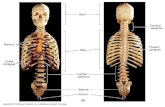
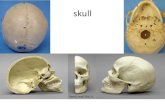
Bones
description
Transcript of Bones

BonesAnisha PatelNicole LinIsabel JacksonMariana Zenteno

Bone Classification• Long Bones: forearm and thigh bone• Short Bones: Bones in the wrists and ankles• Flat Bones: Ribs and part of the skull• Irregular Bones: Bones within the vertebrae• Round Bones: Knee cap

Microscopic Structure• Compact bones• No gaps, osteon units make up the Haversian systems
• Spongy Bones: No central canals• Osteocytes: Bone cells


• Haversian system, or osteon – the structural unit of compact bone• Lamella – weight-bearing, column-like matrix tubes composed
mainly of collagen• Haversian, or central canal – central channel containing blood
vessels and nerves• Volkmann’s canals – channels lying at right angles to the central
canal, connecting blood and nerve supply of the periosteum to that of the Haversian canal• Osteocytes – mature bone cells• Lacunae – small cavities in bone that contain osteocytes• Canaliculi – hairlike canals that connect lacunae to each other and
the central canal
Vocabulary


Cells within the Bones• Osteoblasts – bone-forming cells• Osteocytes – mature bone cells• Osteoclasts – large cells that resorb or break down bone
matrix• Osteoid – unmineralized bone matrix composed of
proteoglycans, glycoproteins, and collagen

Bone Development• Osteogenesis and ossification – the process of bone tissue
formation, which leads to:• The formation of the bony skeleton in embryos• Bone growth until early adulthood• Bone thickness, remodeling, and repair

Classification of Breaks• Bone fractures are classified by:• The position of the bone ends after fracture• The completeness of the break• The orientation of the bone to the long axis• Whether or not the bone ends penetrate the skin

Types of Fractures• Greenstick – incomplete and the break occurs on the convex
surface of the bend in the bone• Fissured – an incomplete longitudinal break• Comminuted – fracture is complete and fragments the bone• Transverse – complete, and the break occurs at a right angle to
the axis of the bone• Oblique – at an angle other than a right angle to the axis of
the bone• Spiral – caused by twisting a bone excessively




Stages of a Healing Bone
1. Hematoma2. Fibrocartilage callus forms3. Granulation tissue (soft callus) forms a few days after the
fracture4. Capillaries grow into the tissue and phagocytic cells begin
cleaning debris5. Bony callus formation6. Bone remodeling


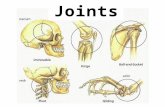
JOINTS• Fibrous Joints
• dense connective tissues connect bones• between bones in close contact
• Cartilaginous Joints• hyaline cartilage or fibrocartilage
connect bones• Synovial Joints• most complex• allow free movement
• synarthrotic• immovable
• amphiarthrotic• slightly movable
• diarthrotic• freely movable

Fibrous Joints• 3 Types
• Syndesmosis• Fibrous sheet that connects the bones together • amphiarthrotic
• Suture• Thin layer of connective tissue that connects two bones
together• Synarthrotic
• Gomphosis• Cone shaped• Synarthrotic

Cartilaginous Joints• 2 Types
• Synchondrosis• Hayline cartilage• Synarthrotic
• Symphysis• Pad of fibrocartilage that lies between two bones• Amphiarthrotic

Synovial Joints• Diarthrotic• Contains Synovial Fluid

Types of Synovial Joints• Ball-and-Socket joint• Hip or shoulder
• Condyloid Joint• Joints in the Metacarpals and Phalanges

• Gliding Joint• Between Carpals and tarsals
• Hinge Joint• Elbow

• Pivot Joint• Between the radius and Ulna
• Saddle Joint• Between carpals and metacarpals

Joint Disorders
• Sprains• damage to cartilage, ligaments, or tendons associated with joints• forceful twisting of joint
• Bursitis• inflammation of a bursa• overuse of a joint
• Arthritis• inflamed, swollen, painful joints
• Rheumatoid Arthritis• Osteoarthritis• Gout