to study the disorders of heart
-
Upload
atheeth-a-naik -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
description
Transcript of to study the disorders of heart

INVESTIGATORY PROJECT REPORT
ON
STUDY OF DISORDERS OF HEART
FOR
THE PARTIAL FULILLMENT OF AISSCE 2015 PRACTICAL EXAMINATION
BIOLOGY
Submitted by-
ATHEETH A NAIKTO
THE DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY,
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA, NO 2 HUBLI.

CERTIFICATEThis is to certify that Atheeth A Naik of class XI has
successfully carried out the project entitled “ Disorders of Heart” under my supervision. All the work related to
this has been done by the candidate himself. The approach towards the subject has been sincere and
scientific.
Guided by Principal
Mrs Wawathsi Sri S.T.Metre
...................... ……………..
Internal Examiner
…………………

Contents ►Introduction
►Disorders of heart
► Risk factors
►References

Introduction The heart is a muscular organ in both humans and other
animals, which pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. Blood provides the body with oxygen and nutrients, and also assists in the removal of metabolic wastes. The heart is located in the middle compartment of the
mediastinum in the chest.
Heart must pump blood throughout the body on a regular and ongoing basis. The heart muscle requires a constant supply of blood containing
nutrients and oxygen to function effectively. The delivery of oxygen and nutrient-rich arterial blood to cardiac muscle tissue and the return of
oxygen-poor blood from this active tissue to the venous system is called the coronary circulation.
In humans, other mammals and birds the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria; and lower left and right ventricles.
Commonly the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. Fish in contrast have two

chambers, an atrium and a ventricle, while reptiles have three chambers. In a healthy heart blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves,
which prevent backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a small amount of fluid. The wall of the
heart is made of 3 layers- epicardium, myocardium & endocardium.
Disorders of heartHigh blood pressure is strongly linked to heart disease. High blood pressure is called hypertension. An increase in blood pressure is believed to be the result of a narrowing of the smaller blood vessels. The elevated pressure in the arteries makes the left ventricle work harder and, if not treated, the left ventricle ultimately fails. This condition is common. The result of this hypertension can be congestive heart failure. Some factors that cause hypertension are smoking, diet, stress, and heredity. The narrowing causes the heart to beat harder to pump the blood. A blood pressure of 140/90 represents borderline hypertension for adults. Higher pressure may be more serious.
Being such a complex organ the heart is prone to several cardiovascular diseases some becoming more prevalent with ageing. Heart disease is a major cause of death, accounting for an average of 30% of all deaths in 2008, globally. This rate varies from a lower 28% to a high 40% in high-income countries.
Coronary artery disease is also known as ischemic heart disease (IHD), and more usually as atherosclerosis. This disease is caused by a build-up of plaque along the inner walls of the arteries which has the effect of narrowing the arteries and so reducing the blood flow to the heart. It is the most common form of heart disease, the cause of heart attacks and the most common cause of death, globally. Coronary artery bypass surgery to improve the blood supply to the heart is often the only treatment option.

Cardiomyopathy is a noticeable deterioration of the heart muscle's ability to contract, which can lead to heart failure. The most common form of cardiomyopathy is dilated cardiomyopathy.
Heart failure which can also be congestive heart failure, happens when the heart is pumping insufficiently and cannot meet the need of blood flow required by the body. Because the heart is a double pump, each side can fail independently of the other, resulting in heart failure of the right heart or heart failure of the left heart either of which through causing strain in the other side can result in the failure of the whole heart. Congestive heart failure results in blood backing up in the systemic circulation. Edema (swelling) of the feet, ankles and fingers is the most noticeable symptom. Pulmonary congestion results from left heart failure. The right side of the heart continues to propel blood to the lungs, but the left side is unable to pump the returning blood into the systemic circulation. As blood vessels within the lungs become swollen with blood, the pressure within them increases, and fluid leaks from the circulation into the lung tissue, causing pulmonary edema. If untreated, the person will suffocate because they are drowning in their own blood. Common causes of heart failure are a heart attack, valvular heart disease and hypertension.
Other conditions can interfere with the regular conduction of impulses across the heart. Damage to the sinoatrial node (SA), (the pace maker of the heart), can result in a slower heart rate. Ischemia, or an inadequate blood supply to the heart muscle, may lead to fibrillation - a rapid, uncoordinated shuddering of the heart muscle, a major cause of fatal heart attacks.
Heart murmurs are abnormal or unusual heart sounds which can be caused by an obstruction in the blood flow. These murmurs can be heard with a stethoscope. Heart murmurs are common in young children and the elderly even if they have perfectly healthy hearts. They may have heart murmurs because their heart walls are thin and vibrate with the rushing blood. However, murmurs in patients who do not fall into either of those categories most often have a valve issue. For example, if a valve does not

close tightly enough, a swishing sound will be heard after that valve has (supposedly) closed, as the blood flows back through the partially open valve. Distinct sounds also can be heard when blood flows turbulently through stenosed (narrowed) valves.
Cardiac tamponade, also known as pericardial tamponade, is the condition of an abnormal build-up of fluid in the pericardium which can adversely affect the function of the heart. The fluid can be removed from the pericardial sac using a syringe in a procedure called pericardiocentesis.
Cardiac arrest is the sudden cessation of normal heart rhythm which can include a number of pathologies such as cardiac dysrhythmia, an irregular and ineffective heart rhythm which can be either an extremely rapid heart beat (tachycardia) or a very slow one (brachycardia), which prevents the heart from effectively pumping blood, and asystole, which is the cessation of heart rhythm entirely.
Exercise results in the addition of protein myofilaments and this can result in hypertrophy where the size of individual cells are increased but not their number.This is a condition known as athletic heart syndrome. The hearts of athletes can pump more efficiently at lower heart rates. However, enlarged hearts can have a pathological cause which can result in a heart of 1000 g (2 lb) in mass. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is one such cause. The cause of an abnormally enlarged heart muscle is unknown, but the condition is often undiagnosed and can cause sudden death in young athletes.
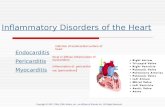
Carditis is inflammation of the heart; this can be specific to regions as in pericarditis, myocarditis, and endocarditis or it can be of the whole heart known as pancarditis.
A rare type of cancer can form in the mesothelium of the pericardium known as a mesothelioma.
Angiogenesis represents a therapeutic target for cardiovascular disease.

Rheumatic heart disease is due to having rheumatic fever. Rheumatic fever is a disease caused by strep bacteria that can result in inflammation of the heart valves and muscle tissue. This swelling can damage and scar the heart valves. The damage may disturb the flow of blood through the heart and cause rheumatic heart disease in later years. The first sign of strep infection is often a sore throat. Treating the initial strep infection with antibiotics prevents heart damage from developing. The infection can lead to destruction of the heart valves.
To sustain life, the heart must pump blood throughout the body on a regular and ongoing basis. The heart muscle requires a constant supply of blood containing nutrients and oxygen to function effectively. The delivery of oxygen and nutrient-rich arterial blood to cardiac muscle tissue and the return of oxygen-poor blood from this active tissue to the venous system is called the coronary circulation. Coronary heart disease results from the narrowing of arteries that nourish the heart. If the coronary arteries are healthy, then the linings remain smooth and clear carrying a steady stream of blood to the heart. If the inner walls become rough and thick deposits have formed. The formed deposits contain cholesterol, connective tissue and smooth muscle cells. These form a process called atherosclerosis or hardening of the arteries. An artery can become clogged completely and when this happens the clogged coronary arteries cut off the blood supply to the heart. A heart attack will occur after the blood supply to the heart ends as heart muscle dies. Angina pectoris is a term used to describe the severe chest pain that occurs when the myocardium is deprived of adequate oxygen. It is often a warning that the coronary arteries are no longer able to supply enough blood and oxygen to the heart muscle. A temporary lack of oxygen in the heart muscle causes a feeling of suffocation and chest pain. Angina is a symptom rather than a disease. Attacks of angina usually occur during periods of heavy physical

or emotional stress. They generally last only as long as the stress continues. People who suffer from angina may never have heart attacks. Angina does indicate that there is some blockage in the coronary arteries.
Risk factorsThere are several risk factors for heart diseases: age, gender, tobacco use, physical inactivity, excessive alcohol consumption, unhealthy diet, obesity, family history of cardiovascular disease, raised blood pressure (hypertension), raised blood sugar (diabetes mellitus), raised blood cholesterol (hyperlipidemia), psychosocial factors, poverty and low educational status, and air pollution. While the individual contribution of each risk factor varies between different communities or ethnic groups the overall contribution of these risk factors is very consistent. Some of these risk factors, such as age, gender or family history, are immutable; however, many important cardiovascular risk factors are modifiable by lifestyle change, social change, drug treatment and prevention of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and diabetes.
Age
Calcified heart of an older woman with cardiomegaly.
Age is by far the most important risk factor in developing cardiovascular or heart diseases, with approximately a tripling of risk with each decade of life. It is estimated that 82 percent of people who die of coronary heart disease are 65 and older. At the same time, the risk of stroke doubles every decade after age 55.
Multiple explanations have been proposed to explain why age increases the risk of cardiovascular/heart diseases. One of them is related to serum cholesterol level. In most populations, the serum total cholesterol level

increases as age increases. In men, this increase levels off around age 45 to 50 years.
Unhealthy diet
High dietary intakes of saturated fat, trans-fats and salt, and low intake of fruits, vegetables and fish are linked to cardiovascular risk, although whether all these associations are causal is disputed. The World Health Organization attributes approximately 1.7 million deaths worldwide to low fruit and vegetable consumption. The amount of dietary salt consumed is also an important determinant of blood pressure levels and overall cardiovascular risk. Frequent consumption of high-energy foods, such as processed foods that are high in fats and sugars, promotes obesity and may increase cardiovascular risk. High trans-fat intake has adverse effects on blood lipids and circulating inflammatory markers, and elimination of trans-fat from diets has been widely advocated. There is evidence that higher consumption of sugar is associated with higher blood pressure and unfavorable blood lipids, and sugar intake also increases the risk of diabetes mellitus. High consumption of processed meats is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, possibly in part due to increased dietary salt intake.

Calcified heart of aged women with cardiomegaly.(↑)
ReferencesI have referred the following books and
websites:-
►www.google.com
►www.wikipedia.org
►http://www.abronexports.com
►class XI ncert textbook

►Expert’s textbook