node Voltage and Mesh Current Methods

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 4
Network Analysis
Determining the unknown branch currents and node voltagesImportant to clearly define all relevant variablesConstruct concise set of equations
• There are methods to follow in order to create these equations
• This is the subject of the next few lectures

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 5
Network Analysis
Network Analysis Methods:Node voltage methodMesh current methodSuperpositionEquivalent circuits
• Source transformation• Thévenin equivalent• Norton equivalent

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 6
Node Voltage Method
Network Analysis

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 7
Node Voltage Method Identify all node and branch voltages
ia+v2
–
vs+_
+v4
–
+ v1 – + v3 –
R2
R1 R3
R4
a b c
d
ic
ib
Node Voltages Branch Voltages
va = vs vs = va - vd
= va
vb = v2 v1 = va - vb
vc = v4 v2 = vb - vd
= vb
vd = 0 v3 = vb - vc
v4 = vc - vd
= vc

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 8
Node Voltage Method The most general method for electrical circuit analysis
Based on defining the voltage at each node One node is selected as a reference node (often ground)
• All other voltages given relative to reference node• n – 1 equations of n – 1 independent variables (node voltages)
Once node voltages are determined, Ohm’s law can determine branch currents
• Branch currents are expressed in terms of one or more node voltages
0
0
:KCL Using
321
321
R
v
R
v
R
v
iii
bdbcab
R
iva vb
R
vR
vvi
ab
ba
+R2
–
+ R1 – + R3 –va vd
vb
vc
i1
i2
i3

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 9
Node Voltage Method1. Label all currents and voltages (choose arbitrary orientations
unless orientations are already given)2. Select a reference node (usually ground)
This node usually has most elements tied to it3. Define the remaining n – 1 node voltages as independent or
dependent variables Each of the m voltage sources is associated with a dependent variable If a node is not connected to a voltage source then its voltage is treated
as an independent variable4. Apply KCL at each node labeled as an independent variable
Express currents in terms of node voltages5. Solve the linear system of n – 1 – m unknowns

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 10
Node Voltage Method
Example1: find expressions for each of the node voltages and the currents
+ R2 –
is
+R1
–
+R3
–

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 11
Node Voltage Method Example1: find expressions for each of the node
voltages and the currents
is
i1 i3
+R1
–
+R3
–
+ R2 –
i2
Node a Node b
Node c
va
vb
vc
1. Label currents and voltages (polarities “arbitrarily” chosen)
2. Choose Node c (vc) as the reference node (vc = 0)
3. Define remaining n – 1 (2) voltages• va is independent since it is not
associated with a voltage source• vb is independent
4. Apply KCL at nodes a and b (node c is not independent) to find expressions for i1, i2, i3

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 12
Node Voltage Method Example1: find expressions for each of the node
voltages and the currents
32
32 0
:b Nodeat KCL
ii
ii
is
i1 i3
+R1
–
+R3
–
+ R2 –
i2
Node a Node b
Node c
va
vb
vc
4. Apply KCL to find expressions for i1, i2, i3
0
:a Nodeat KCL
21 iiis
NB: whenever a node connects only 2 branches the same current flows in the 2 branches (EX: i2 = i3)

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 13
Node Voltage Method Example1: find expressions for each of the node
voltages and the currents
11 R
vi ac
is
i1 i3
+R1
–
+R3
–
+ R2 –
i2
Node a Node b
Node c
va
vb
vc
22 R
vi ab
33 R
vi bc
0
:a Nodeat KCL
21
R
v
R
vi abas
32
:b Node at KCL
R
v
R
v bab
4. Express currents in terms of node voltages

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 14
Node Voltage Method Example1: find expressions for each of the node
voltages and the currents
is
i1 i3
+R1
–
+R3
–
+ R2 –
i2
Node a Node b
Node c
va
vb
vc
5. Solve the n – 1 – m equations
221
111
Rv
RRvi bas
322
111
RRv
Rv ba

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 15
Node Voltage Method Example2: solve for all unknown currents and voltages
I1 = 10mA, I2 = 50mA, R1 = 1kΩ, R2 = 2kΩ, R3 = 10kΩ, R4 = 2kΩ
I1 R1 R4
R2
R3
I2

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 16
Node Voltage Method Example2: solve for all unknown currents and voltages
I1 = 10mA, I2 = 50mA, R1 = 1kΩ, R2 = 2kΩ, R3 = 10kΩ, R4 = 2kΩ
I1 R1 R4
R2
R3
I2
+I1
–
–I2
+
+R4
–
+R1
–
+ R2 –
+ R3 –i3
i1
i2
i4
Node aNode b
Node c

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 17
Node Voltage Method Example2: solve for all unknown currents and voltages
I1 = 10mA, I2 = 50mA, R1 = 1kΩ, R2 = 2kΩ, R3 = 10kΩ, R4 = 2kΩ
1. Label currents and voltages (polarities “arbitrarily” chosen)
2. Choose Node c (vc) as the reference node (vc = 0)
3. Define remaining n – 1 (2) voltages va is independent vb is independent
4. Apply KCL at nodes a and b
+I1
–
+R1
–
+R4
–
+ R2 –
+ R3 –
–I2
+
i3
i2
i1i4
Node aNode b
Node c
va
vb
vc

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 18
Node Voltage Method Example2: solve for all unknown currents and voltages
I1 = 10mA, I2 = 50mA, R1 = 1kΩ, R2 = 2kΩ, R3 = 10kΩ, R4 = 2kΩ
+I1
–
+R1
–
+R4
–
+ R2 –
+ R3 –
–I2
+
i3
i2
i1i4
Node aNode b
Node c
4. Apply KCL at nodes a and b
va
vb
vc
0
0
:a Nodeat KCL
3211
3211
R
v
R
v
R
vI
iiiI
ababa 0
0
:b Nodeat KCL
2432
2432
IR
v
R
v
R
v
Iiii
babab

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 19
Node Voltage Method Example2: solve for all unknown currents and voltages
I1 = 10mA, I2 = 50mA, R1 = 1kΩ, R2 = 2kΩ, R3 = 10kΩ, R4 = 2kΩ
+I1
–
+R1
–
+R4
–
+ R2 –
+ R3 –
–I2
+
i3
i2
i1i4
Node aNode b
Node c
4. Express currents in terms of voltages
va
vb
vc
323211
11111
RRv
RRRvI ba
432322
11111
RRRv
RRvI ba

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 20
Node Voltage Method Example2: solve for all unknown currents and voltages
I1 = 10mA, I2 = 50mA, R1 = 1kΩ, R2 = 2kΩ, R3 = 10kΩ, R4 = 2kΩ
+I1
–
+R1
–
+R4
–
+ R2 –
+ R3 –
–I2
+
i3
i2
i1i4
Node aNode b
Node c
5. Solve the n – 1 – m equations
va
vb
vc
ba
ba
ba
ba
vv
vv
vv
RRv
RRRvI
6.06.110
)1.05.0()1.05.01(10
10105101051001.0
11111
44443
323211

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 21
Node Voltage Method Example2: solve for all unknown currents and voltages
I1 = 10mA, I2 = 50mA, R1 = 1kΩ, R2 = 2kΩ, R3 = 10kΩ, R4 = 2kΩ
+I1
–
+R1
–
+R4
–
+ R2 –
+ R3 –
–I2
+
i3
i2
i1i4
Node aNode b
Node c
5. Solve the n – 1 – m equations
va
vb
vc
ba
ba
ba
ba
vv
vv
vv
RRRv
RRvI
1.16.050
)5.01.05.0()1.05.0(50
105101051010505.0
11111
44444
432322

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 22
Node Voltage Method Example2: solve for all unknown currents and voltages
I1 = 10mA, I2 = 50mA, R1 = 1kΩ, R2 = 2kΩ, R3 = 10kΩ, R4 = 2kΩ
Vv
Vv
b
a
86.52
57.13
+I1
–
+R1
–
+R4
–
+ R2 –
+ R3 –
–I2
+
i3
i2
i1i4
Node aNode b
Node c
5. Solve the n – 1 – m equations
va
vb
vc
ba
ba
vv
vv
1.16.050
6.06.110

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 23
Node Voltage Method Example2: solve for all unknown currents and voltages
I1 = 10mA, I2 = 50mA, R1 = 1kΩ, R2 = 2kΩ, R3 = 10kΩ, R4 = 2kΩ
mA
R
vi a
57.1310
57.133
11
Node a
5. Solve the n – 1 – m equations
+I1
–
+R1
–
+R4
–
+ R2 –
+ R3 –
–I2
+
i3
i2
i1i4
Node b
Node c
va
vb
vc
mA
R
vi ab
65.19102
86.5257.133
22
mA
R
vi b
43.26102
86.523
44
mA
R
vi ab
93.310
86.5257.134
33

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 34
Node Voltage Method Example5: find all node voltages
vs = 2V, is = 3A, R1 = 1Ω, R2 = 4Ω, R3 = 2Ω, R4 = 3Ω
R2 R4
R3
is
R1
+–
vs

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 35
Node Voltage Method Example5: find all node voltages
vs = 2V, is = 3A, R1 = 1Ω, R2 = 4Ω, R3 = 2Ω, R4 = 3Ω
+R2
–
+R4
–
+ R3 –
+is
–
i3
i2 i4
vavc
vd
+ R1 –
+–
i1
vs
vb 1. Label currents and voltages (polarities “arbitrarily” chosen)
2. Choose Node d (vd) as the reference node (vd = 0)
3. Define remaining n – 1 (3) voltages va is dependent (va = vs) vb is independent vc is independent
4. Apply KCL at nodes b, and c

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 36
Node Voltage Method Example5: find all node voltages
vs = 2V, is = 3A, R1 = 1Ω, R2 = 4Ω, R3 = 2Ω, R4 = 3Ω
+R2
–
+R4
–
+ R3 –
+is
–
i3
i2 i4
vavc
vd
+ R1 –
+–
i1
vs
vb
0
0
:b Nodeat KCL
321
321
R
v
R
v
R
v
iii
bcbsb 0
0
:c Nodeat KCL
43
43
R
v
R
vi
iii
cbcs
s
4. Apply KCL at nodes b, and c

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 37
Node Voltage Method Example5: find all node voltages
vs = 2V, is = 3A, R1 = 1Ω, R2 = 4Ω, R3 = 2Ω, R4 = 3Ω
+R2
–
+R4
–
+ R3 –
+is
–
i3
i2 i4
vavc
vd
+ R1 –
+–
i1
vs
vb 4. Express currents in terms of voltages
33211
1111
Rv
RRRv
R
vcb
s
433
111
RRv
Rvi cbs

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 38
Node Voltage Method Example5: find all node voltages
vs = 2V, is = 3A, R1 = 1Ω, R2 = 4Ω, R3 = 2Ω, R4 = 3Ω
+R2
–
+R4
–
+ R3 –
+is
–
i3
i2 i4
vavc
vd
+ R1 –
+–
i1
vs
vb
Vv
Vv
c
b
17.5
62.2
5. Solve the n – 1 – m equations
1853
827
cb
cb
vv
vv

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 39
Node Voltage Method Example6: find the current iv
Vs = 3V, Is = 2A, R1 = 2Ω, R2 = 4Ω, R3 = 2Ω, R4 = 3Ω
Is R4R2
R1
R3
Vs
+ –
iv

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 40
Node Voltage Method Example6: find the current iv
Vs = 3V, Is = 2A, R1 = 2Ω, R2 = 4Ω, R3 = 2Ω, R4 = 3Ω
+Is
–
+R4
–
+R2
–
+ R1 –
+ R3 –
Vsi3
i1
i2 i4
+ –
iv
va vbvc
vd
1. Label currents and voltages (polarities “arbitrarily” chosen)
2. Choose Node d (vd) as the reference node (vd = 0)
3. Define remaining n – 1 (3) voltages va is independent vb is dependent
(actually both vb and vc are dependent on each other so choose one to be dependent and one to be independent)(vb = vc + Vs)
vc is independent4. Apply KCL at nodes a, and c

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 41
Node Voltage Method
Example6: find the current iv
Vs = 3V, Is = 2A, R1 = 2Ω, R2 = 4Ω, R3 = 2Ω, R4 = 3Ω
+Is
–
+R4
–
+R2
–
+ R1 –
+ R3 –
Vsi3
i1
i2 i4
+ –
iv
va vbvc
vd
0
0
:a Nodeat KCL
31
31
R
v
R
vI
iiI
acabs
s
0
0
:c Nodeat KCL
43
43
R
vi
R
v
iii
cv
ac
v
4. Apply KCL at nodes a, and c
12
21 0
:b Nodeat BUT
R
v
R
vi
iii
abbv
v
0
0
:c Nodeat KCL
4123
43
R
v
R
v
R
v
R
v
R
vi
R
v
cabbac
cv
ac

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 42
Node Voltage Method
Example6: find the current iv
Vs = 3V, Is = 2A, R1 = 2Ω, R2 = 4Ω, R3 = 2Ω, R4 = 3Ω
+Is
–
+R4
–
+R2
–
+ R1 –
+ R3 –
Vsi3
i1
i2 i4
+ –
iv
va vbvc
vd
4. Express currents in terms of voltages
3131
1111
Rv
Rv
RRvI cbas
432131
1111110
RRv
RRv
RRv cba

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 43
Node Voltage Method
Example6: find the current iv
Vs = 3V, Is = 2A, R1 = 2Ω, R2 = 4Ω, R3 = 2Ω, R4 = 3Ω
+Is
–
+R4
–
+R2
–
+ R1 –
+ R3 –
Vsi3
i1
i2 i4
+ –
iv
va vbvc
vd
Vv
Vv
Vv
c
b
a
14.2
14.5
64.5
5. Solve the n – 1 – m equations
010912
42
cba
cba
vvv
vvv3 cb vv

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 44
Node Voltage Method
Example6: find the current iv
Vs = 3V, Is = 2A, R1 = 2Ω, R2 = 4Ω, R3 = 2Ω, R4 = 3Ω
+Is
–
+R4
–
+R2
–
+ R1 –
+ R3 –
Vsi3
i1
i2 i4
+ –
iv
va vbvc
vd
5. Solve the n – 1 – m equations
A
R
v
R
vi abbv
32.22
14.564.5
4
14.512

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 45
Mesh Current Method
Network Analysis

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 46
Mesh Current Method Write n equations of n unknowns in terms of mesh
currents (where n is the number of meshes)Use of KVL to solve unknown currents Important to be consistent with current direction
+v_
R
i
NB: the direction of current defines the polarity of the voltage
Positive voltage
+v_
R
i
Negative voltage

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 47
Mesh Current Method Write n equations of n unknowns in terms of mesh
currents (where n is the number of meshes)Use of KVL to solve unknown currents Important to be consistent with current direction
ia
+v2
–
vs+_
+v4
–
+ v1 – + v3 –
R2
R1 R3
R4ib
Two meshes n = 2

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 48
Mesh Current Method Write n equations of n unknowns in terms of mesh
currents (where n is the number of meshes)Use of KVL to solve unknown currents Important to be consistent with current direction
ia
+v2
–
vs+_
+v4
–
+ v1 – + v3 –
R2
R1 R3
R4ib
Two meshes n = 2
i1 (current through R1) = ia but what about i2?According to the current directions of ia and ib, and the polarity of v2:i2 (current through R2) = ia – ib

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 49
Mesh Current Method Write n equations of n unknowns in terms of mesh
currents (where n is the number of meshes)Use of KVL to solve unknown currents Important to be consistent with current direction
0)(
0
:bMesh around KVL
432
432
RiRiRii
vvv
bbba
ia
+v2
–
vs+_
+v4
–
+ v1 – + v3 –
R2
R1 R3
R4ib
0)(
0
:aMesh around KVL
21
21
RiiRiv
vvv
baas
s

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 50
Mesh Current Method Write n equations of n unknowns in terms of mesh
currents (where n is the number of meshes)Use of KVL to solve unknown currents Important to be consistent with current direction
ia
+v2
–
vs+_
+v4
–
+ v1 – + v3 –
R2
R1 R3
R4ib
0)(
)(
:unknowns 2 equations, 2
4322
221
RRRiRi
vRiRRi
ba
sba

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 51
Mesh Current Method1. Label each mesh current consistently
Current directions are chosen arbitrarily unless given2. Label the voltage polarity of each circuit element
Strategically (based on current direction) choose polarity unless already given
3. In a circuit with n meshes and m current sources n – m independent equations result
Each of the m current sources is associated with a dependent variable If a mesh is not connected to a current source then its voltage is treated
as an independent variable4. Apply KVL at each mesh associated with independent
variables Express voltages in terms of mesh currents
5. Solve the linear system of n – m unknowns

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 57
Mesh Current Method Example8: find the voltages across the resistors
Vs1 = Vs2 = 110V, R1 = 15Ω, R2 = 40Ω, R3 = 16Ω, R4 = R5 = 1.3Ω
R2
R4
vs2+_
R1
R3
vs1+_
R5

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 58
Mesh Current Method Example8: find the voltages across the resistors
Vs1 = Vs2 = 110V, R1 = 15Ω, R2 = 40Ω, R3 = 16Ω, R4 = R5 = 1.3Ω
1. Mesh current directions given2. Voltage polarities chosen and labeled3. Identify n – m (3) mesh currents
ia is independent ia is independent ic is independent
4. Apply KVL around meshes a, b, and c
+R2
–
+ R4 –
vs2+_ ia
ib
ic
+R1
– +R3
–
vs1+_
– R5 +

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 59
Mesh Current Method Example8: find the voltages across the resistors
Vs1 = Vs2 = 110V, R1 = 15Ω, R2 = 40Ω, R3 = 16Ω, R4 = R5 = 1.3Ω
+R2
–
+ R4 –
vs2+_ ia
ib
ic
+R1
– +R3
–
vs1+_
– R5 +
4. Apply KVL at nodes a, b, and c
0)()(
0
:cMesh around KVL
123
123
RiiRiiRi
vvv
cbcac
0)(
0
:aMesh around KVL
522
522
RiRiiv
vvv
acas
s
0)(
0
:bMesh around KVL
141
141
RiiRiv
vvv
cbbs
s

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 60
Mesh Current Method Example8: find the voltages across the resistors
Vs1 = Vs2 = 110V, R1 = 15Ω, R2 = 40Ω, R3 = 16Ω, R4 = R5 = 1.3Ω
+R2
–
+ R4 –
vs2+_ ia
ib
ic
+R1
– +R3
–
vs1+_
– R5 +
0)( 32112 RRRiRiRi cba
2252 )( sca vRiRRi
1141 )( scb vRiRRi
4. Express voltages in terms of currents

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 61
Mesh Current Method Example8: find the voltages across the resistors
Vs1 = Vs2 = 110V, R1 = 15Ω, R2 = 40Ω, R3 = 16Ω, R4 = R5 = 1.3Ω
+R2
–
+ R4 –
vs2+_ ia
ib
ic
+R1
– +R3
–
vs1+_
– R5 +
Ai
Ai
Ai
c
b
a
26.11
11.17
57.13
0711540
110153.16
110403.41
cba
cb
ca
iii
ii
ii
5. Solve the n – m equations

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 62
Mesh Current Method Example8: find the voltages across the resistors
Vs1 = Vs2 = 110V, R1 = 15Ω, R2 = 40Ω, R3 = 16Ω, R4 = R5 = 1.3Ω
+R2
–
+ R4 –
vs2+_ ia
ib
ic
+R1
– +R3
–
vs1+_
– R5 +
5. Solve the n – m equations
V
Riv c
16.180
16)26.11(33
V
Riiv cb
75.87
15)26.1111.17(
)( 11
V
Riiv ca
40.92
40)26.1157.13(
)( 22
V
Riv b
24.22
3.1)11.17(44
V
Riv a
64.17
3.1)57.13(55

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 63
Mesh Current Method Example9: find the mesh currents
Vs = 6V, Is = 0.5A, R1 = 3Ω, R2 = 8Ω, R3 = 6Ω, R4 = 4Ω
R2
R1
R4
R3
Is vs–+ia ib
ic

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 64
Mesh Current Method Example9: find the mesh currents
Vs = 6V, Is = 0.5A, R1 = 3Ω, R2 = 8Ω, R3 = 6Ω, R4 = 4Ω
+R2
–
+ R1–
+R4–
+R3 –
Is vs–+ia ib
ic
1. Mesh current directions given2. Voltage polarities chosen and labeled3. Identify n – m (3) mesh currents
ia is dependent (ia = is) ia is independent ic is independent
4. Apply KVL around meshes b and c

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 65
Mesh Current Method Example9: find the mesh currents
Vs = 6V, Is = 0.5A, R1 = 3Ω, R2 = 8Ω, R3 = 6Ω, R4 = 4Ω
+R2
–
+ R1–
+R4–
+R3 –
Is vs–+ia ib
ic
4. Apply KVL at nodes b and c
0)()(
0
:bMesh around KVL
32
32
RiiRiiv
vvv
cbbss
s
0)()(
0
:cMesh around KVL
134
134
RiiRiiRi
vvv
cscbc

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 66
Mesh Current Method Example9: find the mesh currents
Vs = 6V, Is = 0.5A, R1 = 3Ω, R2 = 8Ω, R3 = 6Ω, R4 = 4Ω
+R2
–
+ R1–
+R4–
+R3 –
Is vs–+ia ib
ic
2332 )( RivRiRRi sscb
14313 )( RiRRRiRi scb
4. Express voltages in terms of currents

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 67
Mesh Current Method Example9: find the mesh currents
Vs = 6V, Is = 0.5A, R1 = 3Ω, R2 = 8Ω, R3 = 6Ω, R4 = 4Ω
+R2
–
+ R1–
+R4–
+R3 –
Is vs–+ia ib
ic
Ai
Ai
Ai
c
b
a
55.0
95.0
50.0
5.1136
10614
cb
cb
ii
ii
5. Solve the n – m equations

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 68
Equation Solver Methods
CalculatorMatrix
Cramer’s RuleBrute Force (Substitution)

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 69
TI-89 Equation Solver
1. Press F1 Select option number 8 (Clear Home)
2. Press APPS Select option number 1 (FlashApps) Select Simultaneous Eqn Solver
Select New…
3. In the new box enter n (the number of equations and unknowns)

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 70
TI-89 Equation Solver
4. Input the equation coefficients For the set of 3 equations and 3 unknowns from
example 8:
Input the coefficients as follows:
41.3 0 -40 110
0 16.3 -15 110
-40 -15 71 0
0711540
110153.16
110403.41
cba
cb
ca
iii
ii
ii
1
2
3
a1 a2 a3 b1

Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods
ECEN 301 71
TI-89 Equation Solver
5. Press F5 (Solve)
26.11
11.17
57.13
3
2
1
x
x
x