Block diagram reduction techniques
-
Upload
parimalagandhi-ayyavu -
Category
Engineering
-
view
595 -
download
73
Transcript of Block diagram reduction techniques

Block Diagram Reduction Techniques
Prepared by,A.Parimala Gandhi,
AP(SS)/ECE Department,KIT/CBE
CONTROL SYSTEM ENGINEERING

Block diagram
Transfer Function: Ratio between transformation of output to the transformation of input when all the initial conditions are zero.
A Block diagram is basically modelling of any simple or complex system.It Consists of multiple Blocks connected together to represent a system to explain how it is functioning
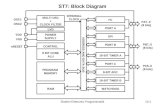
)(sR2G 3G1G
4G
1H
2H
)(sY
)(sG )(sC)(sRG(s)=C(s)/R(s)Simple system:
Complex System:

• It is normally required to reduce multiple blocks into single block or for convenient understanding it may sometimes required to rearrange the blocks from its original order.
• For the calculation of Transfer function its required to be reduced.
Need for block diagram reduction

Block Diagram Reduction techniques
2G1G 21GG
2. Moving a summing point behind a block
G G
G
1G
2G21 GG
1. Combining blocks which are in cascade or in parallel

5. Moving a pickoff point ahead of a block
G G
G G
G1
G
3. Moving a summing point ahead of a block
G G
G1
4. Moving a pickoff point behind a block

6. Eliminating a feedback loop
G
HGHG
1
7. Swapping with two adjacent summing points
A B AB
G
1H
GG1

Example 1
Find the transfer function of the following block diagrams
2G 3G1G
4G
1H
2H
)(sY)(sR
(a)

1. Apply the rule that Moving pickoff/takeoff point ahead of block
2. Eliminate loop I & simplify as
324 GGG B
1G
2H
)(sY4G
2G
1H
AB3G
2G
)(sR
I
Solution:
2G

3. Moving pickoff point B behind block 324 GGG
1GB)(sR
21GH 2H
)(sY
)/(1 324 GGG
II
1GB)(sR C
324 GGG
2H
)(sY
21GH
4G
2G A3G 324 GGG

4. Eliminate loop III
)(sR)(1
)(
3242121
3241
GGGHHGGGGGG
)(sY
)()(1)(
)()()(
32413242121
3241
GGGGGGGHHGGGGGG
sRsYsT
)(sR1G
C
324
12
GGGHG
)(sY324 GGG
2H
C
)(1 3242
324
GGGHGGG
Using rule 6

2G1G
1H 2H
)(sR )(sY
3H
(b)

Solution:
1. Eliminate loop I
2. Moving pickoff point A behind block22
2
1 HGG
1G
1H
)(sR )(sY
3H
BA
22
2
1 HGG
2
221G
HG
1G
1H
)(sR )(sY
3H
2G
2H
BA
II
I
22
2
1 HGG
Not a feedback loop
)1(2
2213 G
HGHH

3. Eliminate loop II
)(sR )(sY22
21
1 HGGG
2
2213
)1(G
HGHH
21211132122
21
1)()()(
HHGGHGHGGHGGG
sRsYsT
Using rule 6

2G 4G1G
4H
2H
3H
)(sY)(sR
3G
1H
(c)

Solution:
2G 4G1G
4H)(sY
3G
1H
2H
)(sRA B
3H4
1G
4
1G
I1. Moving pickoff point A behind block 4G
4
3
GH
4
2
GH

Solution:
2G 4G1G
4H)(sY
3G
1H
2H
)(sRA B
3H4
1G
4
1G
I1. Moving pickoff point A behind block 4G
4
3
GH
4
2
GH

Solution:
2G1G
4H)(sY
43GG
1H
2H
)(sRB
3H4
1G
4
1G
I1. Moving pickoff point A behind block 4G
4
3
GH
4
2
GH

Solution:
2G1G)(sY
1H
2H
)(sRB
3H4
1G
4
1G
I1. Moving pickoff point A behind block 4G
4
3
GH
4
2
GH
2443
43
1 HGGGG

2. Eliminate loop I and Simplify
II
III
443
432
1 HGGGGG
1G)(sY
1H
B
4
2
GH
)(sR
4
3
GH
II
332443
432
1 HGGHGGGGG
III
4
142
GHGH
Not feedbackfeedback

)(sR )(sY
4
142
GHGH
332443
4321
1 HGGHGGGGGG
3. Eliminate loop II & III
143212321443332
4321
1)()()(
HGGGGHGGGHGGHGGGGGG
sRsYsT
Using rule 6

3G1G
1H
2H
)(sR )(sY
4G
2G AB
(d)

Solution:
1. Moving pickoff point A behind block 3G I
1H3
1G
)(sY1G
1H
2H
)(sR
4G
2G A B
3
1G
3G

2. Eliminate loop I & Simplify
3G
1H
2G B
3
1G
2H
32GG B
23
1 HGH
1G)(sR )(sY
4G3
1
GH
23212
32
1 HGGHGGG
II

)(sR )(sY12123212
321
1 HGGHGGHGGGG
3. Eliminate loop II
12123212
3214 1)(
)()(HGGHGGHG
GGGGsRsYsT
4G

End
![CHAP. 7] BLOCK DIAGRAM ALGEBRA AND TRANSFER …wevans/Boxes.pdf · By means of systematic block diagram reduction, every multiple loop linear feedback system may be reduced to canonical](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5fc060bfd49c8d5e8b25ac58/chap-7-block-diagram-algebra-and-transfer-wevansboxespdf-by-means-of-systematic.jpg)