Articulations Junctions between bones Bind parts of skeletal system together
Articulations (Joints) Articulation = joint = point of contact between bones.
-
Upload
evangeline-green -
Category
Documents
-
view
227 -
download
0
Transcript of Articulations (Joints) Articulation = joint = point of contact between bones.

Articulations
(Joints)
Articulation = joint = point of contact between bones

Joint ClassificationFunctional Name Structural Name Movement Example Description
Synarthroses Fibrous Immovable Syndesmoses ligaments
Sutures skull
Gomphoses Teeth to jaw
Amphiarthroses Cartilaginous (hyaline, fibrocartilage)
Slightly movable
Synchrondosis Ribs, epiphyseal plate
Symphyses Pubis, vertebral discs
Diarthroses Synovial Freely movable Uniaxial Hinge, pivot
Biaxial Saddle, ellipsoidal
Multiaxial Ball and socket, gliding

SynarthrosesFibrous Joints

AmphiarthosesCartilaginous

DiarthrosesSynovial
• Most numerous• Most complex• Structures
– joint capsule • sleevelike encasing around bone ends
to bind them together– synovial membrane
• membrane lining capsule to secrete synovial fluid
– bursae • cushions joints and helps tendons
move– joint cavity
• small space between bones– articular cartilage
• hyaline cartilage covering bone ends– menisci
• pads of fibrocartilage between bones– Ligaments
• strong, dense, white fibrous tissue that hold bones firmly together
bursae

Types of Joints
ellipsoidal

Uniaxial Joints permits movement around one axis and one plane
• allows only flexion and extension– examples – elbow, knee
• knee joint – largest joint, most complex, most frequently injured
• projection of one bone articulating with a ring/notch of another bone– examples - between vertebrate

Biaxial Jointspermits movement around two perpendicular axes and planes
• Example– thumb
• only saddle joint in the body
• condyle fits into an elliptical socket
• Example– between radius
and carpals
ellipsoidal

Multiaxial Joints permits movement around three or more axes and planes
• most moveable joints• ball shaped head fits into concave depression• example - shoulder, hip
– humeroscapular joint• most mobile joint
– sacroiliac joint• hip joint
• relatively flat articulating surface that allows gliding movement
• example – between carpals– between tarsals– between vertebrate

Multiaxial
Ball and socket

Multiaxial
Ball and socketMultiaxial
Ball and socket

Multiaxial
Gliding
Herniated Discs
Multiaxial
Ball and socket

Uniaxial
HingeMultiaxial
Ball and socket


Meniscus
Normal Tear of medial meniscus

• __________________– Used to determine extent of injury
and progress of rehabilitation– measures range of motion
(degree of angle)
ROM(Range of Motion)

____________ ROM• flexion – decreases angle,
movement towards body• extension – increase angle,
movement away from body• hyperextension – stretching or
extending beyond anatomical position
• plantar flexion – increase angle between top of foot and front of leg (point up/flex)
• dorsiflexion – decrease angle between top of foot and front of leg (point down)
• ABduction – move AWAY from medial plane
• ADduction – move TOWARDS medial plane

• rotation – pivoting a bone on its axis
• circumduction – distal end of a body part moves in a circle
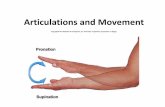
• supination – hand palm side up
• pronation – hand palm side down
____________ROM

Special Movements• inversion – turn foot inward• eversion – turn foot outward• protraction – move part forward• retraction – move part backward• elevation – move part up• depression – move part down

Joint Disorders
• _________________(NIJD)– Osteoarthritis– Tramatic Injuries
• Dislocation• Meniscus tear• Sprain• Ligament tear• Herniated disc
• _________________(IJD)– Rheumatoid arthritis– Gout

Joint Disorders
• Osteoarthritis– Most ____________ NIJD– Wear and tear deterioration– Atrophy of ____________ cartilage– Formation of new _______ at joint surface– Most common in weight-bearing joints– Stiffness, pain, limited movement– Treat symptoms with NSAIDS

Joint Disorders• ________________
– Articular surfaces not in proper contact– Torn vessels, nerves, ligaments, muscles– Pain and swelling– Treat with realignment (reduction)

Joint Disorders
• Meniscus Tear– One of most common athletic injuries– Swelling, pain, instability, limited motion– Treat with arthroscopic surgery

Joint Disorders• ___________
– Stretching of ligaments surrounding joint– Due to twisting motion– Hematoma, limited motion– Treatment: R.I.C.E.

Degree of Sprains• ______ degree ankle sprain
– Some stretching or perhaps tearing may have occurred– No loss of function– Mild pain, little bruising– Little or no swelling– Some joint stiffness or difficulty walking
• ______ degree ankle sprain– Difficulty walking– Moderate to severe pain– Swelling and tenderness in the ankle joint– Bruising may start after 3 to 4 days
• ______ degree ankle sprain– most serious– Total rupture of a ligament– Walking may not be possible– Severe pain initially and substantial swelling– May require surgery

• Ligament Tears (___ degree Sprain)• Bruising, pain, swelling, instability• Physical therapy• Partial tear vs. complete tear
– Partial Tear – boot/brace, crutches– Complete Tear - Surgery after most swelling subsides
Joint Disorders

Knee Injuries

____________________ surgery
• 3-4 very small incisions ¼ in. – fiber-optic light
source – video camera – terile saline solution
is continuously pumped through the knee via a cannula

Video of surgery

Joint Disorders
• Rheumatoid arthritis– Chronic and systemic– Inflammation of ___________ membrane– ______________ destroyed, bone erosion– Progressive crippling and _____________– Pain, inflammation, decreased mobility,
aching, stiffness– Treat with corticosteroid drugs and NSAIDS

Joint Disorders
• Gouty arthritis– Also referred to as just _________– Excessive _______ ________ in blood– Crystals get deposited in _____________fluid– Chronic inflammation and tissue damage– Swelling, tenderness– Pin in wrists, fingers, ankles, knees, elbows– Treat with Allopurinol (inhibits uric acid
synthesis)

Joint Disorders
Osteoarthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis Gout
NIJDC
IJD IJD