The Heart and Lungs. Importance of Blood Brings oxygen, nutrients, and other necessary materials to...
-
Upload
emerald-nelson -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
0
Transcript of The Heart and Lungs. Importance of Blood Brings oxygen, nutrients, and other necessary materials to...

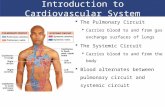
The Heart and Lungs

Importance of Blood
• Brings oxygen, nutrients, and other necessary materials to your body cells and carries waste products away
• Cardiovascular system- provides a pathway through which blood can carry materials throughout your body
• The heart pumps blood through the network of arteries and veins called the cardiovascular system

The Four Chambers of Heart• Right atrium (upper)
– receives blood from the veins and pumps it to the right ventricle • Right ventricle (lower)
– receives blood from the right atrium and pumps it to the lungs, where it is loaded with oxygen
• Left atrium (upper)– receives oxygenated blood from the lungs and pumps it to the
left ventricle • Left ventricle (lower- the strongest chamber)
– pumps oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body. The left ventricle’s vigorous contractions create our blood pressure.

The Heart

Pulmonary System
• Right side of heart pumps blood to the lungs (pulmonary circulation)
• Left side of heart pumps blood to rest of body• Right atrium fills with waste-rich blood, then
contracts, pushing the blood into the right ventricle
• Right ventricle fills and then contracts, pushing the blood into the pulmonary artery which leads to the lungs

Lungs
• In lung capillaries, the exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen takes place
• Fresh, oxygen rich blood enters pulmonary vein and returns to heart
• Another function of the heart is to pump blood to the lungs where the blood exchanges carbon dioxide for oxygen.
• In the pulmonary circuit, the blood leaves the heart through the pulmonary arteries and then makes its way to the lungs and goes back to the heart through the pulmonary veins

Blood Vessels
• Arteries– Carry blood away from the heart– Aorta- largest in body
• Veins– Carry blood to the heart– Valves inside the veins prevent blood from flowing
backward

Blood Pressure
• The force with which blood pushes against the walls of the blood vessels
• 120/80• Systolic (first number)– Force caused by the surge of blood that moves as a result
of the contraction of the ventricle• Diastolic (second number)– Force recorded when the ventricles are relaxed
• BP increases as you exercise, decreases after you relax from exercise (see chart)
• Hypertension- high blood pressure (140/90)

Heart Disorders
• Atherosclerosis- buildup of cholesterol and other fatty acids materials on artery walls, which restricts the flow of blood
• Heart Attack- when blood flow to part of the heart muscle is blocked. Can be caused from Atherosclerosis

Blood Disorders
• Hemophilia– Blood does not clot
• Leukemia– Cancer of bone-marrow tissues that form white
blood cells (produces large number of abnormal white blood cells- interferes white fighting disease)

Blood Disorders cont’d
• Anemia– Too few red blood cells or too little hemoglobin– Blood cannot carry as much oxygen as the body
needs
• Sickle-cell– Red blood cells curve into a sickle shape because
of a flaw in the hemoglobin– Curved cells do not pass through capillaries easily,
blocking the blood flow

Healthy Heart and Lungs
• Avoid smoking– Can damage air passages and lungs
• Control your diet– RBC need iron to transport oxygen– Avoid straining both respiratory and circulatory
systems
• Exercise regularly– Can raise levels of HDL

Changes in Heart Rate

Neural and Hormonal EffectsSympathetic vs Parasympathetic
• Autonomic Nervous System• Sympathetic: increase heart rate by releasing
epinephrine or norepinephrine– Acceleration of the heart= tachycardia
• Parasympathetic: slows heart rate by releasing acetylcholine– Slowing of heart rate= bradycardia

Who cares?
• Exercise changes relationship between sympathetic accelerators and parasympathetic system
• Leads to more involvement of vagus nerves (which carry 80% of parasympathetic fibers)
• With increased vagal dominance, heart rate slows (leads to lower RHR and AHR)

Environmental Stresses
• Heat gain= elevated• Heat loss= lowered• Dry air= elevated• Moist air= elevated• Wind chill= lowered• Altitude= partial pressure increase, causing
increases heart rate