The diagram shows the motion of a boat over a period of time. How far, in meters, did the boat...
-
Upload
eugenia-barker -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
0
Transcript of The diagram shows the motion of a boat over a period of time. How far, in meters, did the boat...







The diagram shows the motion of a boat over a period of time. How far, in meters, did the boat travel in the first 3 seconds of motion? Record and bubble in your answer to the nearest whole number on the answer document.

27 In which container will the water evaporate most quickly?
F H
G J

21 The table shows the time it took to freeze water in two different salt solutions with different salt content. According to the table —
A freezing rates are the same in each trialB water with more salt takes longer to freezeC water loses heat at a rate of 1°C per minuteD salt dissolves more quickly in small amounts of water
Freezing Rates
Solution Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3
50 mL water 45 min 43 min 47 min
50 mL water
and 5 g salt70 min 75 min 82 min
50 mL water
and 10 g salt120 min 125 min 119 min

18 This diagram represents water in a container. What process is taking place?
A FreezingB CondensationC MeltingD Evaporation

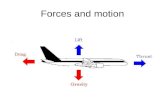
1 Which object requires the most force to move a distance of 1 meter?
A Bird featherB Rubber ballC Block of cementD Block of wood
Masses of Objects
Bird
feather
Rubber
ball
Block of
cement
Block of
wood
0.01 g 1 g 10 g 14 g

Students placed two identical toy cars on these wooden ramps. The students let the cars roll down the ramps.
2 What causes these cars to move down the ramps?
A ElectricityB A force that pullsC MagnetsD A force that lifts

3 A car will skid more on a wet road than on a dry road. This happens because between the tires and the dry road, there is more —
A gravityB magnetismC frictionD heat

4 The picture shows different points along a toy rocket’s path after it blasted off. How much height did the rocket gain between Points Qand R?

5 Which force is most responsible for raindrops falling to Earth?
F FrictionG WindH ThrustJ Gravity

6 The picture shows the process of —
F meltingG boilingH condensingJ freezing

7 If the person in the middle lets go of the rope, in which direction would objects X and Y go?
A X up, Y upB X up, Y downC X down, Y downD X down, Y up

Landfill X
Landfill Y
8 The diagram shows landfills where two communities put garbage. What is the advantage of Landfill Y?
F The waste lasts longer.G The groundwater is safer.H The soil contains more nutrients.J The trucks move faster.

9 The picture shows two bowling balls being held in position with four ropes. The box will be flipped upward
if which rope is cut?
A WB XC YD Z

10 Which of these is a good conductor of electricity?
F GlassG MetalH RubberJ Plastic

11 Which of the following can be attracted to a magnet?
F Gold ringG Glass marbleH Iron needleJ Wool sock

12 Matter can undergo changes. When water boils, a —
F liquid becomes a solidG solid becomes a liquidH liquid becomes a gasJ gas becomes a solid

13 In an experiment salt and sand are mixed together. Which of these procedures could be used to most easily separate the salt from the sand?
A C
B D
• stir the mixture into a glass of
water
• pour the mixture in the glass
through a filter
• evaporate the water
• pour the mixture onto a piece
of paper
• brush the mixture into a pile
• drag a magnet through the pile
• put the mixture in a pan
• heat the pan for 10 minutes
• let the hot mixture cool slowly
• spread the mixture into a thin
layer
• look at the mixture through a
magnifying glass
• separate the crystals with a pin

14 Carbon powder and iron filings are both black powders. When mixed together, they look like one black powder. Which of these would be best to use to separate the iron filings from the carbon powder?
F A magnifying glassG HeatH A magnetJ Water

15 A company collects cans for recycling. Some cans are made of aluminum, and some are made of iron. Which of the following is the best way to separate the two types of cans?
A Heat the iron cans until they meltB Use scissors to cut the cansC Use a magnet to pick up the iron cansD Float the cans in water

16 A student places a sugar cube in a beaker of water. What change will occur?
A The sugar cube will not change.B More water will be formed.C The sugar cube will become smaller.D The water will form crystals

17 In an activity, 20 grams of salt are dissolved in 70 grams of pure water. The water is then heated on a hot plate. When the water evaporates completely, how much salt will be left?
A 0 gramsB 18 gramsC 20 gramsD 22 grams

18 Crystals were grown on a string in a clean glass jar containing sugar dissolved in hot water. The crystals grew on the string for several weeks. What kind of crystals are they?
F StringG WaterH GlassJ Sugar

19 A teaspoon of clean, dry sand is added to a cup of warm saltwater. What is most likely to happen after the mixture is stirred and then placed on a table for five minutes?
A The amount of water will increase.B The salt will float to the top.C The sand will settle to the bottom.D The cup will heat up.

20 Which of the following thermometers shows the boiling point of water in a pan?
F G H J

21 When a chocolate bar is heated by the sun, all of the following are likely to be seen EXCEPT —
F boilingG a liquidH meltingJ a change in shape

22 Some students were studying properties of water. One student placed a cup containing 80 mL of water in a freezer. Another student placed an identical cup containing 40 mL of water in a different freezer. Which of the following will be the same for both cups of water?
A The temperature at which the water freezesB The mass of the frozen waterC The time it takes the water to freezeD The volume of the frozen water

23 What two forms of energy does a flame from a burning candle release?
F Electrical and mechanicalG Chemical and electricalH Light and heatJ Heat and nuclear

24 The diagram above shows a light ray approaching a mirror. Which of the diagrams below shows how the light travels after striking the mirror?
A B C D

25 All the following are examples of light being refracted EXCEPT —
A C
B D

26 Light traveling through a pair of eyeglasses is —
F refractedG transmittedH absorbedJ reflected

27 A student holds a note card behind a jar of water. Which of the following best explains why the part of the note card seen through the jar looks different from the rest of the note card?
A The jar reflects light hitting its surface.B The water absorbs light hitting its surface.C The jar scatters light passing through it.D The water bends light passing through it.

28 Which of these pictures shows the way to use a battery to light a bulb?
A C
B D

29 Which circuit will cause the lightbulb to glow?
A C
B D

30 Which of these is made to change electrical energy to heat energy?
A C
B D

31 The wires connecting the battery and the lightbulb create a closed circuit. What would happen if one of these wires were cut?
F The battery would lose its charge.G The glass would crack.H The light would go out.J The wire would become hot.

32 A student plans to make this lightbulb glow. All of the following objects can be used to complete the circuit EXCEPT —
A a copper pennyB a plastic combC a metal clipD an iron nail

33 Sound is made when a drumstick hits the drum. This happens because the force of the drumstick on the drum causes —
F vibrationsG electrical currentsH heat energyJ a magnetic charge

34 Blowing through a pipe can produce a sound because the —
F air in the pipe vibratesG pipe speeds up the airH pipe cools the airJ air is absorbed by the pipe

35 An insect that produces waves in the water also produces waves in the air. What can these air vibrations produce?
A SoundB LightC OxygenD Carbon

Grade 5
Objective 3
Answer Key

Grade 5 Objective 3 Answer Key
Correct Objective Student
Question Answer Measured Expectation Source – item number
1 D 3 3.6 A 2004 TAKS Info Booklet – 15
2 B 3 3.6 A 2004 TAKS Info Booklet – 22
3 C 3 3.6 A 2003 TAKS – 27
4 5 3 3.6 A 2004 TAKS – 20
5 J 3 5.5 A 2004 TAKS – 18
6 F 3 5.5 B 2003 TAKS – 8
7 C 3 5.5 B 2004 TAKS – 39
8 G 3 5.5 B 2006 TAKS – 26
9 B 3 5.5 B 2006 TAKS – 29
10 G 3 5.7 A 2003 TAKS – 34
11 H 3 5.7 A 2003 TAKS – 38
12 H 3 5.7 A 2004 TAKS – 6
13 A 3 5.7 B 2003 TAKS – 21
14 H 3 5.7 B 2004 TAKS – 22
15 C 3 5.7 B 2006 TAKS – 7
16 C 3 5.7 C 2004 TAKS Info Booklet – 11
17 C 3 5.7 C 2004 TAKS – 31
18 J 3 5.7 C 2004 TAKS – 34

Grade 5 Objective 3 Answer Key
Correct Objective Student
Question Answer Measured Expectation Source – item number
19 C 3 5.7 C 2006 TAKS – 27
20 G 3 5.7 D 2003 TAKS – 40
21 F 3 5.7 D 2004 TAKS – 32
22 A 3 5.7 D 2006 TAKS – 9
23 H 3 5.8 A 2006 TAKS – 2
24 B 3 5.8 B 2002 TAKS Info Booklet – 7
25 D 3 5.8 B 2004 TAKS Info Booklet – 13
26 F 3 5.8 B 2003 TAKS – 16
27 D 3 5.8 B 2006 TAKS – 13
28 B 3 5.8 C 2002 TAKS Info Booklet – 8
29 B 3 5.8 C 2004 TAKS Info Booklet – 12
30 D 3 5.8 C 2004 TAKS Info Booklet – 14
31 H 3 5.8 C 2003 TAKS – 2
32 B 3 5.8 C 2006 TAKS – 19
33 F 3 5.8 D 2003 TAKS – 36
34 F 3 5.8 D 2004 TAKS – 16
35 A 3 5.8 D 2006 TAKS – 17