ARTICULATIONS
description
Transcript of ARTICULATIONS

ARTICULATIONSJoints in the Human Body

WHAT ARE ARTICULATIONS?
Articulations are joints Places where two or more bones meet

THERE ARE 3 MAJOR CATEGORIES:
Fibrous joints, aka synarthrotic joints Cartilaginous joints, aka amphiarthrotic Synovial joints, aka diarthrotic joints

FIBROUS JOINTS - SYNARTHROTIC
Two or more bones joined by fibrous connective tissue
Can have very limited but usually no motion

THREE TYPES OF FIBROUS JOINTS
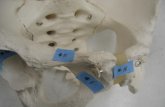
SUTURES: located between bones of the skull. They are immovable.
FONTANELS are areas of unossified bone in children under two years old.

SYNDESMOSES
In a syndesmosis joint, bones are farther apart than in sutures and they are also connected by ligaments.

GOMPHOSES
A Gomphosis is a “peg” held in a socket by fibrous tissue. Teeth held in the maxilla and mandible by periodontal ligaments are examples..

REVIEW: THE THREE FIBROUS JOINTS ARE????
Sutures Syndesmoses gomphoses

THE CARTILAGINOUS
JOINTSAMPHIARTHROTIC JOINTS

CARTILAGINOUS JOINTS: Two or more bones connected by
hyaline or fibrocartilage. This type of joint provides
limited motion

TWO TYPES OF CARTILAGINOUS JOINTS:
Synchondroses:
Bones connected by hyaline cartilage
Little or no motion
Ex: epiphyseal plates
Symphyses: Bones
connected by fibrocartilage
Provide slight motion
Ex: vertebrae and pubic bones