Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter...
Transcript of Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter...

Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle
Chapter 9
Life Functions Common to Living Things
pp. 178-195
WORKBOOK
Name: _____________________________

1
9.1 – Common Life Functions pp. 180-183
Read pp. 180-181
• All things that are considered living do all of the following things:
1. Transportation moving parts or internal materials 2. Nutrition produce or obtain food 3. Growth & Repair build and repair body parts 4. Reproduction making new cells or organisms 5. Regulation responding to changes 6. Metabolism breath, digest, eliminate waste 7. Synthesis create needed substances
Discuss CYU – p. 183 #1-4

2
Characteristics of Life BLM 8-10
Classify each object listed in the following chart as living or non-living. • Use the seven life processes identified on page 180 of your textbook to help you complete the chart. • Make a checkmark in the table if the life process is present in the object. The first one is done for you. • Answer the questions below.
Object Life Process
transportation nutrition growth/repair reproduction regulation metabolism synthesis
goose wind
flower
deer
rain
bacteria
ice
grass
waterfall
mouse
1. (a) Which objects had checkmarks in all seven columns?
(b) What explanation can you suggest for this? 2. Classify each object listed in the chart as living or non-living.
Living Non-living
3. What conclusions can you draw from doing this exercise?

3
Life Processes BLM 9-2
Match the description in column A with the term in column B. Print the correct letter for the term in the space provided.
Hint: You may use a letter more than once.
Answer Column A Column B
i. changing from baby to adult ii. running iii. remaining inactive for a period of time iv. drinking a milkshake v. changing food into smaller particles vi. moving nutrients to other areas vii. breathing viii. getting rid of waste products ix. producing young x. directing organelles in a cell xi. perspiring when overheated
(a) metabolism (b) nutrition (c) synthesis (d) regulation (e) transportation (f) growth and repair (g) reproduction

4
Plant Parts and Processes BLM 9-1
Plants are living things that exhibit all of the life processes, just as animals do. However, some of the life processes in plants are known by different names than those that are used when referring to animals. You are probably already familiar with many of these names.
What to Do
Test your knowledge of plants and their life processes by filling in the blanks below.
stomata translocation flower
root transpiration chlorophyll
carbon dioxide stem photosynthesis
respiration leaves
1. Nutrition The process by which green plants make food is called ____________________ .
2. Transportation The ______________________ system brings water and nutrients into a plant
from its surrounding environment.
3. Nutrition The gas that plants need for photosynthesis is _______________________ .
4. Metabolism Plant leaves have small openings called _______________________ , through which oxygen is released into the air.
5. Reproduction The _______________________ is the reproductive part of the plant.
6. Transportation The process by which water and nutrients are carried from one part of the plant to
another is called _______________________ .
7. Regulation During the cooling process known as _______________________ , water vapour is released by the plant’s leaves.
8. Growth and repair The plant becomes taller as the _______________________ of the plant
becomes longer.
9. Metabolism Plants “breathe” by taking up oxygen through their roots in a process called
_______________________ .
10. Synthesis _______________________ is the green-coloured material used to transform the energy
of the Sun into food for the plant. 11. Regulation The greatest concentration of chloroplasts in a plant will usually be found in its
_______________________ .

5
K-W-L Chart
Photosynthesis
K W L List what you already know about this topic.
List questions about what you want to know about
the topic.
Using your questions as a guide, write all the
information you learned.

6
K-W-L Chart
Cellular Respiration
K W L List what you already know about this topic.
List questions about what you want to know about
the topic.
Using your questions as a guide, write all the
information you learned.

7
9.2 – Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration pp. 183-185
Read pp. 183-184 • All plants and animals need a continual supply of energy in order to grow and function. • Plants make their own food in the chloroplast by the process of
photosynthesis and stores the energy produced. • Animals obtain their energy from the food they eat. • Food obtained by plants and animals undergoes a chemical change and releases the
stored chemical energy through the process of cellular respiration in the mitochondria.
Read p. 185
carbon dioxide + water + energy glucose + oxygen
TASK: Complete the KWL Charts
Discuss CYU – p. 185 #1-3
Cellular Respiration
⇌
Photosynthesis

8
9.3 – Human Organ Systems pp. 186-190
Read pp. 186-189
The Nervous System: • communication network to regulates life functions
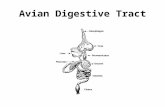
The Digestive System: • Breaks down and digests food into simple chemicals (nutrients) that enter cells. • Body uses these nutrients for energy, growth and repair.
o Nutrients: Carbohydrates, protein, fat, vitamins, minerals, and water • Rids body of solid wastes. • Pathway of food:
esophagus – push food to stomach stomach – muscles contract to mix food, releases acids that activate enzymes to
digest food, this dissolves food to liquid form small intestine – neutralizes stomach acid, absorbs 80-90% of nutrients, releases
digestive juices to digest food. large intestine – absorbs vitamins, minerals and water anus – discharges solid undigested food (feces).
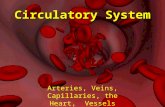
The Circulatory System: • A closed system, no holes or escape for the fluid (blood). • move blood through body to transport food molecules, O2 , CO2 , and wastes
heart – muscle pumps blood through body arteries – vessels bring oxygenated blood from heart to body veins – bring deoxygenated blood back to heart from body capillaries – smallest blood vessels, connecting veins and arteries, where gas
exchange occurs The Digestive and Circulatory Systems work together:
1. Nutrients enter blood from digestive system through capillaries. 2. Circulatory system carries digested food to cells of body. 3. Nutrients travel through all cells in body. 4. Waste molecules pass from cells back to blood through capillaries. 5. Circulatory system disposes of waste and toxins (like salt).
The Urinary System: • Kidney filters blood that has collected wastes from cells, then transports these wastes
to the urinary bladder • Urinary bladder holds wastes until excreted through the urethra
Discuss CYU – p. 190 #1-5

9
The Digestive System BLM 9-10 Study the diagram and label the parts, using the list below. mouth — where food enters body; contains teeth and salivary glands
teeth — chew food into smaller pieces for swallowing
salivary glands — moisten food with enzymes that begin chemical breakdown
esophagus — pushes food to stomach through wave-like muscle spasms
stomach — muscles contract to mix food; releases acids that activate chemicals to digest food; dissolves food into liquid form
small intestine — has chemicals to digest food; neutralizes stomach acid; absorbs 80 to 90 percent of nutrients
large intestine — absorbs vitamins, minerals, and water
gall bladder — stores bile
pancreas — provides most digestive enzymes; produces insulin to extract nutrients from food
rectum — stores solid waste (undigested food)
anus — discharges solid mass of undigested food called feces

10
The Heart BLM 9-12 Your heart is divided into four chambers, which are connected by four valves. Each time the blood moves to a different chamber, the valve behind it closes. This prevents the blood from moving backward, and makes sure the blood travels in only one direction through your circulatory system. When you listen to someone’s heart, the “beat” that you hear is actually the opening and closing of the valves. What to Do Study the diagram and the chart. Use the chart to help you trace the flow of blood through the heart, following the numbered steps on the next page. Note that the oxygenated parts have no shading. You may wish to colour these red. The shading shows deoxygenated parts. You may wish to colour these blue. Note: When you look at the diagram, imagine you are looking at the heart of a person facing you. (Picture someone lying face up beneath the piece of paper.) Therefore, the right side of the heart appears on the left side of the diagram. You can confirm which side is which by placing the back of the sheet of paper against your chest and looking down.
Know Your Heart Parts A superior vena cava carries blood from the upper body to the heart B inferior vena cava carries blood from the lower body to the heart C right atrium receives blood from the body D right ventricle pumps blood to the lungs (through the pulmonary arteries) E pulmonary arteries carry blood away from the heart to the lungs F pulmonary veins carry blood back to the heart from the lungs G left atrium (not visible) receives blood from the lungs H left ventricle pumps blood to the body (through the aorta) I aorta carries blood to the body; other arteries branch from it J valves control the blood flow through the chambers of the heart
• The vena cava vessels are the largest veins in the body. Blood from all other veins is collected
into the superior and inferior vena cava before entering the heart.
• Similarly, the aorta is the largest artery in the body. Smaller arteries branch off from the aorta.

11
Winding Road Through Your Heart BLM 9-12 Start on the RIGHT side of the heart — remember, that’s the left side of the diagram. 1. Deoxygenated blood returns from the body through the largest veins (A and B).
2. The heart relaxes, a valve opens, and blood enters the right atrium (C).
3. The heart contracts, a different valve opens, and blood enters the right ventricle (D).
4. The heart contracts, and the valve leading to the pulmonary arteries opens (E).
5. The right ventricle pushes the blood through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs. TIME OUT from the journey while the deoxygenated blood is off in the lungs getting rid
of waste gases and picking up a fresh supply of oxygen. OK, ready? Now you are on the LEFT side of the heart — the right side of the diagram.
6. Oxygenated blood returns from the lungs through the pulmonary veins (F).
7. The heart relaxes, the valve opens, and blood enters the left atrium (G).
8. The heart contracts, a different valve opens, and blood moves to the left ventricle (H).
9. The heart contracts, and the valve (J) leading to the aorta opens (I).
10. The left ventricle pushes the blood through the aorta to the rest of the body.
• As you know, while out in the body at large, the blood gives away its oxygen and picks up carbon dioxide.
• Before long, it is on its way back to the heart, and you are back at
Step 1 where you started.
9.4 – Keeping an Eye on Life Functions pp. 190-193
Read pp. 190 – 192 Discuss CYU – p. 193 #1-2

12
TASK: Label the following heart pathways diagram.
This image cannot currently be displayed.

13
Body Parts Crossword BLM 9-13
Complete the crossword using the clues provided. Across 1. transports food, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and
wastes to all parts of the body, via blood (2 words)
5. its muscles contract to mix food with acids 6. carries oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the
rest of the body 7. changes food into chemical compounds that the
body uses for energy, growth, and repair (2 words) 9. neutralizes stomach acid; the place where most
nutrients are absorbed into the blood 10. discharges solid mass of undigested food (2 words)
Down 1. an extremely small blood vessel; its walls are one
cell thick 2. located between the mouth and the stomach, it
pushes food along using wave-like muscle spasms 3. the hollow muscle that pumps blood 4. absorbs vitamins, minerals, and water (2 words) 8. returns oxygen-poor blood to the heart from the
rest of the body

Word Search BLM 9-15 Complete the word search puzzle by finding the terms listed below. Circle the words as you find them.
Hint: The words may be hidden in any direction, but will always be in a straight line.
life function specialized photosynthesis cellular respiration glucose
digestive system esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine
anus circulatory system heart artery vein
capillary blood pressure cuff X ray EKG EEG
14

15
Chapter 9 Review Questions
1. List the life functions common to all living things. (9.1) 2. Name four organisms and describe how each adapts to its environment. (9.1) 3. Explain the process of photosynthesis. (9.2) 4. Explain the process of cellular respiration. (9.2) 5. Identify the organs of the digestive system. (9.3) 6. Describe the route of the blood through the circulatory system. (9.3) 7. Explain how the digestive and circulatory systems work together to keep the body
functioning. (9.3) 8. Name three technological devices that you might observe in an emergency clinic. For
each device, list one medical purpose for which it is used. (9.4)

16
Complete Chapter 9 Review Questions – p. 194 #1-9
Please record your answers below or on an attached sheet of loose leaf.