Chapter 8 Photosynthesis - Faribaultmail.faribault.k12.mn.us/~Laura_Childs/S0198C4E2.7/Chapter...
Transcript of Chapter 8 Photosynthesis - Faribaultmail.faribault.k12.mn.us/~Laura_Childs/S0198C4E2.7/Chapter...
I. Chemical Energy & ATP
• NRG: ability to do work
a) Many forms of NRG: heat; electricity
b) Chemical bonds store NRG = released w/breakdown
• Candle: wax + O2 = CO2 + H2O (heat/light released)
c) All life obtains, then uses NRG (for cell activities)
• ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate): basic NRG source for cells
• Adenine (N) + Ribose + 3P groups
1. Storing Energy
• ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate):
a) Adenine (N) + Ribose + 2P groups
b) Like a rechargeable battery
c) Available NRG stored by adding 3rd P group
2. Releasing Energy
• ATP (w/3 P groups)
a) Cells easily break (NRG releasing) and reform (NRG
storing) 3rd P bond for cellular work
b) Ready to be used, full battery, available NRG
3. Using Biochemical Energy
a) Active Transport: uses ATP to move molecules
• Cell proteins pump Na+/K+ in & out to contract muscles
b) Protein synthesis
c) ATP: usable NRG; hard to store; small amts in cell
d) Glucose: un-usable form; 90x the NRG of 1 ATP
e) Cells regenerate ATP from ADP w/NRG in food
w/respiration
II. Heterotrophs & Autotrophs
• Photosynthesis: Sun NRG converted to chemical NRG
stored in bonds of carbs
1. Autotroph: use light NRG to make own food (for ATP)
• Ex: Plants, algae, some bacteria
2. Heterotroph: Consumed food NRG to make ATP
• Ex: herbivores/carnivores/decomposers
8.2 Photosynthesis: An Overview
I. Chlorophyll and Chloroplasts
1. Light: wavelengths seen as visible spectrum colors
2. Pigments: light-absorbing molecules in autotrophs
• Chlorophyll a & Chlorophyll b most important
a) Absorbs blue & red regions of visible spectrum best
b) Green NOT absorb but reflect so plants appear green!
c) Cold destroys chlorophyll 1st; others (carotene) visible
w/fall
3. Chloroplast: photosynthetic organelle
• Thylakoids: saclike photosynthetic membranes
a) Arranged in stacks called grana
b) Contain chlorophyll, protein & pigments
• Stroma: outer fluid portion
4. Energy Collection:
Chlorophyll absorbs light and transfers NRG to own electron
molecules
These high-energy electrons fuel photosynthesis
II. High Energy Electrons (e- ):
• Highly reactive and need special carrier molecule
a) NADP+ = nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
b) NADP+ + 2 e- + H+ NADPH
c) NADPH: traps sun NRG into chemical form
d) NADPH: carry e- produced by light absorption to chem rxn in
cell (used to build carbs)
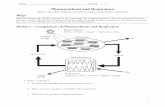
III.Overview of Photosynthesis:
• Uses sunlight NRG to convert carbon dioxide and water (reactants) to sugar and oxygen (products)
a) 6 (CO2) + 6 (H2O) C6H12O6 + 6 (O2)
b) Carbon dioxide + Water Sugars + Oxygen
c) Plants use sugar for NRG and growth
Photosynthesis—2 Steps
1) Light-Dependent Reaction
a) Requires light
b) Occurs in thylakoid membranes
c) Uses energy from light to produce ATP & NADPH:
• Light ATP + NADPH
d) O2 is a by-product
2) Light-Independent Reaction (called Calvin Cycle)
a) Occurs in stroma
b) Does NOT require light
c) Uses ATP & NADPH (from light-dependent) to convert 6 (CO2)
molecules into 1 high-NRG sugar
8.3 (p. 240) Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
1. H20 shortage: may slow or stop photo (desert plant have
waxy leaf coating to slow loss)
2. Temperature: best range 0-35 0C for photosynthetic enzymes
3. Light Intensity: high intensity best up to a point→plant will
reach max photo rate
Light-dependent reactions
Photosynthesis
Light-independent reactions
(Calvin Cycle)
H2O
Stroma
ATP NADPH CO2
Thylakoid membranes
Energy from
Sunlight
Chloroplast
ATP O2 NADPH
NADP High
Energy Sugars
ADP + P
Includes
Uses
To produce
To produce
Takes place in Takes place in
of the
Uses