Text: Chapter 5 Human Biology Stage 3. Keywords Central nervous system (CNS) Cerebrospinal fluid...
-
Upload
pearl-mcdaniel -
Category
Documents
-
view
223 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Text: Chapter 5 Human Biology Stage 3. Keywords Central nervous system (CNS) Cerebrospinal fluid...

The Nervous SystemCNS – the brain and spinal cord
Text: Chapter 5Human Biology Stage 3

KeywordsCentral nervous system (CNS)Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)MeningesNeurons
Cell bodyDentritesAxonSynapse
Myelin sheathSchwann cellsSensory neuronsMotor neurons InterneuronsCerebrum
Cortex
ConvolusionsSulciFissures - Longitudinal fissure
LobesFrontalParietalTemporalOccipital
CerebellumMedulla oblongata
Cardiac centreRespiratory centreVasomotor centre
Spinal cordAscending tractsDescending tracts

The Nervous SystemThe nervous system is the
control centre and communication network of the body
The nervous system can be divided into 2 parts: The central nervous
system (CNS)The peripheral
nervous system (PNS)The CNS includes the
brain and the spinal cord
The PNS is divided into the:Autonomic nervous systemSympathetic nervous
systemParasympathetic
nervous system Somatic nervous systemSkeletal muscle
Both the CNS and the PNS are also involved in maintaining homeostasis in conjunction with the endocrine system

Structure of nerve cellsNerve cells are called
neurons. They are the functional unit of the nervous system.
Neurons have:A cell body that contains
the nucleusDendrites, short extensions
on one side of the cell bodyAn axon, a long extension
on the other side of the cell body

Structure of nerve cells Most axons are covered
in a white, fatty material called the myelin sheath
The myelin sheath is made up of individual cells called Schwann cells
An axon with its covering is called a nerve fibre
There are myelinated fibres and unmyelinated fibres

The myelin sheathFunctions of the
myelin sheath: It acts as an
insulator It protects the axon
from damage It speeds up rate of
impulses It helps with the
repair of injured fibres

The synapseThe axon of one neuron
connects to the dendrites of the next neuron
There is a space in between the axon of the first neuron and the dendrites of the next one
This space is called the synapse
A nerve impulse travels from the dendrites, through the cell body, the axon, across the synapse and into the dendrites of the next neuron

Types of neurons: functionNeurons are classified
according to their function
Sensory neurons carry messages from the receptors to the CNS
Motor neurons carry messages from the CNS to muscles and glands
Interneurons are located in the CNS and are the link between sensory and motor neurons

Types of neurons: structureNeurons can also be classified
according to their structure:Multipolar neurons have
one axon and multiple dendrites extending from the cell body. They are the most common type
Bipolar neurons have one axon and one dendrite, both branching at their ends. They occur in the eye, ear and nose
Unipolar neurons have just one axon extension and the cell body is to one side of the axon

The CNSMost of the neurons in the
CNS are interneurons They have many branches
that are able to send or receive messages
The CNS consists of:grey matter, made up of
neurons with unmyelinated fibres (axons)
white matter, composed of neurons with myelinated fibres (axons)
The brain is the control centre of the body
The spinal cord goes out from the brain and sends a network of nerve fibres to the rest of the body

Protection of the CNSThe brain and spinal
cord are very delicate and important parts of the body and are highly protected
3 structures that support and protect the CNS:BoneMeninges Cerebrospinal fluid
(CSF)

Protection of the CNSThe brain is
protected by the cranium
The spinal cord runs through an opening called the vertebral canal surrounded by bony vertebrae

Protection of the CNSInside the bone covering,
the brain and the spinal cord have 3 layers of connective tissue called the meninges
They cover the entire CNS
Outler layer: tough and fibrous, sticks close to the bone
Middle layer: lose meshInner layer: delicate,
contains blood vessels, close to surface of the brain and spinal cord

Protection of the CNSCSF occupies a space
between the middle and inner layers of the meninges
It circulates through cavities in the brain and spinal cord
It is a clear, watery fluid containing glucose, protein, urea and salts
It acts as a shock absorber It acts as transport, taking
nutrients to the brain and spinal cord and carrying waste away

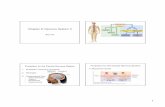
The brain The brain is divided into 3 main sectionsCerebrumCerebellumBrain stem
The cerebrum carries out the higher order functions
Example: languageThe cerebellum is concerned
with fine motor co-ordinationExample: balanceThe brain stem carries out the
lower order functionsExample: breathing & heart
rate

The cerebrum The cerebrum is the
largest section of the brain It consists of two layers of
grey matter sandwiching a layer of white matter
The outer layer is called the cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex is greatly folded to increase surface area
Folding produces convolutions which are separated by shallow downfolds called sulci and deep folds called fissures
Grey matter
White matter
Sulci
Fissures

The cerebrum The deepest fissure is
the longitudinal fissure which separates the cerebrum into 2 halves; the left and right hemispheres
Each cerebral hemisphere is divided into 4 lobes: the frontal, temporal, occipital and parietal lobes.
Longitudinal fissure
Cerebrum
Cerebellum
Spinal cord

The lobes Frontal lobeThe boss –
reasoning, planningParietal lobe
Sensory information – dealing with & reacting to the environment
Occipital lobeVision
Temporal lobeLanguage, hearing,
memory

The functional areas 3 functional areas in the
cortex: Sensory area interprets
impulses from receptors Motor area controls
muscular movements Association areas
concerned with emotional and intellectual processes – deciding how to respond

The cerebellumThe cerebellum lies
under the rear of the cerebrum
It controls: PostureBalanceFine motor
coordination (muscle movement)

The hypothalamus The hypothalamus
lies in the middle of the brain between the two hemispheres
It is mostly
concerned with homeostasis

The medulla oblongata The medulla oblongata
lies within the brain stem and contains the: Cardiac centre -
regulates the rate and force of the heart beat
Respiratory centre –controls the depth and rate of breathing
Vasomotor centre -controls the diameter of blood vessels

The brainhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kMKc8nfPATIThe brain 13 mins

The spinal cord The spinal cord is a continuation of the brain stemIt consists of gray matter in the shape of an H
called the central canal which runs the length of the spinal cord and contains CSF

The spinal cord 3 functions of the spinal cord:
It carries sensory impulses towards the brain
It carries motor impulses away from the brain
Reflexes – impulses that bypass the brain
Myelinated nerve fibres of white matter are arranged in bundles called ascending and descending tracts
Ascending tracts are sensory axons that carry impulses upwards towards the brain
Descending tracts contain motor axons that conduct nerve impulses downwards away from the brain