Biodiesel
-
Upload
ghassan-hadi -
Category
Science
-
view
291 -
download
0
Transcript of Biodiesel


December 10, 2010BRINGING AGRICULTURE AND ENERGY TOGETHER

WHAT IS BIODIESEL?
Fuel from a Source of Oils & Fats... AN ALTERNATIVE GREEN FUEL…
Fatty Acid Methyl Esters can be used directly as Diesel or Blend with Diesel…

RUDOLF DIESELDesigned Diesel Engine in 1894 to Run on Peanut
Oil
“ “The use of vegetable oils for engine fuels may seem The use of vegetable oils for engine fuels may seem insignificant today. But such oils may become in the insignificant today. But such oils may become in the course of time as important as petroleum and the coal tar course of time as important as petroleum and the coal tar products of the present time.products of the present time.""
-An Extract from Diesel’s Speech in 1912

FEED STOCK FOR BIODIESEL • Rapeseed (Germany)
• Sunflower oil
• Soybean oil (USA & Brazil)
• Palm oil (Malaysia)
• Linseed, olive oils (Spain)
• Cottonseed oil (Greece)
• Beef tallow (Ireland), lard, used frying oil (Austria), Jatropha (Nicaragua & South America, India), Guang-Pi (China)
• Used oil ( Austria)

WHAT IS BIODIESEL?Fatty Acid alkyl ester prepared from any oil or fat (animal or vegetable source)
CH2-O-CO
R
CH-O-CO
RAlkaliAcid
+ Methanol RCO
OMe+
CH2-OH
CH-OH
CH2-OHCH2-O-CO
R
OIL / FAT(TRIGLYCERIDE)
Fatty Acid Methyl Ester(Biodiesel)
Glycerol
R-CO
OH+ Methanol
AcidR-C
O
OMe
Fatty Acid Fatty Acid Methyl Ester • Fatty Acid Methyl ester is a well know molecule for vegetable oil industry • Intermediate for fatty alcohols & oleochemicals
TRANSESTERIFICATION
ESTERIFICATION

WHY BIODIESEL?• SUSTAINABILITY
• POLLUTION THREAT
• REDUCTION OF GREEN HOUSE GAS EMISSIONS
• REGIONAL (RURAL) DEVELOPMENT
• SOCIAL STRUCTURE & AGRICULTURE
• SECURITY OF SUPPLY

IMPORTANCE OF BIODIESEL
• Environment friendly• Clean burning• Renewable fuel
• No engine modification• Increase in engine life• Biodegradable and non-toxic• Easy to handle and store

Comprehensive Emissions Analysis for Biodiesel
B20 B100
• NOx 0 +10%• PM -10.1% -47%• HC -21.1% -66%• CO -11.0% -47%• Sulfates -20% -100% (Causes acid rain)• Fuel Economy (B20) -1-2%
B20: 20% biodiesel in diesel

BIODIESEL-WHY LOWER EMISSIONS ?
• Biodiesel has High Cetane• In Built Oxygen Content• Burns Fully• Has No Sulphur• No Aromatics• Complete CO2 Cycle

Exploration
Refining
Use in Cars and Trucks
Fossil CO2 Release to Atmosphere
PETRO-DIESEL CO2 CYCLE13 POUNDS OF FOSSIL CO2 RELEASED PER GALLON BURNED

BIODIESEL CO2 CYCLENO FOSSIL CO2 RELEASED ; NO GLOBAL WARMING
Biodiesel Production
Use in Cars and TrucksOil Crops
Renewable CO2

DIESEL & BIODIESEL DEMAND, AREA REQUIRED UNDERJATROPHA FOR DIFFERENT BLENDING RATES
(Biofuel Document of Indian Govt, 2002)
Year Disel Demand
MMT
Biodiesel @ 5% MMT
Area for 5%
Mha
Biodiesel @ 10% MMT
Area for 10% Mha
Biodiesel @ 20% MMT
Area for 20% Mha
2001-02 39.81 1.99 NA 3.98 NA 7.96 NA
2006-07 52.33 2.62 2.19 5.23 4.38 10.47 8.76
2011-12 66.90 3.35 2.79 6.69 5.58 13.38 11.19
December, 2009 –Indian Biofuel PolicyAn indicative target of 20% by 2017 for the blending of biofuels – bioethanol and bio-diesel

ROAD BLOCKS FOR BIODIESEL INDUSTRY…
• Feedstock Scarcity • Food Vs Fuel Controversy • Initial Enthusiasm Coming Down • Non-edible Oil Production not Encouraging • Effluent-based Traditional Technologies for
High FFA Oils • Pricing of Biodiesel is Not Attractive to
Anybody • Algal Oils – Long way to go…

WHAT IS THE CHALLENGE?• VERY SIMPLE CHEMISTRY…
• Handling multi-feedstock is the real challenge
• VERY LOW FFA – only Transesterification
• HIGH FFA – ESTERIFICATION followed by TRANSESTERIFICATION
• > 99% Yields – to achieve good quality FAME – without distillation!!
• Recovery of good quality glycerol for economic feasibility
• Waste Water Recycling
• Good pre-treatment (lower phosphorus ppm levels)
CH2-O-CO
R
CH-O-CO
RAlkaliAcid
+ Methanol RCO
OMe +
CH2-OH
CH-OH
CH2-OHCH2-O-CO
R
OIL / FAT(TRIGLYCERIDE)
Fatty Acid Methyl Ester(Biodiesel)
Glycerol
R-CO
OH+ Methanol
AcidR-C
O
OMe
Fatty Acid Biodiesel

MAJOR CONCERN…FEED STOCK
• Present Global Production of Biodiesel ~ 14 million metric tons
• Only <50% of Capacity of the Installed Biodiesel Plants Being Utilized…
• This Scenario Indicates Several Road Blocks for Biodiesel Industry
• Main Concern is the Feed Stock. • Edible Vegetable Oil Expected to Remain the Major
Feedstock for the Production of Biodiesel • Countries like India Propagating Non-edible Oils like
Jatropha & Karanja, but not Much Progress • Animal Fats and Used Cooking Oils – Several
Limitations

GLOBAL MAJOR VEGETABLE OIL SCENARIO
Million metric tons
VEGETABLE OIL 2005/06 2006/07 2007/08 2008/09 2009/10
Palm 35.98 37.35 41.31 43.19 45.88
Soybean 34.61 36.39 37.51 36.26 37.88
Rapeseed 17.24 17.03 18.31 20.22 22.12
Sunflowerseed 10.59 10.61 9.73 11.46 11.31
Peanut 4.95 4.50 4.83 5.15 4.56
Palm Kernel 4.38 4.44 4.85 5.10 5.50
Cottonseed 4.62 4.86 5.00 4.72 4.66
Coconut 3.47 3.26 3.49 3.64 3.67
Olive 2.66 2.91 2.84 2.97 2.99
Total 118.49 121.33 127.86 132.70 138.57 Source: Oilseeds: World Markets and Trade, USDA, March 2010

39.05
20.3
11.57
5.06
13
44.62008-09
15.96
9.39
5
11.59
32.89
33.51
2004-05106 mil l ion
134 mil l ion
@ 7 mt/yr
2019-20
@ 5 mt/yr
190 mil l ion
Change in World Vegetable Oil Scenario…
1950’s30 mil l ion
78
50
29
136
14
Palm Soybean
Rape seedSunf low erCot t onseed
Others.

DISTRIBUTION OF VEGETABLE OIL PRODUCTION IN INDIA
OIL 2004-05
MMT 2005-06
MMT 2007-08 MMT
2008-09 MMT
2009-10 MMT
Rape / Mustard 2.13 2.27 1.51 2.15 2.05 Soya 0.87 1.07 1.44 1.33 1.28 Groundnut 1.00 0.99 1.17 0.82 0.61 Rice Bran 0.68 0.73 0.80 0.85 0.80 Cottonseed 0.72 0.77 1.05 0.90 1.08 Sunflower 0.55 0.56 0.51 0.40 0.34 Coconut 0.42 0.42 0.42 0.42 0.43 Castor 0.34 0.38 0.41 0.46 0.42 Sesame 0.19 0.13 0.16 0.17 0.21 Niger 0.04 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.02 Safflower 0.06 0.06 0.05 0.05 0.04 Linseed Palm oil
0.09 0.04
0.09 0.05
0.08 0.06
0.06 0.07
0.07 0.06
Oils from expelled cakes
0.38 0.41 0.47 0.41 0.39
Minor oilseeds 0.08 0.08 0.10 0.10 0.06 TOTAL 7.59 8.03 8.20 8.20 7.88
Source: SEA

INDIAN VEGETABLE OIL PRODUCTION AND IMPORT STATUS
(million tones)
Year Domestic Edible Oil Production
Import of Edible Oils
2009-10 7.9 8.8 2008-09 8.2 8.2 2007-08 8.2 5.6 2006-07 7.72 4.71 2005-06 8.03 4.42 2004-05 7.59 5.04 2003-04 7.78 4.28 2002-03 5.12 5.38 2001-02 6.67 4.42 2000-01 5.81 4.83
Source: SEA

BIODIESEL - INDIAN SCENARIO
• Presently importing about 8.8 million tones of edible oil – ~50% of consumption
• Clean oils are not available for biodiesel production in the country
• Non-edible Oils & Acid Oil – Not more than 5 lakh tones
• To wait till Jatropha / Karanja plantation comes to reality - Oil production only after 2 to 3 years!!

TREE-BORNE OILS
• Tree-borne oils will be major source for Indian Biodiesel
• Most oils are dark
• Possess disagreeable smell
• Contain non-lipid constituents with variety of structural features
• Above problems aggravate by hostile conditions during collection, storage and processing
• Depending on the nature of the non-lipid constituents special processing methods have to be developed
• Any technology in Indian scenario should take care of multi-feed stocks (high FFA and Unsap)

JATROPHA PLANT WITH SEEDS

KARANJA FLOWERS SEEDS

COMPONENTS RESPONSIBLE (PRESENT IN
CURDUE OIL) FOR LOW QUALITY BIODIESEL
• Gums
• Free fatty acids
• Waxes
• Unsaponifiables
• Pigments

Neutralization
Transesterification 2-Stage process
Neutralization & Distillation Washing & Drying
PROCESS FOR BIODIESEL PRODUCTION
Distilation
*Esterification step is only for high FFA oils Not necessary for low FFA oils
Esterification
CRUDE OIL/ DEGUMMED OIL
Acid catalyst* Methanol
FATTY ACID METHYL ESTER TRIGLYCERIDE
Methanol Alkaline catalyst
SETTLING TANK
FATTY ACID METHYL ESTER GLYCERINE LAYER With Methanol and Alkali
METHANOL CRUDE GLYCEROL ≈ 80%
BIODIESEL
POTASSIUM SULPHATE (Fertilizer)

PRE-TREATMENTS BEFORE TRANSESTERIFICATION
TO HANDLE GUMS AND FFA
Physical Refining Degumming and Bleaching followed by removal of FFA by Deacidification (High Temperature Distillation)
Chemical Refining Removal of FFA using alkali neutralization - Heavy loss of Neutral oil along with Soap (2.5 times of FFA)
Esterification Converts FFA to Methyl esters (increases yield of Biodiesel) – Most appropriate option

NEWER APPROACHES • Flexible process for handling variable quality feed stocks with
high FFA and unsaponifiables
• Efficient conversions using traditional catalysts like NaOH / KOH / H2SO4
• Catalyst-free esterification and transesterification • Application of heterogeneous catalysts for both esterification
and transesterification • Biotechnological approaches using lipases • Microbial production of oil or fatty acid methyl ester • Value addition to by-products

ADVANTAGES OF HETEROGENOUS CATALYSTS
• Substantial reduction of waste/by-product generation
• Savings on catalyst cost – Recycling
• Considerably greater increase in reactor throughput
• Smaller heat exchange areas – Reduced costs
• Greater ease of automation and continuous processing
• Sustainable reduction in operating costs
• Reduction in chemical use (Catalysts, reagents used to neutralize catalysts)
• Reduction in effluents

LIMITATIONS OF REPORTED SOLID ACID CATALYSTS
• Most of catalysts reported requires
• Higher temperatures • Pressure
• Reusability of catalyst not so good
• Many of them are water sensitive

LIPASE CATALYZED PREPARATION OF BIODIESEL
CH-O-C-R
O
O
CH2-O-C-R
O
CH2-O-C-R
+CH3OH
R-C-OMe
O
CH-OH
CH2-OH
CH2-OH
Triglyceride FFABiodiesel Glycerol
LipaseR-COOH +
• Both esterification and transesterification at Room-temperature or less than 50°C• Immobilized enzymes can be recycled upto 20 to 30 times • Still unfavorable for commercial exploitation • Methanol or ethanol denatures the lipase• Lot of scope for biotechnological revolution in this area

GLYCEROL + H2SO4 CARBON-ACID CATALYST
In situ Carbonization and Sulfonation
GLYCERL-BASED CARBON ACID CATALYST – NEW INNOVATION
INDIAN & PCT PATENTS FILED, 2007 & 2008ChemSusChem, 2008
CARBON-ACID CATALYST

Powder XRD pattern
13C MAS NMR Spectrum
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) image
FT-IR Spectrum
CHARACTERIZATION OF GLYCEROL-BASED CARBON ACID CATALYST

XSP Spectrum Raman spectrum
CARBON ACID CATALYST
SO3H
GLYCEROL
OH OH
OHSO3HSO3H
SO3H
SO3H
Conc. H2SO4/ heat
SO3H
SO3H
SO3H
HO3S
HO3S
HO3SHO3S
In situ Carbonization & Sulfonation
Elemental Analysis, X-ray Diffraction, SEM, FT-IR, 13C MAS NMR, XSP Spectrum, Raman Spectrum, TG/DTA Analysis, Potentiometric Titration and BET Surface Area
Characterization…

HOW TO MAKE BIODIESEL CHEAPER?
• Efficient Process for Biodiesel Production – Presence of Minimum Amounts of Triglyceride, Diglyceride and Mongoglycerides in the Biodiesel
• Phytochemicals & Nutraceuticals of Oil &
Other Parts of the Tree (Leaves, Flowers, Bark etc.)
• Alternate Applications for Oilseed Cake (Rich
in Starch and Protein • Newer Applications for Glycerol

TREE-BORNE LIPIDS & OTHER USEFUL CONSTITUENTS
• LEAF LIPIDS
- Rich in Biologically Active Constituents - Internal Lipids
Acid glycerols, hydroxyl fatty acids etc., - Epicuticular waxes
Rich in Hydrocarbons, wax esters, aldehydes, ketones, steryl esters, acetates, fatty alcohols, sterols, triterpenols, fatty acids, etc.
• SEED OILS
- Edible oils, Structured fats, Industrial Oleochemicals like Biopesticides, Phytochemicals, Nutraceuticals like Gums (lecithin), Tocopherols, Phytosterols, Glycerol
• SEED CAKES
- Rich Source for protein and starch - Good Fertilizer - Starch and protein based surfactants

KARANJA BIOREFINERY
KARANJA SEEDS
Bioactive Constituents
Cake Oil Lubricant Base Oils & Additives
Protein,Starch, Oil
Varieties of Products like Surfactants, Lubricants,Fertilizer etc.
Fatty Acid AlkylEsters
Crude Glycerol
Minor Constituents
LubricantBase Oils & Additives
Bioactive Constituents
Different Grades of Glycerol
Variety of Value Added Products
Sponsored by Department of Science & Technology Rs. 18.6 Millions

BIODIESEL PROCESS
Esterification Neutralization Transesterification
Separation
Non-edible Oils with FFA
Alcohol +
Acid Catalyst
Alcohol
Alcohol + Base Catalyst
Glycerol
Biodiesel
Nature of this crude glycerol is different from the glycerol produced by Fat Splitting or the Edible oil-based biodiesel glycerol
Glycerol ~ 50% Alcohol Water Biodiesel Catalyst Soap Salts Minor Constituents

POTENTIAL DERIVATIVES OF GLYCEROL
• Structured Lipids
• Oxidation Products
• Glyceryl Ethers
• Prodrugs
• Triacetin, Glycerol carbonate type of by-products (in place of glycerol production)

MAJOR APPLICATIONS OF OILSEED CAKES- PRESENT STATUS
Edible Oilseed Cakes
• Source of Protein in Case of Clean Cakes like Groundnut, Soybean, etc.
• Animal Feed Formulations
Non-edible Oilseed Cakes
• Manure
• To Explore for Variety of Applications

JATROPHA / KARANJA CAKES • Huge Quantities of Jatropha / Karanja Cakes if
these Plantations Suceed…
• Every Tonne of Biodiesel Results in about 2 tonnes of Oilseed Cake
• Oilseed Cakes – Real Asset for the Nation as they are Biodegradable
• Potential Feedstock – To Make Biodiesel Industry More Attractive
• To Develop variety of Products from these Cakes

COMPOSITION OF JATROPHA AND KARANJA OILSEED CAKES
Constituent Jatropha Karanja Nitrogen/Protein (wt %) 4-6/25-40 4-7/25-40 Carbohydrate (wt %) 15-20 15-20 Fibre (wt %) 15-20 15-20 Ash (wt %) 3-5 3-5 Phosphorus (wt %) 1.5-3 1-2 Potassium (wt %) 1-2 0.5-1.5 Calcium (wt %) <1 <1 Magnesium (wt %) <1 <0.5 Zinc, Copper, Magnesium, Boron (ppm) <100 <100 Sulphur (ppm) <3000 <4000
* Compositions may not be authentic as all the results are isolated / very old reports

BIOREFINERY OF OILSEED CAKES – POTENTIAL PATHWAYS
OILSEED CAKE (BIOMASS)
Oil
Deoiled Cake
Protein
Carbohydrates
Composite Materials, Surfactants
Fermentation
Biogas (Methane-rich)
Syngas
Bioactive Constituents
Carbon Source for Microbial Lipids / Enzymes
Protein Hydrolysate Surfactants
Fertilizer
Bioethanol
Fuel, Chemicals
Lubricants, Surfactants, Polymers

BIOETHANOL FROM CAKES • Currently, Ethanol is made from Corn Grain Starch /
Sugarcane Molasses
• Newer Feedstocks Required to Meet the Future Demands
• Oilseed Cakes / Hulls – Potential Feedstock as they are Made up of Cellulosic Materials
• Efficiency of the Pre-treatment and Fermentation Process has to be Optimized based on the Yield of Free Sugars and Ethanol

CARBON SOURCE FOR MICOBIAL GROWTH
• For the Production of Microbial Lipids / Non-lipids or
Enzymes – Carbon Source Required
• Microbial Degradation of Solid Agricultural Waste (Carbon Source) is a Natural Process
• Known / Specific Microbial Strains may Produce Desired Products / Enzymes in Presence of a Carbon Source
• Oilseed Cakes can be Directly Used as Carbon and Energy Source for Microbial Growth / Production of Desired Products for Many Potential Applications
• To Produce Extra Cellular Enzymes such as Proteases, Lipases, Xylanase and Cellulase by Solid-state Fermentation

BIOMETHANATION OF OILSEED CAKES • Several Biogas Plants not in Use for Want of
Feedstock
• Oilseed Cakes – Excellent Feedstock
• 0.25 to 0.35 cubic meters of Biogas can be Produced from 1 kg of Jatropha Cake with ≈ 70-80% Methane Content [Satish Lele (www.Svlele.com)]
• Area of Plot, 300m2 ; Manpower, Two unskilled; Power Supply, 1 kw; Cost, Rs. 5 Lakhs
• Methane gas – For Generating Electricity – To Promote On-farm Energy Self-sufficiency
• Left out Slurry from the Bioreactor – Serves as Organic Manure

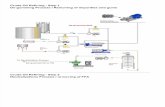
Continuous Biodiesel Pilot Plant (10 kg/hr)
Studies on Physico-chemical Properties of Jatropha/Karanja Seeds (AP State Govt)
60 kg/hr Expeller for Jatropha/Karanja Seeds
Pre-treatment Pilot Plant (15 kg) for Crude Oil
Batch (50 kg) and Continuous (10 kg/hr) Biodiesel Process (AP State Govt & DBT)
Carbon Catalyst from Glycerol for Esterification / Transesterification (CSIR)
Development of Value added products from Karanja oil, cake and glycerol (DST)
Screening of Minor Oils for Biodiesel Production (DST)
Algal Oil-based Biodiesel (Collaborative Project) (DBT, NMITLI)
Exploratory studies on lipase-assisted preparation of biodiesel to enhance
stability to lipase
Established State of Art Facilities for Vegetable Oils, Biodiesel, Lubricants Research (CSIR, DST)
BIODIESEL – IICT’S PROGRAMME
Expeller Pre-treatment Plant

Thank you…