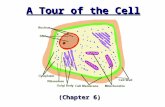
Unit 2 H=Chap. 4 In 1665, the English scientist ROBERT HOOKE, used a microscope to examine a thin...
-
Upload
baldric-hubbard -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
0
Transcript of Unit 2 H=Chap. 4 In 1665, the English scientist ROBERT HOOKE, used a microscope to examine a thin...
- Slide 1
- Slide 2
- Unit 2 H=Chap. 4
- Slide 3
- Slide 4
- Slide 5
- In 1665, the English scientist ROBERT HOOKE, used a microscope to examine a thin slice of cork. He described it as consisting of great many little boxes. It reminded him of the small rooms in which monks lived CELLS!
- Slide 6
- All living things are composed of one or more cells Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all living things. ALL cells come from preexisting cells.
- Slide 7
- Slide 8
- 1. SHAPE - Diversity of form reflects a diversity of function
- Slide 9
- Slide 10
- 2. SIZE visible with unaided eye, microscopic, etc.
- Slide 11
- MOST CELLS ARE SMALL FOR 2 REASONS 1. A SMALL CELL HAS MORE SURFACE AREA THAN A LARGE CELL FOR A GIVEN VOLUME OF CYTOPLASM 2. THE CELL'S NUCLEUS (THE BRAIN) CAN ONLY CONTROL A CERTAIN AMOUNT OF LIVING, ACTIVE CYTOPLASM
- Slide 12
- 3. INTERNAL ORGANIZATION: Organelles, Eukaryotes and prokaryotes
- Slide 13
- Slide 14
- Slide 15
- EQ= What are membranes and what purpose do they serve? Give an example of one.
- Slide 16
- 1. THE PLASMA MEMBRANE (Present in ALL cell types) Functions: Regulates what enters/leaves the cell Separates internal environment from the external environment Composed of a lipid bilayer (Fat) Selectively-permeable membrane
- Slide 17
- Slide 18
- Slide 19
- 2. THE CELL WALL (Plant cells ONLY) Surrounds the cell membrane Helps to protect and support the cell
- Slide 20
- The fluid-filled area BETWEEN the NUCLEUS & the CELL MEMBRANEfluid & organelles cyto = cell plasm = fluid Cytosol = cell fluid only 3. THE CYTOPLASM
- Slide 21
- 4. THE NUCLEUS (Eukaryotic cells) Control center of the cell Contains DNA Double Layer Membrane called the NUCLEAR ENVELOPE covered with many small pores The NUCLEOLUS synthesizes (makes) ribosomes, which are important in making proteins for the cell
- Slide 22
- Chromatin: nuclear DNA (long fibers known as chromosomes) Nuclear Envelope: Double membrane Nuclear Pore: Regulate flow of materials in and out of cell Nucleolus: Ribosome synthesis Nucleoplasm: Fluid of the nucleus
- Slide 23
- Extension of the nuclear membrane regions with ribosomes = ROUGH ER (transport ribosomes) regions w/o ribosomes = SMOOTH ER (lipid synthesis)
- Slide 24
- Slide 25
- Sites of protein synthesis 2 sub-unit
- Slide 26
- The function of the Golgi Apparatus is to sort, chemically alter, and package important molecules. (UPS guy!)
- Slide 27
- Slide 28
- Powerhouse of the cell (generates fuel for cells activities) Sites of cellular respiration
- Slide 29
- Slide 30
- Slide 31
- Slide 32
- Responsible for intracellular digestion. Lysosomes are membranous sacs of acidic enzymes. (Rare in plant cells)
- Slide 33
- Detoxify harmful substances that enter the body.
- Slide 34
- Stores extra material for the cell. Nutrients, water, etc. The garage
- Slide 35
- All CELLS HAVE DIFFERENT SHAPES AND ARE CAPABLE OF SOME TYPE OF MOVEMENT. HELPS SUPPORT CELL STRUCTURE AND DRIVE CELL MOVEMENT.
- Slide 36
- a.Cilia short hair- like extensions on the cell that aid in cell movement b.Flagella long hair-like extension on a cell that helps the cell propel