The Cell in Action Guided Notes. What you should already know… Cell membrane – a phospholipid...
-
Upload
stephanie-bentley -
Category
Documents
-
view
212 -
download
0
Transcript of The Cell in Action Guided Notes. What you should already know… Cell membrane – a phospholipid...

The Cell in Action
Guided Notes

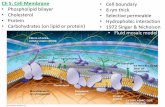
What you should already know…• Cell membrane – a phospholipid layer
that covers a cell’s surface; acts as a barrier between the inside of a cell and the cell’s environment.
• Organelles – the small bodies in a cell’s cytoplasm that are specialized to perform a specific function.
• Multicellular organisms have levels of organization: cell tissue organ organ system. Organ systems form organisms such as you.

Where do cells get the materials they need?
• Like a factory, a cell must be able to get energy and raw materials and get rid of wastes.
• These jobs are done by the organism’s cells.
• Materials, such as water and oxygen, move in and out of the cell across the cell membrane by diffusion.

What is diffusion?• Particles tend to
move from places where they are crowded to places where they are less crowded.
• The movement from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration is called diffusion.

Diffusion of Water• The diffusion of water through a membrane is
called osmosis.• A membrane is selectively permeable or
semipermeable when only some substances can pass through it.

How do small particles enter and leave a cell?
Passive Transport
• Particles can travel through protein channels, or passageways.
• During passive transport, particles move through the cell membrane without using energy from the cell.
• Diffusion and osmosis are examples of passive transport.
Active Transport
• During active transport, the cell has to use energy to move particles through protein channels.
• Particles usually move from areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration.

How do large particles enter and leave a cell?
Endocytosis
• Happens when a cell surrounds a large particle and encloses it in a vesicle.
Exocytosis
• Happens when a cell uses a vesicle to move a particle from within the cell to outside the cell.
Large particles cannot move across a cell membrane in the same ways as small particles.

How does a plant make food?• The sun is the major source of energy for
life on Earth.• Plants use CO2, H2O, and the sun’s energy
to make food in a process called photosynthesis.
• Light energy is absorbed in pigments called chlorophyll, which is found in chloroplasts.
• The food plants make, a simple sugar called glucose, gives them energy.
• Photosynthesis also produces oxygen.

Photosynthesis• Takes place in plants, algae, and some bacteria. • Plants use energy captured by chlorophyll found in
chloroplasts to change CO2 and H2O into glucose.

How do organisms get energy from food?
• When animals eat plants, the plants become a source of energy for the animals.
• Both animals and plants must break down food molecules to get energy from them.
• There are two ways cells get energy: cellular respiration and fermentation.

Cellular Respiration
• Cells use oxygen to break down food.
• Releases more energy from food than fermentation.
• Most eukaryotes, such as plants and animals, use cellular respiration.
Fermentation
• Food is broken down without oxygen.
• Releases less energy from food than cellular respiration.
• Some bacteria and fungi rely only on fermentation to release energy from food.
• Fermentation creates a byproduct called lactic acid.

What happens during cellular respiration?
• In eukaryotic cells, such as plant and animal cells, cellular respiration takes place in structures called mitochondria.
• Also takes place in bacteria.• During cellular respiration, glucose is broken
down into CO2 and H2O, and energy is released.
• Energy is stored in a molecule called ATP.

Cellular Respiration• The mitochondria in the cells of this cow will use
cellular respiration to release the energy stored in the grass.

The connection between Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
• Cellular respiration releases CO2 and H2O. These are used by plant cells in photosynthesis.
• Photosynthesis uses CO2 and H2O and produces glucose and oxygen. Plant and animal cells use glucose and oxygen to make ATP in cellular respiration.

How are new cells made?• In their life cycles, cells pass through different
stages called the cell cycle.• The cycle starts when a cell is made, and ends
when the cell divides to make new cells.• Before the cell divides, it makes a copy of its
DNA, a molecule that contains all the instructions for making new cells.
• DNA is stored in structures called chromosomes. Cells make copies of their chromosomes so that new cells have the same chromosomes as the parent cells.

Making more prokaryotic cells• Prokaryotes have only
one cell with no nucleus or organelles surrounded by membranes.
• DNA for prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria, is found on one circular chromosome.
• The cell divides by binary fission, during which the cell divides into two parts.
• Each part has one copy of the cell’s DNA.

Eukaryotic cells and their DNA• The chromosomes of
eukaryotic cells contain more DNA than prokaryotic cells.
• Different kinds of eukaryotes have different numbers of chromosomes; fruit flies have 8, potatoes have 48, and humans have 46.
• Chromosomes that have the same sequence of genes and the same structure are called homologous chromosomes.
Human body cells have 46 chromosomes, or 23 pairs of
chromosomes.

Making more eukaryotic cells• The eukaryotic cell cycle includes
3 stages;– 1st Stage – Interphase, the cell
grows and copies its organelles and chromosomes. The two copies of a chromosome are called chromatids, which are held together at a region called the centromere.

Making more eukaryotic cells (cont.)– 2nd Stage – Mitosis, the process of cell
division that forms two new nuclei, each of which has the same number of chromosomes.
– Mitosis is divided into 4 phases: PMAT• Prophase• Metaphase• Anaphase• Telophase
– 3rd Stage – Cytokinesis, the division of the cytoplasm of a cell and two daughter cells form. In cells that have a cell wall, a cell plate forms between the two new cells.

Review1. How do cells take in food and get rid of wastes?2. What is diffusion?3. How do plant cells make food?4. How do plant and animal cells get energy from
food?5. How are new cells made?6. What is mitosis? What are the four phases of
mitosis?7. How is cell division different in animals and
plants?