08/10/20151 Cardiovascular system (CVS) CVS consists of the heart and a series of blood vessels...
-
Upload
jason-summers -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
2
Transcript of 08/10/20151 Cardiovascular system (CVS) CVS consists of the heart and a series of blood vessels...

19/04/23 1
Cardiovascular system (CVS)
CVS consists of the heart and a series of blood vessels (arteries, veins and capillaries).

Introduction1) A functional cardiovascular system is vital for 2)supplying oxygen and nutrients to tissues and removing wastes from them.3)The heart is the strongest muscle in the body 4)The heart must pump blood throughout the body day & night 5)The heart is 2 pumps working side by side. On your right side is the heart that pumps blood to your lungs where it picks up O2.

1) On your left side is the heart that pumps this O2-soaked blood out to your body.
2) Heart pumps 200,000000L blood in a lifetime
3) Both pumps are divided into 2 spaces called chambers so your heart is actually a 4-chambered pumper
4) The 2 sides do not work independently; they are precisely timed.

19/04/23 4

Main functions of the circulatory system
1) Transport and distribute essential
substances to the
tissues.
2) Remove metabolic byproducts.
3) Adjustment of oxygen and nutrient
supply in different physiologic
states.
4) Regulation of body temperature.
5) Humoral communication.

Cardiovascular system

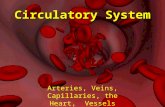
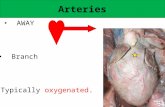
The Blood Vessels• The CVS has three types of blood vessels:• Arteries (and arterioles), Capillaries, Veins
(and veinules)• The Arteries and arterioles take blood
away from the heart. • The largest artery is the aorta. • The middle layer of an artery wall consists
of smooth muscle that can constrict to regulate blood flow and blood pressure.
• Arterioles can constrict or dilate, changing blood pressure

• Capillaries have walls only one cell thick to allow exchange of gases and nutrients with tissue fluid.
• Capillary beds are present in all regions of the body but not all capillary beds are open at the same time.
• Contraction of a sphincter muscle closes off a bed and blood can flow through an arteriovenous shunt that bypasses the capillary bed.
• Veins• Venules drain blood from capillaries, then join to form veins that
take blood to the heart. • Veins have much less smooth muscle and connective tissue than
arteries. • Veins often have valves that prevent the backward flow of blood
when closed.• Veins carry about 70% of the body’s blood and act as a reservoir
during hemorrhage.

Figure 15-3: Metarterioles


. The heart is divided into 4 hollow chambers-2 atria (upper) & 2 ventricles (lower)
Right chambers & valves:1)right atrium Receives blood from 2 large veins called the superior vena cava & the inferior vena cava; coronary sinus also drains blood into the right atrium from the myocardium
1)Tricuspid valve (3 cusps) guards the atrioventricular orifice between the right atrium & the right ventricle; it permits blood to move from the right atrium into the right ventricle & doesn’t allow it to move in the opposite direction;

Chambers of the heartChambers of the heart The atria are smaller with thin walls, while the ventricles are
larger with thick walls (much stronger): The left ventricle has thicker wall than the right because it needs to pump blood to the whole body.

Right ventricle pumps blood a short distance to the pulmonary trunk (lungs); blood goes to pulmonary
trunk which divides to form the left & right pulmonary arteries (deoxygenated blood)
1) Pulmonary valve (3 cusps) – guards the base of the pulmonary trunk; opens as the right ventricle contracts Left chambers & valves:1)left atrium receives blood from the lungs through 4 pulmonary veins – 2 from right & 2 from left lungs2) The blood passes from the left atrium into the left ventricle through the atrioventricular orifice; bicuspid or mitral valve guards the left atrioventricular orifice; it prevents blood from flowing back into the left atrium from the ventricle when the ventricle contracts3)The left ventricle pumps blood by way of the aorta (large artery) into systemic circulation an aortic valve guards the base of the aorta

The left ventricle’s myocardium is thicker than the right ventricle’s
myocardium in order to: contract with a greater pressure



Heart Valves

- Which blood vessel receives blood from the left ventricle
during systole? aorta

Heart Valves
Atrioventricular
1) Tricuspid
2) Bicuspid or mitral
Prevent blood from
flowing back to
Right or left atrium
• Semilunar
valves
1)Aortic
2)Pulmonary
• Prevent blood
from flowing
back to Right
or left
Ventricle

When aortic pressure is greater than the ventricular pressure:
the aortic semilunar valve closes

- When aortic pressure is less than ventricular pressure, this causes:
. the aortic semilunar valve to open

The Heart: PumpsThe Heart: Pumps1) The right heart pump: receives deoxygenated blood from all parts
of the body except the lungs (through superior & inferior vena cava)
pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs Pulmonary circulationPulmonary circulationThe left heart pump: receives oxygenated blood from the lungs
(through pulmonary veins)pumps oxygenated blood to the rest of the
body Systemic circulationSystemic circulation

Type of circulation



19/04/23 26
Blood Flow Through Heart

20-27
Blood Flow Through Heart

Cardiovascular system
Cardiac cycle- It is the period which passes from the beginning of
one beat until the beginning of the next one.- The cardiac cycle takes 0.8 sec. when the heart
rate is 75 beats per minute.- During the cardiac cycle there are certain stages
which are:1.Stage of filling of the heart with blood.2.Stage of contraction of the cardiac muscle.3.Stage of ejection of blood.4.-stage of relaxation.

The HeartbeatEach heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle.When the heart beats, the two atria contract
together, then the two ventricles contract; then the whole heart relaxes.
Systole:- is the contraction of heart chambers;Diastole:- is the relaxation of heart chambersThe heart sounds:- Lub-dup, Lub:- is due to the closing of the
atrioventricular valves, Dup:- is due to closing of the semilunar valves.

The tricuspid valve is normally closed:
while the ventricles are in systole

The Heart: The Heart: SystoleSystole
Systole:Systole:It is the contraction of the entricles.
• When the ventricles contract they force the blood
into the great arteries. From the left ventricle into
the aorta From the right ventricle into
the pulmonary artery. The increased pressure that
result due to the contraction of the ventricles is called systolic pressure.

The Heart: The Heart: DiastoleDiastole
Diastole : It is the relaxation of the ventricles.
When the ventricles relax they receive the blood
from the atria. The decreased pressure
due to the relaxation of the ventricles is called diastolic pressure.

Cardiac out put• Is the volume of blood ejected by the
left ventricle per minute• The cardiac output=C.O.P= S V x HR
S V : Stroke volume: is the volume of
blood ejected by each ventricle per
beat. = 75 ml of blood
HR: = Heart rate: is the number of heart
beat per minute = 72 beat/ minute
COP= 75x 72= 5,400 L/ minute33

Cardiovascular system
Stroke volume - It is the volume of blood pumped by each ventricle per
beat.- Normally it is about 70 ml/beat.- The stroke volume of left ventricle = that of right side ‼- The stroke volume is determined by the venous return.- Cardiac output (COP)- It is the amount of the blood pumped by each ventricle
per minute.- It is about 6 liters / minute at rest.- It can increase to 25 liters/min. during violent exercise.

Cardiovascular system
_ Cardiac output = stroke volume x heart rate.
- So, the COP is increased by an increase in stroke volume or heart rate or both.
- Factors affecting cardiac output.1.Venous return.2.Force of heart contraction.3.Frequency of the heart rate.4.Blood pressure.

- Excessively high heart rate (>180) can reduce cardiac output
because: it reduces the time for ventricular
filling which reduces stroke volume








![1 a veins arteries capillaries · veins arteries capillaries First _____ next _____ last _____ [1 mark] b Choose from the list of organs in the box to answer the question. From which](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5f1fa4f65f10160d415d4180/1-a-veins-arteries-capillaries-veins-arteries-capillaries-first-next-.jpg)