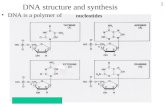
1 DNA structure and synthesis DNA is a polymer of nucleotides.
WALT - To understand the structure of DNA as a polymer of nucleotides To understand the differences...
-
Upload
roger-sharp -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
1
Transcript of WALT - To understand the structure of DNA as a polymer of nucleotides To understand the differences...

WALT -
To understand the structure of DNA as a polymer of nucleotides
To understand the differences between DNA and RNA
To understand the base pair ruling and the bonds involved in the helical DNA Structure
WILF
For you to describe in detail the structure of DNA and RNA including the nucleotides
To be able to explain how DNA is held together


The DNA monomer:

Nucleotides are formed by condensation reactions Nucleotides are formed by condensation reactions
HH22OO
HH22OO

Each polynucleotide chain has two distinct ends a 3’ (‘three prime’) end
carbon 3 of the deoxyribose is closest to the end
and a 5’ (‘five prime’) end carbon 5 of the deoxyribose is closest to the end

With the phosphate group missing the sugar base molecule is called a nucleoside


Classify the following structure as that of a Classify the following structure as that of a nucleoside or a nucleotide. Identify its nucleoside or a nucleotide. Identify its components (sugar? base? phosphate?). components (sugar? base? phosphate?).
Is this a purine or a pyrimidine?Is this a purine or a pyrimidine?

The compound contains a The compound contains a sugar and a nitrogen base, sugar and a nitrogen base, but no phosphate group, so but no phosphate group, so it is a nucleoside. it is a nucleoside.
The sugar has an -H in the 2' The sugar has an -H in the 2' position and is therefore position and is therefore deoxyribose.deoxyribose.
The base has 1 ring, so it is a The base has 1 ring, so it is a pyrimidine pyrimidine

Numbering the carbon atoms on deoxyribose:


THE GENERALIZED "FLATTENED HELIX" STRUCTURE REPRESENTING DNATHE GENERALIZED "FLATTENED HELIX" STRUCTURE REPRESENTING DNA


THERE ARE TWO HYDROGEN BONDS BETWEEN THERE ARE TWO HYDROGEN BONDS BETWEEN ADENINE AND THYMINEADENINE AND THYMINE

THERE ARE THREE HYDROGEN BONDS BETWEEN THERE ARE THREE HYDROGEN BONDS BETWEEN GUANINE AND CYTOSINEGUANINE AND CYTOSINE

What sequence of bases of one strand of DNA is complementary to the sequence...?
T-A-T-G-C-A-G
Complement: A-T-A-C-G-T-C

Sugar – deoxyriboseSugar – deoxyribose
Phosphate Phosphate
Hydrogen bondsHydrogen bonds
Purine basesPurine bases
Pyrimidine basesPyrimidine bases

2) Explain the base pair rule that applies in double 2) Explain the base pair rule that applies in double stranded DNAstranded DNA
ADENINE binds with THYMINE,ADENINE binds with THYMINE, GUANINE binds with GUANINE binds with CYTOSINECYTOSINE
3) Explain how this differs in mRNA3) Explain how this differs in mRNAURACIL binds withURACIL binds with ADENINE replacing THYMINEADENINE replacing THYMINE4) Describe the purpose of the hydrogen bonds in 4) Describe the purpose of the hydrogen bonds in
double stranded DNAdouble stranded DNAThe Hydrogen bonds keep the base pairs together The Hydrogen bonds keep the base pairs together
when in the DNA double helix. These can be broken when in the DNA double helix. These can be broken easily which is important as the strands need to be easily which is important as the strands need to be unzipped during DNA replication and protein unzipped during DNA replication and protein synthesis. synthesis.
5) Describe the functional role of nucleotides5) Describe the functional role of nucleotidesNucleotides are the building blocks of DNA and there Nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA and there
precise sequence determines the genetic precise sequence determines the genetic instructions for the organisminstructions for the organism

6) Complete the following table6) Complete the following table
DNADNA RNARNA
Sugar PresentSugar Present
Bases presentBases present
Number of Number of strandsstrands
Relative Relative lengthlength
DeoxyriboseDeoxyribose RiboseRibose
Adenine, guanine, Adenine, guanine, cytosine and cytosine and thyminethymine
Adenine, guanine, Adenine, guanine, cytosine and cytosine and uraciluracil
22 11
Very long Very long moleculemolecule
Relatively shortRelatively short