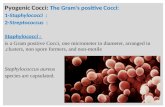
Staphylococcus aureus Ali Somily MD,FRCPC Gram Positive Cocci.
-
date post
22-Dec-2015 -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
2
Transcript of Staphylococcus aureus Ali Somily MD,FRCPC Gram Positive Cocci.
Staphylococcus aureusStaphylococcus aureus
Ali Somily MD,FRCPCAli Somily MD,FRCPC
Gram Positive CocciGram Positive Cocci
Staphylococcus aureusStaphylococcus aureus Staphyloccocci - derived from Greek “stapyle” (bunch of Staphyloccocci - derived from Greek “stapyle” (bunch of
grapes)grapes) Gram Stain : Gram Positive CocciGram Stain : Gram Positive Cocci AerobicAerobic ExtracellularExtracellular FeaturesFeatures
• Morphology : CocciMorphology : Cocci• Arrangement : ClustersArrangement : Clusters• Colonies: White /yellow , rounded on blood agar plateColonies: White /yellow , rounded on blood agar plate
Non motile Non motile • Non motileNon motile
No capsuleNo capsule No glycocalyxNo glycocalyx
Virulence FactorsVirulence Factors ExotoxinsExotoxins ΒΒ-Lactamase-Lactamase
• Plasmid ,Penicillin resistantPlasmid ,Penicillin resistant Mutant Penicillin –Binding –Protein (PBP)Mutant Penicillin –Binding –Protein (PBP)
• MRSAMRSA CoagulaseCoagulase
• Free and boundFree and bound• Thrombin Thrombin Fibrin Fibrin
Protein AProtein A• Bind to Fc of IgG, Block complement and opsonizationBind to Fc of IgG, Block complement and opsonization
Other enzymesOther enzymes• Lipase, Protease, Hyaluronidase, Nuclease, FibrinolysinLipase, Protease, Hyaluronidase, Nuclease, Fibrinolysin
ExotoxinsExotoxins Hemolysins of RBCsHemolysins of RBCs
• Alpha toxin ( septic Shock and Dermonecrosis)Alpha toxin ( septic Shock and Dermonecrosis)• Beta toxin (Shingomyelinase)Beta toxin (Shingomyelinase)• Delta toxin (Leukocidin)Delta toxin (Leukocidin)• Gamma toxin (Tissue Necrosis)Gamma toxin (Tissue Necrosis)
Panton –Valentine Leukocidin (PMNs and Micros)Panton –Valentine Leukocidin (PMNs and Micros)• Influx of Ca++,Degranulation and LysisInflux of Ca++,Degranulation and Lysis
EnterotoxinsEnterotoxins• Toxin A (Food Poisoning) and F (Similar to TSST)Toxin A (Food Poisoning) and F (Similar to TSST)
Toxic Shock Syndrom Toxin(TSST)Toxic Shock Syndrom Toxin(TSST)• Release of IL2 CD4 T-cell and IL1Release of IL2 CD4 T-cell and IL1
Exfoliation ( Phage Group II , Epidermolytic; intraepithelial Exfoliation ( Phage Group II , Epidermolytic; intraepithelial Separation at Stratum Granulosum)Separation at Stratum Granulosum)
Laboratory TestsLaboratory Tests
Catalase : +veCatalase : +ve Coagulase: +veCoagulase: +ve DNase: +veDNase: +ve Mannitol: +veMannitol: +ve Hemolysis: BetaHemolysis: Beta 6.5 % NaCl : Growth6.5 % NaCl : Growth
Source and TransmissionSource and Transmission
ColonizationColonization• HumanHuman : Nose, Skin, Groin, Other moist area : Nose, Skin, Groin, Other moist area • Horizontal TransmissionHorizontal Transmission : Human contact, Sneeze : Human contact, Sneeze
and Contaminated environmentand Contaminated environment• Nosocomial TransmissionNosocomial Transmission: :
Clinical SyndromsClinical Syndroms Skin Infections (Furuncles, Boils, Carbuncles, Scalded Skin Skin Infections (Furuncles, Boils, Carbuncles, Scalded Skin
Syndrom (SSS), Burn and Wound)Syndrom (SSS), Burn and Wound) Food Poisoning (Enterotoxin A, No Bacteria, N&V)Food Poisoning (Enterotoxin A, No Bacteria, N&V) Toxic Shock Syndrom (Tampons, Wound, Nasal Packing)Toxic Shock Syndrom (Tampons, Wound, Nasal Packing) Oseomyelitis (Most Common Cause, Meta in Childern and Oseomyelitis (Most Common Cause, Meta in Childern and
Epiphysis in Adult, Truma or Hematogenous)Epiphysis in Adult, Truma or Hematogenous) Infective Artheritis (Most Common Cause in Adult)Infective Artheritis (Most Common Cause in Adult) Acute Endocarditis (Most Common Cause Normal Abnormal Acute Endocarditis (Most Common Cause Normal Abnormal
and Prosthetic Valves )and Prosthetic Valves ) Post viral lobar Pneumonia ( Especially Flu)Post viral lobar Pneumonia ( Especially Flu) Bacteremia and Sepsis (Most Common Cause ,Community Bacteremia and Sepsis (Most Common Cause ,Community
Acquired)Acquired) Parotitis ( Gland and Duct of Stensen)Parotitis ( Gland and Duct of Stensen)
TOXIN MEDIATED DISEASESTOXIN MEDIATED DISEASES
1. Staphylococcal food poisoning1. Staphylococcal food poisoning• Due to production of entero toxinsDue to production of entero toxins• heat stable entero toxin acts on gutheat stable entero toxin acts on gut• produces severe vomiting following a very short produces severe vomiting following a very short
incubation periodincubation period• Resolves on its own within about 24 hoursResolves on its own within about 24 hours
2. Toxic shock syndrome2. Toxic shock syndrome
High fever, diarrhoea, shock and erythematous High fever, diarrhoea, shock and erythematous skin rash which desquamateskin rash which desquamate
Mediated via ‘toxic shock syndrome toxin’Mediated via ‘toxic shock syndrome toxin’ 10% mortality rate10% mortality rate Described in two groups of patientsDescribed in two groups of patients
• Associated With young women using tampones during Associated With young women using tampones during menstruationmenstruation
• Described in young children and menDescribed in young children and men
3. Scalded skin syndrome3. Scalded skin syndrome
Disease of young childrenDisease of young children Mediated through minor Staphylococcal Mediated through minor Staphylococcal
infection by ‘epidermolytic toxin’ producing infection by ‘epidermolytic toxin’ producing strainsstrains
Mild erythema and blistering of skin Mild erythema and blistering of skin followed by shedding of sheets of epidermisfollowed by shedding of sheets of epidermis
Children are otherwise healthy and most Children are otherwise healthy and most eventually recovereventually recover
Host Defense and ImmunityHost Defense and Immunity
Opsonization (IgG, C3b or IgM +C3b)Opsonization (IgG, C3b or IgM +C3b) Phagocytosis (by PMNs)Phagocytosis (by PMNs) Cytokines (By CD4+T-Cells)Cytokines (By CD4+T-Cells)
No Immunity Gained by InfectionNo Immunity Gained by Infection
TreatmentTreatment
Methicillin : Drug of ChiceMethicillin : Drug of Chice Penicillin : If sensitivePenicillin : If sensitive Vancomycin: If MRSAVancomycin: If MRSA Linazolid : If vancomycin RsistantLinazolid : If vancomycin Rsistant Cephalosporins : First GenerationCephalosporins : First Generation Bacitricin : TopicalBacitricin : Topical Special Special
Situation :Rifampin ,Doxycyclin ,TrimethopriSituation :Rifampin ,Doxycyclin ,Trimethoprime / Sulphamethoxazoleme / Sulphamethoxazole
PreventionPrevention
MRSAMRSA Infection controlInfection control Isolation, Treatment , DecolonizationIsolation, Treatment , Decolonization Contact percussionContact percussion
Vaccine and Toxoid : Not Available yet Vaccine and Toxoid : Not Available yet
Staphylococcus epidermidisStaphylococcus epidermidis
Gram Stain : Gram Positive CocciGram Stain : Gram Positive Cocci AerobicAerobic ExtracellularExtracellular FeaturesFeatures
• Morphology : CocciMorphology : Cocci• Arrangement : Clusters, TetradsArrangement : Clusters, Tetrads• Colonies: White/yellow , rounded on blood agar plateColonies: White/yellow , rounded on blood agar plate
Non motile Non motile No capsuleNo capsule Glycocalyx : ExopolysaccharideGlycocalyx : Exopolysaccharide
Virulence FactorsVirulence Factors
GlycocalyxGlycocalyx ΒΒ- Lactamase- Lactamase Mutant PBPMutant PBP
Exotoxins : NoneExotoxins : None
Laboratory TestsLaboratory Tests
Catalase : +veCatalase : +ve Coagulase: -veCoagulase: -ve DNase: -veDNase: -ve Mannitol: -veMannitol: -ve Hemolysis: NoneHemolysis: None Novobiocin : SusceptibleNovobiocin : Susceptible
Source and TransimissionSource and Transimission
Normal Flora : Skin and Mucous membrane Normal Flora : Skin and Mucous membrane Infections : Trauma and Foreign bodies Infections : Trauma and Foreign bodies
ClinicalClinical
Bacteremia and SepsisBacteremia and Sepsis Subacte EndocarditisSubacte Endocarditis Neonatal BacteremiaNeonatal Bacteremia
Host Defense and ImmunityHost Defense and Immunity
OpsonizationOpsonization PhagocytosisPhagocytosis Cytokines Cytokines
No Immunity Gained by InfectionNo Immunity Gained by Infection
TreatmentTreatment
VancomycinVancomycin Cephalosporins : First generation if SensitiveCephalosporins : First generation if Sensitive
Vaccine and Toxoid : Not Available yet Vaccine and Toxoid : Not Available yet
Staphylococcus saprophyticusStaphylococcus saprophyticus
Gram Stain : Gram Positive CocciGram Stain : Gram Positive Cocci AerobicAerobic ExtracellularExtracellular FeaturesFeatures
• Morphology : CocciMorphology : Cocci• Arrangement : Clusters, TetradsArrangement : Clusters, Tetrads• Colonies: White /yellow , rounded on blood agar plateColonies: White /yellow , rounded on blood agar plate
Non motile Non motile No capsuleNo capsule No Glycocalyx No Glycocalyx
Virulence FactorsVirulence Factors
Multiple Drug ResistantMultiple Drug Resistant Hemagglutinin proteins and Surface ProteinsHemagglutinin proteins and Surface Proteins UreaseUrease
Exotoxins : NoneExotoxins : None
Laboratory TestsLaboratory Tests
Catalase : +veCatalase : +ve Coagulase: -veCoagulase: -ve DNase: -veDNase: -ve Mannitol: -veMannitol: -ve Hemolysis: NoneHemolysis: None Novobiocin : ResistantNovobiocin : Resistant
Source and TransimissionSource and Transimission
Normal Flora : of genitourinary SkinNormal Flora : of genitourinary Skin Poor Hygiene : Sexual ActivityPoor Hygiene : Sexual Activity Urinary Urinary
Tract Tract
ClinicalClinical
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)• Healthy, young, sexual active womenHealthy, young, sexual active women• Cystitis (Lower UTI) or Pyelonephritis (upper Cystitis (Lower UTI) or Pyelonephritis (upper
UTI) UTI) • Pyuria : Most casesPyuria : Most cases
Host Defense and ImmunityHost Defense and Immunity
OpsonizationOpsonization PhagocytosisPhagocytosis Cytokines Cytokines
No Immunity Gained by InfectionNo Immunity Gained by Infection