BIOLOGICAL SCIENCE~protein synthesis
-
Upload
eligardi-enterprises-inc -
Category
Technology
-
view
770 -
download
0
description
Transcript of BIOLOGICAL SCIENCE~protein synthesis

PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
Celeste Roderno-Desingaño

PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
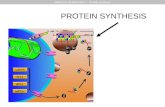
Genetic information is found in the nucleus, though protein synthesis actually occurs in ribosomes found in the cytoplasm and on rough endoplasmic reticulum.
If protein is to be synthesized, then the genetic information in the nucleus must be transferred to these ribosomes. This is done by mRNA.

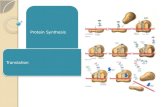
STAGES OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS

TRANSCRIPTION PROCESS If the DNA has
uncoiled, it will allow the mRNA to move in and transcribe (copy) the genetic information.
Once the mRNA has the codon, it moves out of the nucleus and away from the DNA towards the ribosomes.

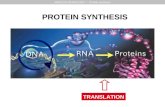
TRANSLATION PROCESS This is the process
of transfer of the information in the RNA into a protein,
The mRNA with the codon that migrates into the cytoplasm will form complementary base pairs with the tRNA anticodon.

TRANSLATION PROCESS The rRNA comes in,
proceeds to the elongation phase of protein synthesis, reads the nucleotide code as translated into polypeptidic sequence, with the proper amino acid.
At the end, a release factor binds to stop codon, termination translation and releasing the complete polypeptide from the ribosome.

EXAMPLE:
Parent strandTAC CCG GCC TTA ATT
anticodonAUG GGC CGG AAU
UAA
Amino Acid FormedMet Gly Arg Asn stop
GENETIC CODE CHART