Chapter 3 Carbohydrates and Lipids. You Must Know The cellular functions of carbohydrates and...
-
Upload
hester-short -
Category
Documents
-
view
235 -
download
0
Transcript of Chapter 3 Carbohydrates and Lipids. You Must Know The cellular functions of carbohydrates and...

You Must Know• The cellular functions of carbohydrates and
lipids.
• How the sequence and subcomponents of carbohydrates and lipids determine their properties.
• (You are not going to be asked about nucleic acids on the Chapter 3 Test.)

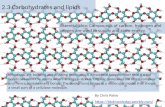
Concept 3.3: Carbohydrates serve as fuel and building material
• Carbohydrates include sugars and the polymers of sugars

• Monosaccharides – serve as a major fuel for cells and as raw material
for building molecules.
– have molecular formulas that are usually multiples of CH2O
– classified by the number of carbons in the carbon skeleton and the placement of the carbonyl group

Figure 3.7c
6-carbon sugars (C6H12O6)
Glucose Fructose
Carbonyl
Aldehyde – because the carbonyl group is at the end of the carbon skeleton.
Ketone – because the carbonyl group is within the carbon skeleton.

Figure 3.9-2
Glucose Fructose
Sucrose
glycosidic linkage

Polysaccharides
• Polysaccharides, the polymers of sugars, have storage and structural roles
• The structure and function of a polysaccharide are determined by its sugar monomers and the positions of glycosidic linkages.
© 2014 Pearson Education, Inc.

Storage Polysaccharides
• Starch, a storage polysaccharide of plants, consists entirely of glucose monomers
• Plants store surplus starch as granules• The simplest form of starch is amylose
© 2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Starch granulesin a potato tuber cell Starch (amylose)
Glucosemonomer

• Glycogen is a storage polysaccharide in animals• Humans and other vertebrates store glycogen
mainly in liver and muscle cells
© 2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Glycogen granulesin muscletissue

Glucose!

Figure 3.11(a) and glucose
ring structures
Glucose Glucose
(b) Starch: 1–4 linkage of glucose monomers
Hydroxyl Hydroxyl
(c) Cellulose: 1–4 linkage of glucose monomers
Starch (and glycogen) are largely helical
Cellulose molecules are relatively straight.

Figure 3.10c
Cellulose microfibrilsin a plant cell wall
Cellulosemolecules
Hydrogen bondsbetween —OH groups oncarbons 3 and 6

© 2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Chitin: another structural polysaccharide

Concept 3.4: Lipids are a diverse group of molecules
• What do these molecules have in common?
© 2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
fat Steroid
phospholipid

Fats
OH
OH
OH
Glycerol
Hydroxyl
HO
HO
HO
Fatty Acid
carboxyl
triglyceride
Ester linkage

• Fatty acids vary in length (number of carbons) and in the number and locations of double bonds
© 2014 Pearson Education, Inc.

(a) Saturated fat
Structuralformula of asaturated fatmolecule
Space-fillingmodel ofstearic acid,a saturatedfatty acid
Saturated fatty acids have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms possible and no carbon carbon double bonds.

(b) Unsaturated fat
Structuralformula of anunsaturated fat molecule
Space-fillingmodel of oleic acid, an unsaturatedfatty acid Double bond
causes bending.
Unsaturated fatty acids have one or more carbon carbon double bonds.

• The major function of fats is energy storage• Fat is a compact way for animals to carry their
energy stores with them
© 2014 Pearson Education, Inc.

Figure 3.14ab
(a) Structural formula (b) Space-filling model
Choline
Phosphate
Glycerol
Fatty acids
Hyd
rop
hili
c h
ead
Hyd
rop
ho
bic
tai
ls
Phospholipids

Figure 3.14cd
Hydrophilichead
Phospholipid bilayer
Phospholipid
Hydrophobictails

Steroids