PERSONAL HYGIENE OF THE STUDENTS Dr. Shahzadi Tayyaba Hashmi [email protected].
DNT 353 Dr. Shahzadi Tayyaba Hashmi. To describe caries process To describe sites that are...
-
Upload
iris-clarke -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
1
Transcript of DNT 353 Dr. Shahzadi Tayyaba Hashmi. To describe caries process To describe sites that are...

DNT 353
CARIOLOGYDr. Shahzadi Tayyaba Hashmi

LEARNING OBJECTIVES
To describe caries process To describe sites that are vulnerable to
caries List bacterial strains most responsible for
caries Explain importance of carbohydrates
exposure to caries

INTRODUCTION The study of dental caries and cariogenesis is
known as cariology
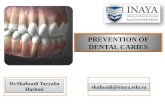
DENTAL CARIES also known as tooth decay or a cavity It is defined as an infection which is bacterial in
origin and causes demineralization and destruction of hard tissues of teeth (enamel, dentine and cementum)
CARIOGENESIS The Production of dental caries is termed as
cariogenesis

ETIOLOGY OF DENTAL CARIES
Dental caries is a multifactorial disease of teeth.
The major factors in the etiology of dental caries are as follows:
Diet Bacteria Susceptible tooth surface Time

Essential requirements for development of dental caries Cariogenic (acidogenic) bacteria Bacterial plaque Stagnation areas Fermentable bacterial substrate(sugar) Susceptible tooth surfaces time

1) Essential properties of cariogenic bacteria
Streptococci are essential for development of dental caries
Acidogenic Able to produce a pH low enough (<5) to
decalcify tooth substance Able to survive and produce acid at low
levels of pH Able to produce polysaccharides (glucans) It adheres to pellicle and contributes to
plaque formation


Microbiological aspects of dental caries
Dental caries is a bacterial disease The organisms mainly responsible are
specific strains of Streptococcus mutans The presence of S.mutans in the human
mouth is associated with caries activity Other bacteria including lactobacilli and
other strains of streptococci are weakly cariogenic

2) Bacterial plaque
Plaque is a tenaciously adherent deposit that forms on tooth surfaces
Consist of an organic matrix containing a dense concentration of bacteria
In microbiological terms, plaque is a biofilm Biofilm consist of hydrated viscous phase
formed from bacteria and their extracellular polysaccharide matrices
Biofilm may be resistant to antimicrobials

Clinical appearance of bacterial plaque
Clinically, bacterial plaque is a tenaciously adherent deposit on the teeth
It can only be readily removed by tooth brushing
However no tooth brushing removes plaque from inaccessible areas or pits (stagnation areas)
Plaque becomes visible, particularly on the labial surfaces of incisors, when tooth brushing is stopped for 12-24 hours
Appears as a translucent film

DENTAL PLAQUE
Appears as translucent film

Stages of plaque formation
Deposition of cell-free pellicle of salivary glycoprotein
Further deposition of pellicle enhanced by bacterial action
Colonisation of cell free layer by bacteria, particularly by S.sanguis and S.mutans within 24 hours
Progressive build-up of plaque substance by bacterial polysaccharides


3)Factors determining the cariogenecity of
sucrose Sucrose forms up to a third of the
carbohydrate content of many person’s diet
It promotes colonisation of teeth by streptococcus mutans
Its small molecular size allows it to diffuse rapidly into plaque
Its dissacharide bond contains enough energy to react with bacterial enzymes to form extracellular dextran matrix