Upper Motor Neuron Lower Motor Neuron Motor Neuron David Brewer DVM, DACVIM (Neurology) Objectives...
Transcript of Upper Motor Neuron Lower Motor Neuron Motor Neuron David Brewer DVM, DACVIM (Neurology) Objectives...

Upper Motor Neuron Lower Motor Neuron
David Brewer DVM, DACVIM (Neurology)

Objectives
• Fundamental differences between the UMNand LMN systems
• Typical symptoms seen with dysfunction• Role in neurolocalization
• Cases examples


UMN? LMN? Who Cares?
• Localization
4

Definitions
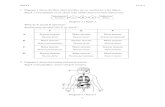
• UMN- The neurons of the brain that control motor activity of the body
5

Definitions
• UMN- Cell bodies arelocated in the cerebrumand brainstem
• Entire UMN is confinedto CNS
6

Definitions • LMN- the neurons that directly innervate
the muscles.
7

Definitions • LMN- Cell bodies are located in the ventral
gray horn of the spinal cord
8

Functions • UMN
• ‘Tells’ the LMN what to do • Stimulate or inhibit the LMN • Initiation of voluntary
movement • Maintenance of muscle
tone and support against gravity
• Regulation of posture
9

Functions • LMN-
• Receives inputs from the UMN
• Connects the CNS with the muscles
• Spinal reflexes
10

Dysfunction of the UMN • Paretic (weakness) to paralysis • Gait: (if still walking)
• Long strided • Crossing • Scuffing
• Loss of inhibition: • Spasticity • Hyperreflexia / hypertonia /
abnormal reflexes • Abnormal postures (brain lesion)
• Ex. opisthotonus
11
UMN Ataxia

Dysfunction of the UMN
• Gait Generation ▪ Dogs/cats- brainstem ▪ People- cerebrum

Romy

Romy

Romy

Romy

Loss of Inhibition 1.Gravity (pleximeter) stimulates muscle spindle 2. Firing along Ia afferent 3. Stimulation of alpha motor neuron and muscle contraction ** Must be controlled by UMN system
Tonic Gamma Loop Mechanism 2
3
1


Crossed Extensor Reflex

Dysfunction of the LMN • Paretic (weakness) to paralysis • Gait: (if still walking)
• Short-strided • Choppy • Lame
• Hypotonia • Hyporeflexive • Rapid muscle atrophy
20

Postural Reactions
• Both UMN and LMN lesions can cause abnormal postural reactions
• More so with UMN • Depends on severity

Goal: • How do we use UMN and LMN
symptoms to help localize a lesion?
22
Neurolocalization

Goal: Neurolocalization
• The location of the lesion along the neuroaxis will determine which limbs are affected ▪ UMN symptoms will be present in limbs
downstream from a CNS lesion ▪ LMN symptoms will only be present if the
motor nerve or the intumescence is affected

24

Goal: Neurolocalization
• Symptoms can be isolated to one limb or generalized to all limbs.
• Not every symptom needs to be present to localize a region

26
Brain C1-C5 C6-T2 T3-L3 L4-S3 Diffuse LMN
TL UMN UMN LMN Normal Normal LMN
PL UMN UMN UMN UMN LMN LMN

UMN or LMN Bladder?
27

28
Brain C1-C5 C6-T2 T3-L3 L4-S3 Diffuse LMN
TL UMN UMN LMN Normal Normal LMN
PL / Bladder UMN UMN UMN UMN LMN LMN

Bladder
• UMN Bladder ▪ Seen with lesions cranial
to L4 ▪ Loss of inhibition causes
excess tone on the urethral sphincters
▪ Large difficult to express ▪ Overflow incontinence

UMN Bladder Treatment
• Relax Internal Urethral Sphincter ▪ Alpha-adrengeric antagonist ▪ Ex. Phenoxybenzamine or Prazosin
• Relax External Urethral Sphincter ▪ Skeletal muscle relaxant ▪ Ex. Diazepam

Bladder • LMN Bladder ▪ Seen with lesions caudal
to L4 ▪ Hypotonia of the
urethral sphincters ▪ Fills partially ▪ Continuous dribbling ▪ Easy to express

LMN Bladder Treatment
• Promote Bladder Contraction ▪ Stimulate muscarinic receptors
• Ex. Bethanechol

Technically Speaking
• LMN is referencing just the nerve
• What about the muscle or the junction between the nerve and muscle?

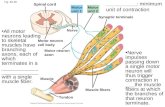
Neuromuscular System
• LMN (Neuropathy) • Muscle (Myopathy) • NMJ (Junctionopathy)

Neuromuscular System
Myopathy Neuropathy NMJ
Muscle mass/tone Normal to ↓ ↓ Normal
Gait Paresis Paresis Paresis may be episodic
Postural Reactions Normal ↓ Normal
Reflexes Normal ↓ Normal

Case Example 1
• Middle-age German Shepherd • CC: Wobbly in the pelvic limbs

37

38
Brain C1-C5 C6-T2 T3-L3 L4-S3 Diffuse LMN
TL UMN UMN LMN Normal Normal LMN
PL / Bladder UMN UMN UMN UMN LMN LMN

Differentials
• C6-T2 myelopathy ▪ Degenerative - IVDD ▪ Anomalous – Wobbler’s syndrome ▪ Metabolic - ?? ▪ Neoplastic- Extradural or intramedullary ▪ Inflammatory- Immune-mediated or infectious ▪ Traumatic / Toxic- Contusion ▪ Vascular- FCE

Diagnostics

Diagnosis
• C6-T2 myelopathy
▪ Anomalous – Wobbler’s syndrome

Treatment and Outcome
• Treatment ▪ Owner elected conservative management
• Outcome ▪ Fair to good response to prednisone and life
long gabapentin

Case Example 2
• Young Bichon • CC: Down in pelvic limbs

44

45
Brain C1-C5 C6-T2 T3-L3 L4-S3 Diffuse LMN
TL UMN UMN LMN Normal Normal LMN
PL / Bladder UMN UMN UMN UMN LMN LMN

Differentials
• T3-L3 myelopathy ▪ Degenerative - IVDD ▪ Anomalous – Malformation, cyst ▪ Metabolic - ?? ▪ Neoplastic- Extradural or intramedullary ▪ Inflammatory- Immune-mediated or infectious ▪ Traumatic- Contusion ▪ Vascular- FCE

Diagnostics

Diagnosis
• T3-L3 myelopathy ▪ Degenerative - IVDD

Treatment and Outcome
• Treatment ▪ Hemilaminectomy
• Outcome ▪ Normal at 6 weeks post surgery

Case Example 3
• Young adult Giant Schnauzer • CC: Down in all 4



53

54
Brain C1-C5 C6-T2 T3-L3 L4-S3 Diffuse LMN
TL UMN UMN LMN Normal Normal LMN
PL / Bladder UMN UMN UMN UMN LMN LMN

Differentials
• Diffuse LMN Disease ▪ Degenerative – Hereditary?, Storage diseases ▪ Anomalous – ? ▪ Metabolic – Endocrine (DM, cortisol, thyroid) ▪ Neoplastic- Lymphoma, paraneoplastic ▪ Inflammatory- Polyradiculoneuritis, infectious – protozoal,
(botulism) ▪ Traumatic / Toxic- (Tick paralysis) ▪ Vascular- ?

Diagnostics

Diagnostics
• CBC – Normal • Chem – Normal • Urinalysis – Normal • 3 view chest radiographs – Normal • Abdominal Ultrasound – Normal • Baseline cortisol and T4 – Normal

Additional Diagnostics
• Electrodiagnostics ▪ Electromyography ▪ Motor Nerve Conduction Velocity ▪ F-Waves
• +/- Muscle nerve biopsy

Updated Differentials
• Diffuse LMN Disease ▪ Degenerative – Hereditary?, Storage diseases
▪ Neoplastic- Lymphoma, paraneoplastic ▪ Inflammatory- Polyradiculoneuritis, infectious – protozoal,
(botulism) ▪ Traumatic / Toxic- (Tick paralysis)

Treatment and Outcome
• Treatment ▪ Frontline application
• Outcome ▪ ~2 weeks later – 90% ▪ ~4 weeks later – 100%

Presumptive Diagnosis
• Diffuse LMN Disease
▪ Inflammatory- Polyradiculoneuritis,

Case Example 4
• 2 yr old Newfoundland • CC: Unable to walk

Case Example 4

Take Home Points
• UMN disease should have distinctly different signs from LMN disease • Cervical spinal cord disease and diffuse LMN disease can sometimes be
confused without thorough examination
• Diseases that affect the neuromuscular system can look very similar
• Gait evaluation is probably the most important aspect of the exam
• Acute localization is key!

QUESTIONS?