Unit 2 – The Cell b Chapter 11~ Cell Communication.
-
Upload
andrew-mccormick -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
0
Transcript of Unit 2 – The Cell b Chapter 11~ Cell Communication.

Unit 2 – The CellUnit 2 – The Cell
Chapter 11~Chapter 11~Cell Cell
CommunicationCommunication

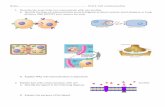
Signal-transduction Signal-transduction pathwaypathway
DefDef: Signal on a cell’s surface is converted into a : Signal on a cell’s surface is converted into a specific cellular responsespecific cellular response
Local signaling Local signaling (short distance): (short distance): √ Paracrine (growth factors)√ Paracrine (growth factors)
√ Synaptic (neurotransmitters)√ Synaptic (neurotransmitters) Long distanceLong distance: hormones: hormones

Stages of cell signalingStages of cell signaling
Sutherland (‘71)Sutherland (‘71) Glycogen depolymerization by epinephrineGlycogen depolymerization by epinephrine 3 steps:3 steps:
•Reception: target cell detection •Reception: target cell detection •Transduction: single-step or series of changes•Transduction: single-step or series of changes
•Response: triggering of a specific cellular •Response: triggering of a specific cellular responseresponse

Protein phosphorylationProtein phosphorylation
Protein activity regulationProtein activity regulation Adding phosphate from Adding phosphate from
ATP to a protein ATP to a protein (activates proteins)(activates proteins)
Enzyme: protein kinases Enzyme: protein kinases (1% of all our genes) (1% of all our genes)
Example: cell Example: cell reproductionreproduction
Reversal enzyme: Reversal enzyme: protein phosphatasesprotein phosphatases

Second messengersSecond messengers
Non-protein signaling Non-protein signaling pathway (pathway (
Example: cyclic AMP Example: cyclic AMP (cAMP)(cAMP)
Ex: Glycogen Ex: Glycogen breakdown with breakdown with epinephrineepinephrine
Enzyme: adenylyl Enzyme: adenylyl cyclasecyclase
G-protein-linked receptor G-protein-linked receptor in membrane (guanosine in membrane (guanosine di- or tri- phosphate)di- or tri- phosphate)

Cellular responses to Cellular responses to signalssignals
Cytoplasmic Cytoplasmic activity regulationactivity regulation
Cell metabolism Cell metabolism regulationregulation
Nuclear Nuclear transcription transcription regulationregulation