Aim: How are coordinate covalent bonds different than regular covalent bonds? Do Now: 1.Take out a...
-
Upload
primrose-pitts -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
0
Transcript of Aim: How are coordinate covalent bonds different than regular covalent bonds? Do Now: 1.Take out a...

Aim: How are coordinate covalent bonds different than regular covalent
bonds?
Do Now:1.Take out a calculator and reference tables.
2.Draw a dot diagram for the following molecules: •MgCl2
•H2O
•NH3

Answers to the do now
• MgCl2
• H2O
• NH3

What type of bond do those compounds have?
• MgCl2
• H2O
• NH3
• What happens to electrons in a covalent bond?• In a covalent bond, the atoms involved share
electrons. Example: H2O

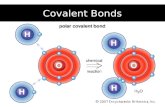
A new type of bond…• Coordinate covalent bonds – a pair of shared
electrons is supplied by a single atom. • Example: The H+ ion is a particle that can accept a
pair of electrons (remember that H+ is basically a proton). It can join a water molecule to form H3O+ . This is called a hydronium ion. It can be written as shown above or H+
(aq) .
• Let’s draw the dot diagram.

Another Example
• NH3 – Let’s draw the dot diagram.
• If NH3 accepts a H+ what does it become?
• Let’s draw the dot diagram.

How can we tell which bond is the coordinate covalent bond?
• You can’t. Once the coordinate covalent bond is formed, it is indistinguishable from an ordinary covalent bond.
• What is the result? • Now, you have a polyatomic ion with a positive or
negative charge. • Most polyatomic ions contain coordinate covalent
bonds. • Where can we find a list? • Reference Table E

Activity
• Textbook page 400 – Copy and Answer Questions 18-24

Homework #