CPR/First Aid
-
Upload
casey-perez -
Category
Documents
-
view
31 -
download
0
description
Transcript of CPR/First Aid

CPR/First Aid
Mrs. Gennaro

Chain of Survival
1. Early access to EMT2. Early EMT3. Early Defibrillation4. Early Advanced Care

Four Life Threatening Emergencies in Adults
Heart Attack Cardiac Arrest Stroke Choking

Life Threatening Emergencies in Adults
Heart Attack- Occurs when one of the heart’s major blood vessels becomes blocked so that no oxygen is delivered to the heart muscles. Without oxygen the heart muscle begins to die, producing pain and other symptoms.
Heart attack video 1 Heart attack video 2

Heart Attack
Signs/Symptoms Often awake and can talk, describes pain
or pressure or tightness in the chest. May feel lightheaded, short of breath, nauseated, or cold sweats (flu-like symptoms). May describe pain as an ache, heartburn, or indigestion.

Life Threatening Emergencies in Adults
Cardiac Arrest- Occurs when the heart stops pumping blood. Circulation to the brain and major organs stop. Victim collapses, becomes unresponsive, and stops breathing normally (shallow breathing or gasping).
Cardiac Arrest video 1 Cardiac Arrest video 2

Cardiac Arrest
Signs/Symptoms No response, no normal breathing, no
signs of circulation.

Stroke
Stroke- Occurs when part of the brain does not receive blood flow or oxygen. May be caused by blockage in blood vessel or bleeding in the brain.
YouTube - Stroke Animation Video YouTube - What causes a stroke? YouTube - What Does a Stroke Do?

Stroke
Signs/Symptoms- Sudden numbness/weakness on one side of face, arm, or leg. Sudden confusion, trouble speaking or understanding, sudden trouble seeing out of 1 or both eyes, sudden trouble walking, dizziness or loss of balance. Severe headache with no known cause.

Choking
Choking- Occurs when a foreign body blocks the airway. Victim cannot get oxygen into lungs and the brain and body becomes deprived of oxygen.
Field of Dreams Movie Clips & Scenes - Doc Saves Karin
How to Treat a Conscious Choking Adult

Choking Signs/Symptoms- Victim clutching throat
(Universal sign of choking), trouble breathing, wheezing or high-pitched noises.

What is CPR?
CPR (Cardiopulmonary resuscitation)- A life-saving first-aid procedure that combines rescue breaths with chest compressions, supplying oxygen to the body until normal body functions can resume.

Emergency Action Steps Check- the scene and the ill or injured
person for safety. Check responsiveness “are you ok”?
Call- call 9-1-1 Care- ABCD
Good Samaritan Laws- Statutes that protect rescuers from being sued for giving emergency care.

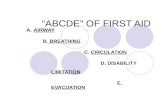
Care- ABCD ABCD
A- Airway (Check Airway) Look inside the victim’s mouth. Remove anything you see blocking the airway.
B- Breathing (Check Breathing) Look, listen and feel for breathing. Look for chest movement. Listen at the victim’s mouth for breathing. Feel for exhale air on your cheek. Normal Breathing/ Chest Rising?
If they are breathing- Roll into recovery position If they aren’t breathing- Give 2 breaths (1 sec), Look for
chest to rise. If they don’t- Reposition and give 2 more breaths.
If the victim is choking, check for object in-between breaths and compressions, sweep if you see it, if you don’t, continue CPR

Care- ABCD C- Compressions (Begin Compressions)-
30 Compressions to 2 breaths Pump fast and hard Continue cycles until victim recovers, help arrives, or
scene becomes unsafeCPR Techniques: Adult
Hands locked, fingers interlaced, heel of hand directly over sternum, mid-chest, between the nipples
Elbows locked, shoulders square over victim Child
Perform compressions with one hand Infant
Perform compressions with 2 fingers

Care- ABCD D- Defibrillation (AED) Device that delivers an
electric shock to the heart to restore its normal rhythm.
AED Tips Remove water, lotion, medicine Turn on, place pads, follow prompts, shock if
advised Do not shock of not commanded, continue
CPR Upon Shock- Clear victim and press shock
button once Once on- Leave on- NEVER remove pads

Choking Choking occurs when an object, such
as piece of food, becomes stuck in a person’s windpipe, cutting off the flow of air. Signs of choking
Inability to speak Difficulty breathing Inability to cough forcefully, turning blue in
the face or lips, Loss of consciousness

Choking Continued Adult Choking
Immediately perform abdominal thrusts If someone is close- ask them to call 911
Infant Choking Perform back blows and chest thrusts to dislodge the
object If choking victim is unconscious- Lower the person
down to the floor and try to clear the airway Reach into the mouth and sweep the object out with
one finger (Be careful not to push the obstruction deeper into the throat)
If the obstruction cannot be dislodged, begin performing CPR (the chest compressions may dislodge the object)


Choking Continued
Choking when along- Perform abdominal thrusts on yourself Cover your fist with the other hand and
push upward and inward Another method- Bend over and position
your abdomen over a rigid structure (countertop, back of a chair) Press against it to thrust your abdomen upwards and inward

First Aid
Mrs. Gennaro

First Aid
First Aid- Immediate, temporary care given to an ill or injured person until professional medical care can be provided
Emergency Action Plan Check Call Care

First Aid Precautions
Wear sterile gloves whenever you could come into contact with someone's blood or body fluids
Wash hands immediately after providing first aid
Using a mouthpiece, if one is available, when providing rescue breathing.

Questions
Why is it important to wash your hands after administering firs aid, even if you wear cloves

Additional Answers
Gloves may rip or tear, resulting in potential exposure to pathogens
Gloves may have tiny holes that you cannot see, but that can still permit blood or other body fluids to get through

Open Wounds Abrasion- Skin scrapes against a hard
surface Dirt and bacteria can easily enter the site
Important to clean the wound to prevent infection and speed healing
Laceration- Cut caused by a sharp object, (such as a knife or broken glass) Lacerations are accompanied by bleeding and
deep lacerations can result in heavy bleeding Deep lacerations may cause damage to nerves,
large blood vessels, and other soft tissue Infection may also occur

Open Wounds Puncture-Small but deep hole caused by a pin, nail,
fang, or other object that pierces the skin. Do not usually cause heavy external bleeding, but
they may cause internal bleeding if penetrating object damages major blood vessels or internal organs
Puncture wounds carry a high risk of infection, including tetanus
Avulsion- Tissue is partially or completely separated from the body A partially avulsed piece of skin may remain
attached, but it hangs like a flap Heavy bleeding is common Immediately call for professional medical assistance

First Aid for Bleeding Control bleeding
Raise the wounded body part above the level of the heart (if possible)
Cover wound with sterile gauze or a clean clot Press palm of hand firmly against the gauze. Apply steady
pressure to the wound for 5 minutes or until help arrives Do not stop to check the wound (clotting of the blood may be
interrupted) If blood soaks through the gauze, add another gauze pad on
top of the first and continue to apply pressure Once bleeding stops- secure the pad firmly in place with a
bandage, strip of gauze, or other material Pad should be snug- but not so tight that you can’t feel the
victims pulse If you can’t stop the bleeding after 5 minutes or if the wound
starts bleeding again, call for medical help (if you haven’t done it already) Continue to apply pressure until help arrives

Burns

First Aid for Burns Cool the burn area by hold it under cold, running
water for at least 5 minutes. (may also immerse the burned area in cool water or wrap it in cold wet clothes Do not use ice- May cause frostbite and further
damage to skin Cover burn loosely with a sterile gauze bandage Some second degree burns and all third-degree burns
require immediate medical care- Call 911 Cover the burned area with a clean, moist cloth, but
do not remove burned clothing unless it is smoldering Do not immerse a large burned area in cold water
(Victim could go into shock)