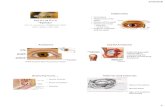
Vision: Accessory structures of the Eye! (pg. 581) Eyelids- shade and protect the eyes and provide...
-
Upload
june-douglas -
Category
Documents
-
view
225 -
download
0
Transcript of Vision: Accessory structures of the Eye! (pg. 581) Eyelids- shade and protect the eyes and provide...
Vision: Accessory structures of the Vision: Accessory structures of the Eye! (pg. 581)Eye! (pg. 581)
EyelidsEyelids- shade and protect the eyes and - shade and protect the eyes and provide lubricationprovide lubrication
Eyelashes and Eyebrows-Eyelashes and Eyebrows- protection from protection from perspiration, direct sun light and foreign perspiration, direct sun light and foreign objects (Yes, eyelashes secrete oil as well!)objects (Yes, eyelashes secrete oil as well!)
Lacrimal apparatus-Lacrimal apparatus- a group of structures that a group of structures that produce and drains lacrimal fluid- tears. produce and drains lacrimal fluid- tears. Apparatus includes glands, ducts, canals, sacs.Apparatus includes glands, ducts, canals, sacs.
Eye muscles-Eye muscles- six total that move each eye. six total that move each eye.
Main structures of the EYE (pg. 582)Main structures of the EYE (pg. 582)
Eyeball-Eyeball- three layers: fibrous tunic, vascular tunic, three layers: fibrous tunic, vascular tunic, retinaretina
Sclera-Sclera- the white of your eye- gives shape- the white of your eye- gives shape- connective tissue. connective tissue. “white of the eye”“white of the eye”
Iris-Iris- colored part of the eye-colored part of the eye- smooth muscle fibers smooth muscle fibers w/ melanocytes- regulates lightw/ melanocytes- regulates light
Pupil-Pupil- hole in the eye- leads to the retina hole in the eye- leads to the retina Cornea-Cornea- Transparent central anterior portion of Transparent central anterior portion of
the sclera through which light enters the eye.the sclera through which light enters the eye.
Main structures, continued!Main structures, continued!
Retina-Retina- lines the posterior ¾ of the eyeball and lines the posterior ¾ of the eyeball and is the beginning of the visual pathway- is the beginning of the visual pathway- contains rods (gray scale) and cones (color). contains rods (gray scale) and cones (color). Has 3 sets of color receptors that are Has 3 sets of color receptors that are sensitive to blue, green and red visible light sensitive to blue, green and red visible light wavelengths.wavelengths.
Optic disc-Optic disc- place where the optic nerve leaves place where the optic nerve leaves the eyeball and enters the brain! the eyeball and enters the brain! The “blind The “blind spot” of the eye.spot” of the eye.
Main structures, continued!Main structures, continued!
Lens-Lens- located behind the pupil and iris- helps located behind the pupil and iris- helps focus images on the retina- dense tissuefocus images on the retina- dense tissue
Aqueous humor-Aqueous humor- nourishes lens and cornea nourishes lens and cornea Vitreous body-Vitreous body- gives retina an even surface for gives retina an even surface for
the reception of clear images. the reception of clear images. “gel-like”“gel-like”
Eye conditionsEye conditions ConjunctivitisConjunctivitis- inflammation of the conjunctiva, the - inflammation of the conjunctiva, the
membrane that lines the eyelids and covers exposed membrane that lines the eyelids and covers exposed areas of the sclera. areas of the sclera. “pink-eye”“pink-eye”
GlaucomaGlaucoma- damage to the optic nerve; excess of - damage to the optic nerve; excess of aqueous humor aqueous humor
Macular Degeneration-Macular Degeneration- when tissue in the macula, the when tissue in the macula, the part of your retina that's responsible for central part of your retina that's responsible for central vision, deteriorates vision, deteriorates
CataractCataract- - a clouding of the normally clear lens of a clouding of the normally clear lens of your eye your eye
Night Blindness-Night Blindness- inability to see images in the dark; inability to see images in the dark; images are not portrayed on the retina; may be caused images are not portrayed on the retina; may be caused by lack of vitamin A by lack of vitamin A
Color Blindness-Color Blindness- an inability to distinguish between an inability to distinguish between certain shades of color; pigments in the cones are certain shades of color; pigments in the cones are missing.missing.
Hearing: Structures of the Ear Hearing: Structures of the Ear (pg. 596)(pg. 596)
External Ear-External Ear- auricle or pinna, external auricle or pinna, external auditory canal and tympanic membrane or ear auditory canal and tympanic membrane or ear drum- collects sound wavesdrum- collects sound waves
Middle Ear-Middle Ear- ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes) ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes) and auditory tube (regulates pressure)- and auditory tube (regulates pressure)- conveys sound waves to the oval windowconveys sound waves to the oval window
Inner Ear-Inner Ear- semicircular canal, cochlea, semicircular canal, cochlea, vestibular membrane- houses receptors for vestibular membrane- houses receptors for hearing and equilibriumhearing and equilibrium
Balance- equilibrium!Balance- equilibrium! Two types: Two types: StaticStatic (body at rest) and (body at rest) and Dynamic Dynamic
(body in response to a sudden movement).(body in response to a sudden movement). The receptor organs for equilibrium are called The receptor organs for equilibrium are called
the vestibular apparatus, which consist of the the vestibular apparatus, which consist of the saccule, utricle and semicircular ducts.saccule, utricle and semicircular ducts.
In the walls of the saccule and the utricle is a In the walls of the saccule and the utricle is a region called the macula, that contain hair cells region called the macula, that contain hair cells that detect motion.that detect motion.
As hair cells depolarize and repolarize, As hair cells depolarize and repolarize, messages are sent from the vestibulocochlear messages are sent from the vestibulocochlear nerve to the brain.nerve to the brain.
Fetal DevelopmentFetal Development
Eye formation- 22 days after fertilizationEye formation- 22 days after fertilization Ear formation- 22 days after fertilizationEar formation- 22 days after fertilization Taste- 14 weeks after fertilization*Taste- 14 weeks after fertilization* Smell- 15 weeks after fertilization*Smell- 15 weeks after fertilization* Last two only* Last two only*
http://www.birthpsychology.com/lifebefore/fetalsensehttp://www.birthpsychology.com/lifebefore/fetalsense.html.html
Olfaction- Sense of SmellOlfaction- Sense of Smell The sense of smell The sense of smell
goes straight to the goes straight to the brain!brain!
From the nasal From the nasal cavity, to the cavity, to the receptors, to the receptors, to the olfactory nerve, to olfactory nerve, to the bulbs, to the the bulbs, to the limbic system and limbic system and finally to the cerebral finally to the cerebral cortex.cortex.
Process of Smell…Process of Smell… Smells are sensed by olfactory sensory neurons in the Smells are sensed by olfactory sensory neurons in the
olfactory epithelium.olfactory epithelium. Molecules pass through the nasal passages, mix with Molecules pass through the nasal passages, mix with
the lining of the cavity and are detected by receptors the lining of the cavity and are detected by receptors on the dendrites of the olfactory sensory neurons.on the dendrites of the olfactory sensory neurons.
Olfactory receptors are in the roof of the nasal cavityOlfactory receptors are in the roof of the nasal cavity Neurons with long ciliaNeurons with long cilia Chemicals must be dissolved in mucus for Chemicals must be dissolved in mucus for
detectiondetection Impulses are transmitted via the olfactory nerve.Impulses are transmitted via the olfactory nerve. Interpretation of smells is made in the cortex.Interpretation of smells is made in the cortex.
Smell- Olfaction…Smell- Olfaction…
Contained in the olfaction epithelium, which is Contained in the olfaction epithelium, which is in the superior part of the nasal cavity.in the superior part of the nasal cavity.
Smell plays a major role in flavor perception.Smell plays a major role in flavor perception. Smell is the sense of odor- the detection of Smell is the sense of odor- the detection of
chemicals dissolved in air.chemicals dissolved in air. Mammals generally have about 1000 genes for Mammals generally have about 1000 genes for
odor receptors.odor receptors. Of these genes, only a portion code for Of these genes, only a portion code for
functional odor receptors.functional odor receptors.
Smell, continued…Smell, continued…
Odor information is easily stored in long Odor information is easily stored in long term memory and has strong connections term memory and has strong connections to emotional memory.to emotional memory.
This is possible due to the olfactory This is possible due to the olfactory system’s close ties to areas of the brain system’s close ties to areas of the brain that have long been known to be involved that have long been known to be involved in emotion and place memory.in emotion and place memory.
Gustation- tasteGustation- taste
Refers to the ability to detect flavorRefers to the ability to detect flavor Stimulated by chemical receptorsStimulated by chemical receptors The sense of taste partners with The sense of taste partners with
olfaction in the brain’s perception of olfaction in the brain’s perception of flavorflavor
Flavor is based on chemical Flavor is based on chemical composition of the item tastedcomposition of the item tasted
Taste- continued…Taste- continued…
Taste is a sensory function of the central Taste is a sensory function of the central nervous system.nervous system.
Receptor cells are found on the tongue and in Receptor cells are found on the tongue and in the back of the throat.the back of the throat.
Three cranial nerves carry impulses from the Three cranial nerves carry impulses from the taste buds to the brain:taste buds to the brain: Facial nerveFacial nerve Glossopharyngeal nerveGlossopharyngeal nerve Vagus nerveVagus nerve
Gustation- Sense of TasteGustation- Sense of Taste
You have five primary You have five primary taste buds:taste buds: SourSour SweetSweet BitterBitter SaltySalty UmamiUmami
Found in the papillae- Found in the papillae- rough, raised part of your rough, raised part of your tongue.tongue.
Classification of TasteClassification of Taste
Sweet receptorsSweet receptors SugarsSugars SaccharineSaccharine Some amino Some amino
acidsacids Sour receptorsSour receptors
AcidsAcids
Bitter receptorsBitter receptors AlkaloidsAlkaloids
Salty receptorsSalty receptors Metal ionsMetal ions
Connection….Connection…. An adult has over 10,000 taste buds, An adult has over 10,000 taste buds,
which are located primarily on the which are located primarily on the tongue (papillae).tongue (papillae).
The human tongue can only The human tongue can only distinguish among 7-8 distinct types distinguish among 7-8 distinct types of taste, while the nose can of taste, while the nose can distinguish among hundreds of distinguish among hundreds of substances, even in minute quantities.substances, even in minute quantities.
Smell amplifies the sense of taste!Smell amplifies the sense of taste!