The Nervous System NS and Endocrine System Transmit info from 1 part of body to another...
-
Upload
mildred-jacobs -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
1
Transcript of The Nervous System NS and Endocrine System Transmit info from 1 part of body to another...

The Nervous System
NS and Endocrine System
•Transmit info from 1 part of body to another
Communication—Integration--Control
Nervous System
•Rapidly & short duration via nerve impulses
Endocrine System
•Slowly via hormones (chemicals) secreted by
ductless glands into blood stream circulated
from glands to other parts of the body (target cells)

Homeostasis: Balanced & Controlled internal
environment of body essential to fx of
all body systems
relies on physiological control &
integration
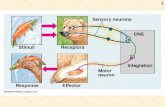
NS: Monitors & Responds to In/External stimuli

Nervous System
brain & spinal cord nerves & associated
cells not part of CNS
CNS PNS
Motor Nerves Sensory Nerves
Respond to stimuli from Env
Sensory Receptors w/in sense organs
(Eyes, Ears, Taste, Touch, Smell)
Somatic NS Autonomic NS
To skeletal muscles/voluntary
To cardiac & smooth muscles, glands, involuntary
sympathetic parasympathetic
Fight/Flight
Antagonistic
gas ↑ brake ↓

Coverings & Fluid Spaces of Brain & Spinal Cord
Meninges: Tough, fluid containing membrane
surrounded by bone (skull & vertebrae)
3 Layers of Spinal Meninges
Dura Mater (tough outer layer, lines vertebral canal)
Pia Mater ( innermost layer covering spinal cord)
Arachnoid Layer ( middle layer between Dura & Pia)
cob web like w/ fluid (CSF) filling spaces
Meninges (protective) extend up & around enclosing brain



Fluid fills Arachnoid spaces of brain meninges & spinal cord
Cerebral Ventricles: Fluid filled spaces w/in brain
2 lateral ventricles deep w/in brain
w/in Lt & Rt cerebrum
(lgst part of brain conscious, voluntary,
mental processes, emotions)
CSF: cerebral spinal fluid forms continuously from fluid
filtering out of blood
network of brain capillaries (choroid plexus) & into
ventricles

From lateral ventricles CSF 3rd ventricle & flows ↓
aqueduct of Sylvius 4th ventricle subarachnoid
spaces subarachnoid spaces of meninges that
surround spinal cord blood via veins in the brain
***CSF forms continuously from blood, circulates & is reabsorbed into blood again
**Pressure on Aqueduct of Sylvius (Ex. brain tumor) blocks return path of CSF blood
CSF accumulates in ventricles or meninges.
Hydrocephalus water on the brain
Treatment catheter to drain fluid back to body

****
****
****

3 Types of Neurons
Sensory Neurons (Afferent): Carry impulses from sense
organs to spinal cord/brain (CNS)
Dendrites can be very long
Motor Neurons (Efferent): Carry impulses from CNS (brain/sc)
(Effecter) to muscles & glands
Interneurons (Central or Connecting): Connect sensory & motor
neurons in spinal cord
Lie w/in gray matter of
CNS

Cells of the Nervous System
Neurons & Neuroglia Basic Neuron Structure
sensory, motor, &
interneurons (between
sensory & motor
neurons in spinal column)
Impulse received by dendrites
Saltatory conduction
**vertebrates
Soma
Cell body
Axon terminals vesicles w/ neurotransmitters
Many dendrites
Myelinated axon carries impulse from cell body axon terminals

Saltatory Conduction: carries impulse node to node (vertebrates)
200 m/s vs few mm/s in unmyelinated (gray matter)
Mostly outside CNS
80% lipid 20% protein
Insulated sheath
White Matter
Indentations between
Schwann cells
Extend thru axon from cell body
Axons in brain & sc have no neurilemma no regeneration but those in nerves do regeneration

Neuroglias (connective tissue)
Special connecting & supporting tissues of brain & spinal cord don’t transmit impulses
Glia (glue): hold neurons together & protects them
Glioma: common type of brain tumor develops from
neuroglia cells
3 Types of Neuroglia
Astrocytes:

Microglia: usually stationary can move & become phagocytic
(scavengers)

Oligodendroglia: hold nerve fibers together & produce fatty
myelin sheath that covers nerve fibers (axons) in brain &
spinal cord (not Schwann Cells outside CNS)
Myelinated fibers (high fat white matter)
Nonmyelinated (gray matter)

Myelin Disorder Diseases associated with Oligodendroglia
Multiple Sclerosis: Most common 10 of CNS
Characterized by myelin loss/ destruction
w/ oligodendroglial cell injury/death
demyelination of white matter of CNS
nerve conduction impaired
weakness, in-coordination, visual impairment,
speech disturbances
Afflicts more women between 20-40
MS ??? Related to autoimmunity & viral type infections
Prolonged disease w/ relapses & remissions

White Matter in brain & Spinal cord made up of Tracts
Tract: bundle of myelinated axons
White Matter outside brain & spinal cord = nerves
Nerves bundles of myelinated axons
single group of nerve fibers surrounded by
connective tissue sheath
Nerve Trunk group of bundled nerves



7 cervical vertebrae
12 thoracic vertebrae
5 lumbar vertebrae
Fused vertebrae
8
12
5
5
1 coccyx
Nerve prs

Reflex Arcs impulse conduction in 1 Direction
2 neuron arc (sensory motor)
3 neuron arc (sensory interneuron motor neuron)
Interneurons w/in gray matter (H-zone)

Synapse: (microscopic space between neurons that
neurotransmitters released from axon terminals
diffuse across)

Sensory neuron receptors w/ dendrites pick up stimulus
impulse created cell body axon of sensory neuron
Synapse interneuron (dendrite cell body axon)
synapse motor neuron (dendrite cell body axon)
neuromuscular junction



Posterior root ganglion
Anterior root spinal nerve
Patellar Tendon Knee Jerk Reflex

Infant Reflexes
Rooting Reflex: stroke cheek/ turns head towards touch
Gripping Reflex: grasp anything placed in palm
Toe Curling Reflex: Inner sole of foot stroked toes curl
Outer sole of foot stroked toes spread
Stepping Reflex: Held up w/ feet on surface walk/march
Sucking Reflex: when something touches roof of mouth
Startle/Moro Reflex: sudden sound/mvmt throw arms &
legs out & head back then pull limbs back into body
Galant Reflex: stroke middle or lower back body curves
towards side stroked
Tonic Neck Reflex: place on stomach whichever side head is facing limbs on that side straighten, opposite side curl

The Nerve Impulse
Initiated by a stimulus (pressure, temp, chemical changes, etc)
Resting Neuron Outisde +++ (Resting Potential)
Inside ---
Na+ ions pumped out and K+ ions pumped in
Na/K pump run by ATP Active Transport
More K+ ions leak out than Na+ ions leak in
- - - charge inside c.m
+++ charge outside
(Also other ions present Ex. Cl-)
C.M has gates/channels that allow ions to pass thru
normally closed

Steps of an Action Potential (Nerve Impulse)
Neuron stimulated nerve impulse generated
Na+ gates open & flow inside C.M.
Inside becomes more + than outside Action Potential
Nerve Impulse
Depolarization
As impulse passes, K+ gates open and K+ ions flow out
Inside becomes – and outside + again (Reploarization)
Threshold: minimal level of stimulus required to create
impulse All or none
Impulse moves in 1 direction b/c Na+ gates close after impulse & can’t be reopened for short time (Refractory Period)

http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/matthews/actionp.html
Link to Action Potential Animation w/ Saltatory Conduction
Resting Potential
Action Potential Na+ rush in Depolarization
Re-polarization – Action Potential – Resting Potential

Re-polarization
Refractory Period
Resting Potential

Action Potential reaches Axon Terminal
Vesicles w/ neurotransmitters rupture chemicals released diffuse across synaptic cleft (assist, stimulate or inhibit postsynaptic neurons)
Neurotransmitters: chemicals used by neuron to transmit impulse across synapse to another neuron or cell (Ex. muscle)
*neuromuscular
junction

• Impulse arrives at axon terminal
•Vesicles release neurotransmitters into synaptic cleft/gap
•Neurotransmitters diffuse across synapse & attach to
receptors on next cell
•Stimulus causes rush of Na+ to rush into cell
•If threshold met/exceeded new impulse or Rx occurs
Ex. muscle contraction
Neurotransmitters quickly: broken ↓ by enzymes
taken up/recycled by axon terminal
diffuse away

Certain Illnesses associated w/ abnormal levels of Neurotransmitters
Depression: ↓ serotonin & norepinephrine
(Exercise releases these)
Schizophrenia: associated w/ ↑ levels of dopamine
Parkinson’s Disease: progressive NS disease most often after age of 50, associated with the destruction of brain cells that produce dopamine, characterized by muscular tremor, slowing of movement, partial facial paralysis, peculiarity of gait and posture.
Endorphins & Enkephalins: Inhibit conduction of pain
impulses
How do abnormal levels of neurotransmitters affect Fx of NS?
Either ↑ or ↓ transmission of nerve impulse

Nerve Gas: Class of Lethal Weapons
Fx: Inactivate certain enzymes of nerve transmission
Normal: neurotransmitters diffuse away, recycled, inactivated
Neurotransmitter Acetylcholine is inactivated by cholinesterase enzymes that deactivate acetylcholine quickly efficient, precise synaptic transmission
Nerve Gas: binds to & inhibits cholinesterase so acetylcholine remains in synapse continuous stimulation of nerves
Uncontrollable convulsions, muscular contractions, death

Synaptic Integration: Provides checks & balances in NS
At each neuron, Excitatory & Inhibitory receptors compete for membrane control
Signals can totally/partially cancel each other out or augment each other’s effect
Net outcomes depend on strength, direction & location of each signal.
Clostridium tetani Produces toxin that interferes w/ Inhibitory Receptors & Motor Neurons in CNS (brain/sc)
Lock jaw unbalanced excitation of muscle cells
constant (tetanic) contraction spastic paralysis death

Structure of the Spinal Cord
• Avg adult spinal cord 17-18” long
• Lies inside spinal column in spinal cavity
• Extends from occipital bone to 1st lumbar vertebrae
• Hands on hips L4
• Spinal meninges extend beyond spinal cord
almost to end of spinal column
• Allows for spinal tap (lumbar puncture) to extract CSF (test)
insert needle just above L4

Spinal Cord
• H- shaped gray matter ( dendrites & cell bodies of neurons)
• White matter outer part (bundles of myelinated nerve fibers) spinal tracts
• Ascending tracts conduct impulses ↑ cord to brain Ex. sensory fx (pain, touch pressure, etc)
• Descending tracts conduct impulses ↓ cord from brain Ex. vol. mvmts, skeletal muscle activity


Spinal Cord fxs as Switchboard
Carries impulses to & from brain
To brain via ascending tracts
From brain via motor tracts
Contains centers for Reflex Arcs
Interneurons switch/transfer incoming sensory impulses
to outgoing motor impulses Spinal Cord Reflex Arc
2 kinds withdrawal reflex (Ex. from hot/sharp surface)
knee jerk reflex
Injury cuts spinal cord across impulses can’t pass produces
Loss of sensation Anesthesia
Loss of ability to move paralysis

Spinal Nerves (31 prs)
8 cervical (7 cervial vertebrae)12 thoracic (12 thoracic vertebrae)5 lumbar 5 (5 lumbar vertebrae)Sacrospinal (fused vertebrae)1 coccygeal (coccyx)
Conduct impulses between spinal cord & areas not supplied by 12 cranial nerves
Contain both sensory & motor fibers sensation mvmt

7 cervical vertebrae
12 thoracic vertebrae
5 lumbar vertebrae
Fused vertebrae
8
12
5
5
1 coccyx
Nerve prs

Dermatome: skin surface area supplied by single nerve
Herpes Zoster/Shingles: viral infection of single dermatome caused by varicella zoster virus of chicken pox
Virus travel thru cutaneous nerve & remains dormant in dorsal root ganglion long after chicken pox infection
↓ Immune Response (Ex. elderly, stress, radiation, immunosuppresive drugs virus may reactivate
Virus travels over sensory nerve to skin of single dermatome painful eruption vesicles, crust & clear 2-3wks


PNS
Outside CNS
Nerves & associated cells not part of CNS (brain & s.c)
Consists of: cranial nerves that pass thru skull
stimulate head & neck
Spinal nerves: 31 prs
Ganglia: (nerve cell bodies)

Sensory Division of PNS: transmits impulses from sense organs CNS
Motor Division of PNS: transmits impulses from CNS muscles/glands (Effectors)
Somatic NS voluntary
Skeletal muscle contraction
Some also use reflex arc
Autonomic NS Involuntary
Ex. smooth muscles, digestion
pupils reflex
Sympathetic
↑ Effect (gas)
Parasympathetic
↓Effect (brake)

Running: Sympathetic NS ↑ heart rate, blood flow to skeletal
muscles, stimulates sweat & adrenal glands
Parasympathetic NS ↓ smooth muscle contractions
in digestive system
Stop Running: Parasympathetic NS ↓ heart rate & blood
flow to skeletal muscles
Sympathetic NS ↑ contractions of smooth
muscles in digestive system
Important Fx Maintaining Homeostasis

Divisions of the Brain
Billions of Neurons
1.4kg Must have continuous supply of O2
Part of brain that is damaged determines effects
Wavy bumps/folds: gyri (gyrus)
Shallow grooves: sulci (sulcus)
Folds/Grooves ↑S.A for more neurons
(S&F)

Gyri: folds
Sulci: grooves

Cerebrum: Largest part of brain
Voluntary, Conscious activities
Intelligence, Learning, Judgment
Divided into LT & RT hemispheres
by deep longitudinal fissure
Hemispheres connected by corpus callosum
Each hemisphere divided into 4 lobes
named after skull bones
Frontal (vol muscle mvmt)
Parietal (behind frontal)
Temporal (sides)
Occipital (back)


Myelinated fibers join
LT & RT HemispheresFx produces automatic mvmts & posture
Parkinson’s disease of basal ganglia shaking/tremors

Each ½ of Cerebrum deals w/ opposite side of body
• Sensations from LT body Rt hemisphere
• Sensations from RT body Lt hemisphere
Commands to move muscles also opposite
• LT hemisphere controls RT side of body
• RT hemisphere controls LT side of body
Studies suggest
RT hemisphere associated w/ artistic/creative
Lt hemisphere associated w/ analytical/mathematical

2 Layers to Cerebrum
Outer Cerebral Cortex gray matter (densely pkd cell
bodies & unmyelinated axons)
Processes info from sense organs
Controls body mvmts
Inner Cerebral Medulla white matter (bundles of
myelinated axons)
Connects Cerebral Cortex
& Brain Stem

3 Regions of Cerebral Cortex (Outer layer of Cerebrum))
Spinal Cord damage disconnects
ascending & descending tracts
Motor Centers: Instructions for motor response coordinated
Motor Cortex connects to Descending Motor Tracts
Stimulation of different point on Motor Cortex
muscles in different parts of body to contract
*** Lg area of motor cortex devoted to muscles that control
tongue & thumb mvmts Reflects amount of control
req’d for hand mvmts & speech

Regions of Motor Cortex cont’d
10 Receiving Centers: Receive sensory input from PNS
(Sensory) Somatic Sensory Cortex
(behind motor cortex)
is 10 receiving center for sensory
input from skin & joints via
Ascending Tracts
Association Centers: Separate from Motor & 10 Rec. Centers
but connected to motor & sensory thru
neural pathways

Brain Studies
1940’s Wilder Penfield surgically exposed Cerebral Cortex
Used weak electrical stimulation on patients still awake
Brain pkd w/ neurons but NO pain receptors!!!!
Stimulated part of Cerebral Cortex at a time & patients described sensations
Motor Cortex = areas where stimulation muscle
contraction
Sensory Cortex = areas where stimulation taste, touch,
sound
Areas where stimulation memories = physical location of
memories



Sensory control

Sensory Neurons (Affecter) brings message to spinal cord
Neurons in spinal cord carry impulses to Thalamus
via Ascending Tracts
Thalamus: switching station relays impulses to Sensory Cortex (in Cerebrum) for action
Motor Cortex sends message ↓ spinal column via descending tracts to synapse w/ Motor Neuron (Effecter)
??? Cases where parts of spinal cord destroyed & still sensation at different parts of body, despite no connections to carry impulse to cerebral cortex!!!

Brain Studies
Hebel & Wiesel (Harvard) studied visual cortex in kittens
Thought all nerve connection in brain genetically determined
Kittens: Kept 1 eye closed since birth
Nerve connection failed to develop!!!
Other eye nerve connections developed normally
Determined: Pattern of connections depends on kinds of visual stimulation experienced in early development after birth
Concluded: Abnormal nerve development env. not genetic influence
Env & sensory input develops neural pathways (plasticity)
*Babies & visual stimuli ↑ visual stimuli ↑ Nerve Connections

Cerebellum: 2nd largest part of brain (outer gray, inner mostly white)
Back of skull
Commands to move come from Cerebral Cortex
but Cerebellum coordinates & balances actions of
muscles smooth, efficient, graceful mvmt
Involuntary
Damaged Cerebellum muscle weakness
↓ Coordination
Simple tasks (walk, run) difficult
Train Cerebellum to coordinate muscle use
Practice helps develop connections to Cerebellum
make task easier (but not under conscious control)
***Occupational Therapy Importance

*
*
*****
*
**
brainstem
Brain Stem Midbrain
Pons
Medulla Oblongata

Brain Stem
Foramen Magnum opening in occipital bone for spinal cord to pass thru
Medulla: Extension of spinal cord just inside cranial cavity
Gray & White matter intermingle Reticular
Formation
*Remember in spinal cord inner (H) = gray
outer = white
Pons: (middle/bridge) between Medulla & Midbrain
Midbrain: above Pons


Brain Stem is 2 way conduction path
Sensory fibers impulses spinal cord brain
Motor fibers impulses brain spinal cord
Many Vital Reflex Centers lie in Medulla of Brainstem
Cardiac, Respiratory, Vasomotor Centers
Impulses that control heartbeat
respirations
blood vessel diameter

Diencephalon: Between midbrain & cerebrum
Contains Hypothalamus & Thalamus
(below thalamus)
Hypothalamus: Contains Posterior pituitary gland
Control over Paraventricular & Supraotic Nuceli
All internal organs (2 clusters of neuron cell bodies)
Appetites Make hormones Posterior Pituitary
Body Temp Gland stores/ secretes into blood.
Hunger Ex. ADH affects urine
Thirst volume to maintain body’s H2O
Fatigue balance
*** Coordinates Nervous System & Endocrine System

Some Neurons in hypothalamus
Fx as Endocrine (ductless) Glands
Axons secrete Releasing Hormones into blood
RH’s control release of
Anterior Pituitary Hormones
that influence hormone secretion by
other Endocrine Glands

Thalamus (above hypothalamus)
• Helps produce sensations (relays impulses to cerebral
cortex from sense organs, (except smell)
• Associates sensations w/ emotions
• Arousal/alerting mechanism

Brain Waves
Brian neurons capable of Action Potential (electrical activity)
Voltage sensitive electrodes on scalp
record weak electrical current
EEG: Electroencephalogram
Records electrical activity on scalp
Measures average activity of thousands of neurons
general idea of brain activity


Sleep: Activity of Cerebral Cortex ↓ to lowest level
unconsciousness deep unresponsive to light sleep
RAS (Reticular Activating System)
Network of neurons in Medulla Oblongata (brain stem)
helps control consciousness
Level of RAS ↓ sleep begins
Special group of neurons in brainstem activate light sleep
During deep sleep
↓ in heart rate, BP, respiration rate, energy use
During REM (Rapid Eye Mvmt) sleep dreaming occurs

Memory
Short Term: Not permanent
Stored as pattern of nerve impulses
in Cerebral Cortex
Vanishes w/in few days
unless interesting or effort to remember
Long Term: More permanent
Some last lifetime
May require effort to recall
Can become part of person’s consciousness
Some patients w/ severe brain injuries keep long term memory (even w/ Cerebral Cortex damage)
Suggests long term memory stored in structure of brain itself