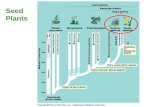
Unit 7--Plants Chapter 24 Reproduction in Seed Plants.
-
Upload
felicia-russell -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
0
Transcript of Unit 7--Plants Chapter 24 Reproduction in Seed Plants.

Unit 7--Plants Chapter 24
Reproduction in Seed Plants

p. 536

Flower Parts (non-essential)
• Sepals (outermost, leaf-like) for protecting inner parts – Calyx = all sepals together
• Petals (colorful, with nectar) to attract pollinators
which see different patterns in ultraviolet light
– Corolla = all petals together

What we see…
What they see:
NECTER GUIDES

What we see…
What they see:

What we see…
What they see:

Flower Parts (essential)–Stamens (male reproductive organs)
• filaments = slender stalk supporting…• anther = produce pollen (containing sperm)
–Pistils (female reproductive organs)• stigma = sticky top to catch pollen• style = slender stalk supporting…• ovary = base contains ovules -> eggs & later
houses seeds


Fruit = ripened ovary & associated parts

Flower to Fruit
After Pollination… Petals & stamens dry and fall off
Within ovary, seedsdevelop in ovules…
Ovary becomes “core” of the apple
Receptacle swellsaround ovary…
Receptacle becomesfleshy part of fruit
Sepals dry, but don’t fall off…
Calyx forms “crusty”bottom of apple

ovary cross section showing ovules

Fruit = for seed dispersal

Seeds
• Seed coat = to protect embryo (softens when wet)
• Nutrients = endosperm (monocots) & fleshy cotyledons (dicots)
• Embryo plant (attached to cotyledon)– radicle = embryonic root– hypocotyl = embryonic stem– epicotyl = embryonic shoot (or bud)– plumule = embryonic leaves

Hypocotyl (stem)
(leaves)
Epicotyl (shoot)