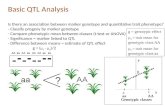
What is a QTL?
description
Transcript of What is a QTL?

What is a QTL?
• Quantitative trait locus (loci)• Region of chromosome that contributes to
variation in a quantitative trait• Generally used to study “complex traits”, i.e.,
controlled by many genes and environmental factors

Why would you want to map QTL?
• Identify genes responsible for variation, e.g.,• Medicine – disease susceptibility, reaction to
drugs• Agriculture – crop/livestock improvement• Evolution

Why would you want to map QTL?
• Identify genes responsible for variation• Understand genetic architecture

What is genetic architecture?
• Number of loci that contribute to a trait• Distribution of effect sizes• “Mode of action” of loci

Genetic architecture: Number of loci• Number of loci contributing to differences in a trait
between two lines/ strains• Historically, estimated in various ways, especially the
Castle-Wright index/ estimator• Castle-Wright index assumes
– Two homozygous parents are crossed, one only has increasing alleles and the other only has decreasing alleles for the trait
– All loci affect the trait equally– Loci affecting the trait are unlinked– No dominance or epistasis
• More modern methods avoid some of these assumptions

Genetic architecture: Distribution of effect sizes
Flint and Mott 2008; Nature 456: 724
Behavioural traits Non-behavioural traits

Genetic architecture:Additive and dominance effects
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mendelian_genetics
Red is dominant over white No dominance

Why care about genetic architecture?Can the identification of QTL useful if
you do not identify the underlying genes?
• How big are the largest effect sizes? Is a QTL worth pursuing?
• Why are traits correlated? Do they share QTL (pleiotropy)? E.g.,
• Medicine – QTL for reading disability and ADHD

Why care about genetic architecture?• Evolution – adaptation, e.g., Peichel et al
2001, Nature 414: 901-905

Why care about genetic architecture?• Evolution – speciation, e.g., Hawthorne and
Via 2001, Nature 412: 905-907

Why care about genetic architecture?• Evolution – do QTL from different studies co-
localize?

Marker assisted selection (MAS) in agriculture
• Advantages/disadvantages

QTL mapping vs. other strategies
• What is the question?– Which genes contribute to variation?– Which genes contribute to trait?

QTL mapping vs. other strategies
• QTL mapping• Candidate gene studies• Mutagenesis• Microarray, serial analysis of gene expression
(SAGE) – gene vs. network focus (Flint and Mott 2008, Nature 456: 724-727)
• Other?