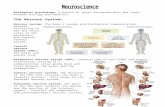
The Nervous System Dont get nervous about the nervous system.
The Nervous System Nervous System the body ’ s speedy, electrochemical communication system ...
-
Upload
marilynn-robinson -
Category
Documents
-
view
223 -
download
0
Transcript of The Nervous System Nervous System the body ’ s speedy, electrochemical communication system ...

The Nervous System
Nervous System the body’s speedy, electrochemical communication
system consists of all the nerve cells of the peripheral and
central nervous systems Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system (CNS) to the rest of the body

The Nervous System
Central(brain and
spinal cord)
Nervoussystem
Autonomic (controlsself-regulated action of
internal organs and glands)
Skeletal (controlsvoluntary movements of
skeletal muscles)
Sympathetic (arousing)
Parasympathetic (calming)
Peripheral

The Nervous System
Somatic Nervous System the division of the peripheral nervous system that
controls the body’s skeletal muscles Autonomic Nervous System
the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart)

The Nervous System
Sympathetic Nervous System division of the autonomic nervous system that
arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
Parasympathetic Nervous System division of the autonomic nervous system that
calms the body, conserving its energy

Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
Sympathetic NS “Arouses”
(fight-or-flight)
Parasympathetic NS “Calms”
(rest and digest)

Brain and Spinal Cord
Central Nervous System (CNS) the brain and spinal cord
Brain part of the CNS that plays important roles in sensation,
movement, and information processing. Spinal Cord
plays a role in body reflexes and in communication between the brain and the peripheral nervous system.

The Nervous System Reflex
a simple, automatic, inborn response to a sensory stimulus
Skinreceptors
Muscle
Sensory neuron(incoming information)
Motor neuron(outgoing information)
Brain
Interneuron
Spinal cord

Central Nervous System
The Spinal Cord and Reflexes
Simple Reflex

The Nervous System
Neural Networks interconnected neural
cells with experience,
networks can learn, as feedback strengthens or inhibits connections that produce certain results
computer simulations of neural networks show analogous learning
Inputs Outputs
Neurons in the brain connect with one
another to form networks
The brain learns by modifyingcertain connections in response to feedback



• Have you ever wondered how a woman's brain works? Well....it's finally explained here in one, easy-to-understand illustration: and I bet there is not one man out there that will disagree......

•
Every one of those little blue balls is a thought about something that needs to be done, a decision or a problem that needs to be solved NEEDS NO FURTHER DISCUSSION.

The Brain

The Brain
Techniques to Study the Brain
A brain lesion experimentally destroys
brain tissue to study animal behaviors after
such destruction.
Hubel (1990)

Clinical Observation
Clinical observations have shed light on a number of brain disorders. Alterations in brain
morphology due to neurological and psychiatric diseases are now being catalogued.
Tom L
anders/ Boston G
lobe

Electroencephalogram (EEG)
An amplified recording of the electrical waves sweeping across the brain’s surface, measured
by electrodes placed on the scalp.
AJ P
hoto/ Photo R
esearchers, Inc.

The Brain CT (computed tomography) Scan
a series of x-ray photographs taken from different angles and combined by computer into a composite representation of a slice through the body; also called CAT scan
PET (positron emission tomography) Scan a visual display of brain activity that detects where a
radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain performs a given task

PET Scan
PET (positron emission tomography) Scan is a visual display of brain activity that detects a radioactive form of glucose while the brain performs a given task.
Courtesy of National Brookhaven N
ational Laboratories

PET Scan

The Brain MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
a technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images that distinguish among different types of soft tissue; allows us to see structures within the brain
Stimulation Electrical stimulation of the brain involves sending a weak
electric current into a brain structure to stimulate it. (It is not painful because the brain has no pain receptors

MRI Scan
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images that distinguish among different types of brain tissue. Top images show ventricular enlargement in a schizophrenic patient. Bottom image shows brain regions when a participants lies.
Both photos from Daniel Weinberger, M.D., CBDB, NIMH
James Salzano/ Salzano Photo Lucy Reading/ Lucy Illustrations

The Brain
Brainstem the oldest part and central core of the brain,
beginning where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull
responsible for automatic survival functions

Developing Brain
•Neural tube—beginning of nervous system develops at 2 weeks after conception
•Neurogenesis—development of new neurons

Figure 2.16 The brainstem and thalamusMyers: Psychology, Eighth EditionCopyright © 2007 by Worth Publishers