The New Farmer’s Almanac Agriculture and Climate Change
description
Transcript of The New Farmer’s Almanac Agriculture and Climate Change

The New Farmer’s AlmanacAgriculture and Climate Change
Anne Royer & Tomomi SuwaGK-12 Fall Workshop
October 3, 2012

How will climate change impact farmers?
• Understanding the difference between climate and weather
• Specific predictions of climate change• Using real long-term data to understand
how predicted changes may affect crops

Weather vs. Climate
WEATHER• Local• Short-term (days to
months)• Prediction based on
current conditions• Current atmospheric
conditions
CLIMATE• Regional or broader• Long-term (years to
decades)• Prediction based on less
labile long-term trends• Big picture of how
atmosphere behaves

Illustrating weather vs. climatehttp://www.climate.gov/#education

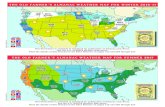
HOW will the climate change?Everywhere:• Warmer temperatures• Higher annual precipitation• More rain in winter and spring• Increase in extreme weather events – less
predictable weatherWhat will this mean for agriculture?


HOW will the climate change?In Michigan:• Warmer temperatures• Higher annual precipitation• More rain in winter and spring• Increase in extreme weather events – less
predictable weatherWhat will this mean for agriculture?


HOW will the climate change?In Michigan:• Warmer temperatures• Higher annual precipitation• More rain in winter and spring• Increase in extreme weather events – less
predictable weatherWhat will this mean for agriculture?

Effects of Climate Change on Agriculture

LTER - Since 1987

Corn Wheat Soybean

Biomass over time
1990 1995 2000 2005 20100
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
1400
1600
Corn
1991 1996 2001 2006 20110
100200300400500600700800900
Wheat
1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 20150
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
Soy
Biom
ass (
g/m
2)

Research Questions
Does climate change affect crop yields?Any guesses?

Hypothesis and predictionsIf (hypothesis) then (prediction)
Data we have:-Biomass (g/m2)-Total precipitation (May – Sept)-Average soil moisture (May-Sept)-Average temperature(May-Sept)
Does climate change affect crop yields?
Hypothesis: Educated guess, general statementPrediction: What you think will happen, more specific

e.g. If climate change affect crop yield, then increased soil moisture will
increase crop production.

MethodsPrediction: Increased soil moisture will increase biomass
Soil Moisture (%)
Bio
mas
s (g
/m2 )

MethodsTitle: The Effect of the independent variable on the
dependent variable
Independent Var (unit)
Dep
ende
nt V
ar (u
nit)
Cause: Something that is affecting the dependent variable but not affected by dependent variable.
Effect: Something that might be affected by the change in the independent variable

Plotting in Excel
e.g. moisture vs. precipitation

Let’s analyze the data!
• Divide into 3 groups (corn, wheat, soy)• Spend 15 min plotting graphs• Share the results with the class
• Plot:– Biomass vs Precipitation (mm)– Biomass vs Soil Moisture (%)– Biomass vs Temperature (°C)

Results

200 300 400 500 600 7000
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
1400
f(x) = − 0.237913362782616 x + 1320.70364992666R² = 0.0296733212008734
Corn
200 300 400 500 600 700
f(x) = 0.445060051903132 x + 421.850972122727R² = 0.146406562232492
Wheat
200 300 400 500 600 700
f(x) = − 0.510060688953362 x + 826.514769862717R² = 0.0294168233794435
Soy
Effects of Precipitation on CropsBi
omas
s (g/
m2)
Accumulative Precipitation between May - Sept (mm)

8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
f(x) = 7.46643113869275 x + 487.939432163857R² = 0.00140864281336817
Soy
8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
f(x) = 35.2648542727135 x + 122.487642611366R² = 0.380962407189675
Wheat
8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 170
200400600800
1000120014001600
f(x) = − 45.1440389076482 x + 1803.41330971116R² = 0.191453435399398
Corn
Effects of Soil Moisture on Crops
Soil Moisture (%) Soil Moisture (%) Soil Moisture (%)
Biom
ass (
g/m
2)

16 16.5 17 17.5 18 18.5 19 19.5 200
500
1000
1500f(x) = 144.651179798355 x − 1481.42575948191R² = 0.483413991894531
Corn
16 16.5 17 17.5 18 18.5 19 19.5 20
f(x) = − 1.99460414805363 x + 668.765737423689R² = 0.000199192756034305
Wheat
16 16.5 17 17.5 18 18.5 19 19.5 20
f(x) = 44.7512903859991 x − 209.219849378496R² = 0.0280008252645215
Soy
Effects of Temperature on Crops

200 300 400 500 600 700 8000
2
4
6
8
10
12
f(x) = NaN x + NaNR² = 0 Moisture vs. Precipitation
9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 1715.5
1616.5
1717.5
1818.5
1919.5
2020.5
f(x) = − 0.176265753576823 x + 20.8647961946407R² = 0.145703308613617
Moisture vs. Temp
16.5 17 17.5 18 18.5 19 19.5 20 20.50
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
f(x) = − 25.4625593382805 x + 910.108947488661R² = 0.0579099465247263
Precipitation vs. Temp
Precipitation (mm)
Prec
ipita
tion
(mm
)
Soil
Moi
stur
e (%
)
Soil Moisture (%)
Tem
pera
ture
(°C)
Temperature (°C)

Hypothesis: Climate change will increase yields
RESULTS (supported predictions in red)• Corn– Increased temperature, increased yield– Increased soil moisture, decreased yield
• Soy– Increased precipitation, slightly decreased yield
• Wheat– Increased soil moisture, increased yield– Increased precipitation, increased yield

Hypothesis: Climate change will increase MI yields
Conclusions• Hypothesis supported for corn and wheat, but
not soy• Climate change is likely to have different effects
on different crops• Caveats:
• May be unmeasured correlated variables• Simplified data –e.g., we didn’t control for
when and how the precipitation arrived

Wrap-up
• Will climate change increase yields?• IT DEPENDS!• Weather vs. climate: we’re using– variation in WEATHER – to predict the result of changes in CLIMATE

Helpful resources• http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/noaa-n/
climate/index.html (NASA explanation of climate vs. weather)
• http://www.climate.gov/#education (NOAA interactive climate change graphs)
• http://www.msue.msu.edu/kr/default.cfm?node_id=59525 (MSU extension pamphlets)