02 Lipids DLevy
-
Upload
sushil-dombe -
Category
Documents
-
view
38 -
download
1
Transcript of 02 Lipids DLevy

Electron crystallographyUC DAVIS, 2006
Lipids in 2D crystallization
Daniel Lévy

- Structure of lipids
- Properties of lipids
- Lipids in preparation of purified solubilized proteins
- Solubilisation of lipids by detergent
- Reconstitution of lipids upon detergent removal
- Lipids in 2D crystallization
- Lipid/detergent phases
- Lipid ligand for 2D crystallization

2D crystallyzation of membrane proteins
Parameters
-Lipid/protein ratio-Type of lipids
-Type of detergent- Rate of detergent removal
- Buffer composition-T°C
- Inhibitors, substrates
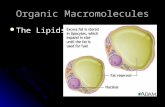
detergent
lipid

Amphiphiles
phosphatidyl choline lyso- phosphatidylcholine dodecylsulphate
Polar
Non-polar

What’s the difference between amembrane lipid and a detergent?
• Water solubility.• Membrane lipids are soluble to about 10-9M• Detergents are soluble in the range 10-6 to 10-2M• This is because the non-polar regions of detergents are
smaller and only one alkyl chain• Lyso -phospholipids are detergents.

LIPIDS


Lα
Lc
Lβ’
θ
θ

Transition Temperatures gel to liquid phase
Increases with the number of CH2
Increases with the unsaturation
Lipid extracts are in fluid phase

Cell membrane compounds
---3070Chloroplast innermembrane
trace---
4522
5578
Mitochondrionouter membraneinner membrane
102664Golgi complex102762Endoplasmic reticulum23266Nuclear envelope
81043
43364279
49545418
Plasma membranes:red blood cellsliver cellsamoebamyelin
CarbohydrateLipidProteinMembranes
% of dried compoundsAdvanced Cell Biology ed. by L.M. Schwartz and M.M. Azar. Van Nostrand (New York; 1981).
Eucaryote
Lipid/protein < 0.3 - 4 w/w >

Lipids are usually co-purified with solubilized proteinsand increase the protein stability
Wang lab,http://saturn.med.nyu.edu/research/sb/wanglab/
% monomer/polydispersity
Purification of Glut1 from human erythrocytes
Purification of the ABC transporter BmrA from B. subtillis expressed in E. coli (Ravaud, 2006)
Dimerization of PSII by DGDGKruse, 2000

Lipids spontaneouly form bilayers in presence of water
The morphology of liposomes depends on methods of formation

Cryo-EM is a powerfull technique for the characterization of the liposomes(Negatively stain usually leads to artefactual images of lipidsl)
unilamellar multilamellar
tubesAngular shaped

OD
400
nmSolubilization of liposomes by detergent
For a lipid concentration of L (mM)Onset of solubilization at Dsat=Dw+Rsat (L)End of solubilization at Dsol=Dw+Rsol (L)

DETERGENT DwatermM mg/ml
Rsatmol/mol w/w
Rsolmol/mol w/w
TRITON X100 0.18 0.12 0.64 0.5 2.5 2.0
C12E8 0.20 0.11 0.66 0.45 2.2 1.5
Octylglucoside 17 4.9 1.3 0.48 3.0 1.1
DDM 0.3 0.15 1 0.65 1.6 1.0
Cholate 3 1.29 0.3 0.16 0.9 0.5
The minimal amount of detergent needed to solubilized lipidsin 2D crystallization trials can be calculated (usefull for the dialysis)
For P=0.5mg/ml, LPR 0.5, Lipid 0.25 mg/mlFor full solubilization of lipid/protein inDDM 0.025%, OG 18mM

- Fast equilibration of lipid/det/protein micelles (Bio-Beads): addition as liposomes- Taking care of the solubilization dynamic
- slow equilibration between micelles (dialysis)- Addition as solubilized lipids at Rsol
Kinetic of solubilization of lipid by detergents
OG
DDM
DOPC
DPPC
OG
C12E8 DDM
DOTM FOS-F16
AFM of planar lipid bilayer treated withdetergent at the cmc 4°C, 30 min
liposomes
micelles

DIALYSIS
DILUTION
GEL CHROMATOGRAPHY
POLYSTYRENE BEADS
PROTEOLIPOSOMESMIXED MICELLES
Reconstitution by detergent removal

Detergent removal by dialysis
Dialysis bagCut-off 14kD
High cmc detergents 1-2 daysLow cmc detergents 1-2 weeks
Simplicity and low costFlowthrough dialysis cellBio-Beads ouside

COMPOUND ADSORPTIVE CAPACITY
(mg/g beads).
DETERGENT
TRITON X 100 185
C12 E8 190
DODECYL MALTOSIDE 105
CHOLATE 80
CHAPS, CHAPSO. 85
HECAMEG 110
OCTYL GLUCOSIDE 117
PHOSPHOLIPID
LIPOSOMES 1
LIPID-DETERGENT MICELLES
(Rsol)*
2
LIPID-DETERGENT MICELLE
(3. Rsol)
4
LIPID-DETERGENT-PROTEIN
MICELLES 0.5-1
PROTEIN
BR, Ca++ATPase, F0F1, melibiose
permease, cytochrome b6f
0-0.2
Detergent removal by Bio-Beads

C12E8(0.2mM)
OG (17mM)Hecameg
DDM(0.2mM)
J.Struct.Biol (1997) 118, 226
Bio-Beads adsorb low andhigh cmc detergents
Time courses of detergent removal
Complete detergent removal using Bio-Beads and relative control of the ratedetergent removal

detergent
lipid
Lipids in 2D trials
Preparation of lipids
Lipids are usually solubilized in CHCL3(in EtoH for cholesterol)-Keep at -80°C under Argon
For mixture of lipids, mix CHCL3-solubilized lipidsDry the solutionResuspend in water, vortex, sonicate with a tip sonicatorAliquot and freeze

Statistically used lipids for crystallization
DMPC(C14, no insaturation)
DOPC (C18, insaturations)DOPC/DOPGDOPC/POPC
E.Coli lipids(Polar extract)
- not native membrane lipids- highly different lipids- no report with mixture containing cholesterol

Membrane proteins are usually reconstituted in different kind of lipids at low LPR(in protein non-aggregation conditions)
Part I: lipids are not important for 2D crystallization

Lipid/protein ratio is often the major parameter
LPR 0.35 w/wtubes
vesiclesLPR=0.25 w/w
PPase(thermotoga marinatus)
Stahlberg, 1998

Proteins crystallized in different types of lipids
Even synthetic lipids lead to highest resolution 2D crystals
Gonen, 2005
Hasler, 1998

D.Stokes, 1998
2D crystallisation of purified Ca-Atpasefrom sarcoplasmic reticulum induced by vanadate
Part II: Lipids are important for 2D crystallization
+ vanadate
- a) Specific defaults in lipid bilayer induce 2D crystallization

Lipids as defaults in the bilayer
Lacapere, 1998

T° phase transition(DMPC)
BR crystallisationinproteoliposomesof DMPC
25°C
4°C
Watts, A. 1995

Micellar equilibration
Post-vesiculation
I
II
Bila
yer
clos
ure
III
Part III: lipid/detergent phases are crucial for 2D crystallization
Lipid/detergents intermediates are detergent and rate specifics

Slow detergent removal at 4°C Fast detergent removal at 20°C
2D crystals of DDM purified Melibiose permease
The rate of detergent removal is a parameter of 2D crystallization

Specific lipid/DDM or DOTM phases
Lambert, (1998)

1µm
DOTM(BB)
DOM(BB)
OG/cholate(BB)
2D crystals of LH1-RC from Rb. sphaeroidesSame rate of detergent removal

Octyl-thio-glucoside/lipid phase
Reconstitution of liposomes from different detergents solubilized lipids
OG DDM
LDAO LDAO + OTG

250 nm
FhuA LH2
PSI
LDAO
LDAO+OTG
LDAO LDAO+OTG
DDM OTG
Chami, 2001

Wilson-Kubalek, 2005
Lipid ligand mediated crystallizationPart I: helical crystallization
Hist-perfringolysin
Gal-cerebroside tubesDoped with Ni-NTA lipid
10µm

Lipid ligand mediated crystallizationPart II: 2D crystallization of soluble proteins at theair/water interface
1
2
3Fromhertz, 1971, NatureUzgiris and Kornberg, 1983, Nature
Lipid ligands for specific recognition
- Negatively and positively charged- Lipid toxin receptor (GM1, Gb3)- substrate modified lipids
-Ni-NTA lipid for His-prot

Binding of ternary micelles
Reconstitutionin lipid bilayer
2D crystallization
Detergent removal
Lipid ligand mediated crystallizationPart III: 2D crystallization of membraneproteins at the air/water interface

Lipid/detergent interaction at the air/water interface

Set-up for 2D crystallization by the lipid layer method
OM EM

Characteristics of the lipid layer method - Protein concentration up to 20µgr/ml (1µg/trial)- Unic orientation of the proteins
Lipid layer In volume

Hist-tag Membrane proteins crystallized using Ni-NTA DOGS
1µm1µm
BmrA
Nd (M.Chami)OmprN
25 Å(Senior)Pgp
Nd(S.Scheuring)
Aqp1
17 ÅBmrA
Nd (J.Walker)EF1FO
25 ÅTF1FO
15 ÅFhuA
ResolutionProteins

Charged membrane proteins crystallized on oppositively charged lipid layer
BR
LH1-RCΔX
ANC2

Conclusion
Characterization of the endogeneous lipids to improvethe stability of the purified proteins
Reconstitution are poorly specific to lipidsbut a large set of lipid increases the chance of 2D crystallization
Lipid/detergent intermediates are important andshould be study for any new detergent
Cholesterol and sphingomylin should be tried with eucaryot proteins