Circulatory System Structures, Functions, and Disorders · 19 Veins a. carry deoxygenated blood...
Transcript of Circulatory System Structures, Functions, and Disorders · 19 Veins a. carry deoxygenated blood...
2
Structure of the Heart
� Size, shape and location
� 1. Size of a closed fist
� 2. In thoracic cavity
� 3. Apex: the tip of the heart that lies on the diaphragm and points to the left of the body
� 4. Four chambers
3
� Layers
� 1. Pericardium: Sac (membrane) that surrounds the heart
� 2. Myocardium: muscular layer of the heart
� 3. Endocardium: smooth membrane that lines the inside of the heart and heart valves
� 4. Septum: partition between the R and L sides of the heart
4
� Structures to and from heart
� 1. Superior and inferior vena cava-veins that bring blood from the body to the heart
� 2. Pulmonary artery and vein- take blood to the lungs and return it to the heart
� 3. Aorta: large artery that blood enters as it leaves the L ventricle of the heart
5
� Chambers and valves� 1. Atria (atrium):
have two, top chambers of the heart
� 2. Ventricles (ventricle): have 2, bottom chambers of the heart
Heart Valves
� 3. Tricuspid valve: between the right atrium and right ventricle
� 4. Mitral (bicuspid) valve: between the left atrium and left ventricle
� 5. Pulmonary semilunar valve: between right ventricle and pulmonary artery
� 6. Aortic semilunar valve: between left ventricle and aortic artery
6
8
Function of the Heart
� Four main functions of circulatory system
� 1. pump
� 2. blood transport system around body
� 3. carries oxygen and nutrients to cells, carries away waste products
� 4. lymph system: returns excess tissue fluid to general circulation
9
� Heart
� 1. average 72 beats per minute, 100,000 beats per day
� 2. superior ( upper body) inferior (lower body) vena cava bring deoxygenated blood to right atrium
� 3. cardiopulmonary circulation: circulation from the heart to the lungs
10
� 4. pulmonary artery takes blood from right ventricle to lungs
� 5. pulmonary veins bring oxygenated blood from lungs to left atrium
� 6. aorta takes blood from left ventricle to rest of the body
� 7. four heart valves permit flow of blood in one direction
11
� Pump� 1. heart is a double
pumpright heart right atrium tricuspid valve right ventricle pulmonary semilunarvalve
Pulmonary artery lungs (for Oxygen)
12
� Left Heart
Lungs
Pulmonary veins
Left atrium
Mitral valve
Left ventricle
Aortic semilunar valve
Aorta
General circulation
14
Electrical Activity The Natural Pacemaker of the
Heart� a. SA (sinoatrial)
node = conducting cells that originate an electrical impulse that begins and regulates the heart beat
� b. AV (atrioventricular) node = carries impulse
to bundle of His
15
c. Bundle of His = conducting fibers in septum,
Divides into right and left branches in ventricles to Purkinje fibers
d. Purkinje fibers= cause ventricles to contract
16
Analyze circulation and the blood vessels
� Cardiopulmonary circulation: the circulation of the blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen
1. oxygenated and
Deoxygenated blood
2. oxygen/carbon dioxide exchange
17
Systemic Circulation
� Systemic Circulation:
Blood that travels from the heart to the tissues and cells
1. coronary arteries: vessels that are located on the outer surface of the heart
2. aorta: large artery, blood flows to body after it leaves the aorta
3. systemic circulation
18
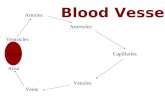
Blood vessels
� Blood vessels
1. Arteries
a. carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to the capillaries
b. elastic, muscular and thick-walled
c. transport blood under very high pressure
2. Arterioles
19
� Veins
a. carry deoxygenated blood away from capillaries to heart
b. less elastic and muscular than arteries
c. thin walled, collapse easily when not filled with blood
d. superior and inferior vena cava carry blood to heart
Venules: smaller and less muscular than veins
20
� Capillaries
a. smallest blood vessels
b. one cell thick and are made of endothelial cells
c. connect arterioles and venules
d. walls are one-cell
thick, allow for selective permeability
24
� Blood pressure
1. Systolic: average=120
(Systole is contraction phase of the heart)
2. Diastolic:
Average = 80
(Diastolic is the relaxation phase of the heart
The Brachial Artery in the arm is usually used to measure BP
25
� Pulse:
Alternating expansion and contraction of an artery as blood flows through it:
1. brachial 2. carotid
3. Femoral 4. pedal
5. popliteal 6. radial
26
Cardiac and Circulatory Disorders
1. Symptoms of Heart disease: usually experience cyanosis
a. arrythmia (dysrrhythmia): any change from normal heart rate or rhythm
b. Bradycardia: slow heart rate <60 pulse
c. Tachycardia: rapid heart rate >100 pulse
27
2. Coronary artery disease:
a. Angina pectoris: chest pain due to the lack of oxygen to heart muscle, treat with nitroglycerine
b. Edema: venous congestion; heart failure can cause poor circulation that results in edema
28
3. Myocardial infarction: (MI, heart attack)
a. lack of blood supply to myocardium
b. symptoms: severe chest pain radiating to left shoulder, arm, neck and jaw, N&V,
diaphoresis, dyspnea
29
Vascular Disease 1. Aneurysm: abnormal condition, ballooning or
protrusion of the wall of an artery
2. Arteriosclerosis: arterial walls thicken and lose elasticity
3. Atherosclerosis: fatty deposits form on walls of arteries and block circulation reducing the amount of blood going to an organ
4. Hypertension: High blood pressure: over 140/90, called the silent killer because there are usually no symptoms, occurs 1 of 5 Americans
30
5. Hypotension: low blood pressure
Patient becomes dizzy especially when standing up suddenly.
6. Embolism: traveling blood clot
a. transient ischemic attacks (TIAs)
b. Cerebral vascular accident (CVA) stroke
7. Varicose veins: swollen, inflamed and painful: enlarged veins result from a slowing of blood flow back to the heart
31
Diagnosis and treatment:
� 1. EKG/ECG; electrocardiogram; electrical tracing of the heart
� 2. Coronary bypass:
� 3. AED: automated external defibrillator
� 4. Defibrillator: electrical shock bringing heart back to normal sinus rhythm









































![1 a veins arteries capillaries · veins arteries capillaries First _____ next _____ last _____ [1 mark] b Choose from the list of organs in the box to answer the question. From which](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5f1fa4f65f10160d415d4180/1-a-veins-arteries-capillaries-veins-arteries-capillaries-first-next-.jpg)