Unit 3: Behaviour, Populations and environment Chapter 26: Organisation of the nervous system...
-
Upload
elfrieda-hunt -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
0
Transcript of Unit 3: Behaviour, Populations and environment Chapter 26: Organisation of the nervous system...

Unit 3: Behaviour, Populations and
environment
Chapter 26: Organisation of the nervous system
21/04/23 Mrs Smith Ch26 The Nervous Sysem
1
Higher Human Biology

Learning Intentions
To examine the workings of the brain and the nervous system.
Success Criteria2. Define the terms;
a.Central nervous system
b.Peripheral nervous system
c. Somatic nervous system
d.Autonomic nervous system
21/04/232Mrs Smith Ch26 The Nervous
Sysem

The Nervous The Nervous SystemSystem
Image source: www.drstandley.com
The nervous system is a network of specialised cells that communicate information about an
individual’s surroundings and itself.
It processes this information and causes
reactions in other parts of the body.
21/04/23 3Mrs Smith Ch26 The Nervous Sysem

Summary: The Nervous System
21/04/23 4Mrs Smith Ch26 The Nervous Sysem

CNS (central nervous system)
PNS (peripheral nervous
system)
Structural Division: The Nervous SystemStructural Division: The Nervous System
Based on the structure and location of the component parts, the nervous system can be divided as shown in the diagram.
Brain Spinal Cord
21/04/23 5Mrs Smith Ch26 The Nervous Sysem

Central Nervous System
21/04/23 6Mrs Smith Ch26 The Nervous Sysem
Peripheral Nervous System
• Somatic – some involuntary reflex actions, mostly voluntary actions
• Autonomic - involuntary actions

Autonomic (involuntary - muscles)
PNS (peripheral nervous system)Crainial nerves + spinal nerves)
Somatic (mostly voluntary)
Functional Division: The Nervous Functional Division: The Nervous SystemSystem
ParasympatheticSympathetic
ANTAGONISTIC have opposite effects
A further method of dividing up the nervous system is
based on different functions performed by the two
separate branches of the peripheral nervous system as
shown in the diagram 21/04/23 7Mrs Smith Ch26 The Nervous
Sysem

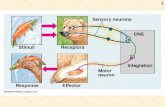
The Somatic Nervous SystemThe Somatic Nervous SystemThe peripheral nervous system has 2 branches, called the somatic and the autonomic nervous systems.
The somatic nervous system (including spinal nerves) controls the skeletal muscles. Most movements that it controls are voluntary but it also controls certain involuntary reflex actions (e.g. limb withdrawal).
SENSORY NERVE
C.N.S MOTORNERVE
Brain & Spinal cord - processes informatio
n.
STIMULUS RESPONSE
21/04/23 8Mrs Smith Ch26 The Nervous Sysem

The autonomic nervous system (ANS) controls involuntary responses to stimuli by the body, so there is no conscious control, but under exceptional some people can suppress certain autonomic responses intentionally.
The Autonomic Nervous The Autonomic Nervous SystemSystem
The nerves start at the nerve cells in the brain, pass down the spinal cord then emerge at the appropriate
organ.
Autonomic nerves regulates the heart, blood vessels, bronchial tubes, alimentary canal & sweat glands.
21/04/23 9Mrs Smith Ch26 The Nervous Sysem

Autonomic Nervous System
21/04/23 10Mrs Smith Ch26 The Nervous Sysem

Antagonistic nature of the Autonomic Nervous System
• The sympathetic and parasympathetic systems which make up the autonomic nervous system are described as being antagonistic.
• i.e. They affect many of the same body structures but exert opposite effects on them.
21/04/23 Mrs Smith Ch26 The Nervous Sysem
11

Image source: www.biocomtech.com
Parasympathetic v SympatheticParasympathetic v SympatheticHomeostasis Response to stressANTAGONISTIC have
opposite effects
•Tries to maintain a stable internal environment
• ‘Flight or flight’ response
Adrenal gland only connected
to sympatheti
c nerves
• Calms the body down after stress
• Helps body conserve resources & store energy
21/04/23 12Mrs Smith Ch26 The Nervous Sysem

Harmonious Balance
• The autonomic nervous system is concerned with maintaining a stable internal environment by playing a part in homeostasis.
• The sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems are constantly working in an opposite but equal manner (neither wins).
21/04/23 Mrs Smith Ch26 The Nervous Sysem
13

Fight or flight
In response to a crisis the sympathetic system prepares the body for action and the expenditure of energy by•Increasing heart rate and blood pressure.•Diverting blood to skeletal muscle.•Increasing perspiration.
The hormone ADRENALINE helps to sustain this state till the emergency is over.
21/04/23 Mrs Smith Ch26 The Nervous Sysem
14

Calming DownWhen the crisis is over, the parasympathetic system briefly takes over by;•Returning heart rate and blood pressure to normal.•Peristalsis in the digestive tract increases.•Blood is diverted away from skeltal muscles and back to the intestine (allowing digestion to resume).
THIS ALLOWS THE BODY TO STORE ENERGY AND CONSERVE RESOURCES.
21/04/23 Mrs Smith Ch26 The Nervous Sysem
15

Task: Torrance-TYK pg 215 Qu’s 1-4
21/04/23 16Mrs Smith Ch26 The Nervous Sysem

Task: Torrance AYK pg215/216 Qu’s 1-4
21/04/23 17Mrs Smith Ch26 The Nervous Sysem