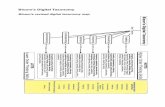
Revised Blooms Taxonomy Designing Aligned Instruction.
-
Upload
esmond-carr -
Category
Documents
-
view
232 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Revised Blooms Taxonomy Designing Aligned Instruction.

Revised Bloom’s
Taxonomy
Designing Aligned Instruction

Teachers Are Expected To:
Work collaboratively to
create a professional
learning community in order to plan instruction
appropriate for students.Voice
Over Somewhere

Teachers Are Expected To:
Understand how students learn and make the
curriculum responsive to
cultural diversity and to individual learning needs.Voice
Over Somewhere

Teachers Are Expected To:
Engage students in the learning process and
understand that instructional plans must be constantly
monitored and modified to
enhance learning.Voice Over S
omewhere

Teachers Are Expected To:
Collaborate with their colleagues and use a variety of data sources for short and long range planning
based on the North Carolina
Standard Course of Study.Voice
Over Somewhere

Importance of Alignment
• Alignment is an even stronger predictor of student achievement on standardized tests than are socioeconomic status, gender, race, and teacher effect.
(Elmore & Rothman, 1999: Mitchell, 1998; Wishnick,1989)

Learning occurs best when there is:
• A purposeful process that aligns what is:– Written– Taught– Tested
• Attention to both:– Content– Cognitive Type

Taxonomies are tools for aligning

Bloom’s is familiar to MOST educators
• Show old model
• Voiceover, “It has its limitations”

…So it was revised

Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy Looks like….
• Rework slides from Lorin Anderson PPT– Replicate PPT slides (update graphics)– Maybe re-voice (or not)
“All instructional objectives have the same basic structureSubject Verb Object”

Dr. Anderson Part I Content

Activity to apply learning“How does what you know best align with this taxonomy?”
• Think about your content area(use his words “the most important thing”)
• Consider the various ways that learners “process” your content
• Consider where & when cognitive process are a part of your content (the “ing” words)
Link to PDF of Cognitive Processes

Think about all who are responsible for student
achievement

• The Department of Public Instruction Deploys STANDARDS
• The District Designs LOCAL CURRICULUM
• The Teachers Design INSTRUCTION
Student Achievement is a
Shared Responsibility

INSTRUCTION• Provides learning experiences, aligned with local
curriculum expectations, to prepare students to meet the standards set by the state
• Instruction includes but is not limited to: – Essential Learning Outcomes– Lesson Timelines– Content Learning Experiences– Opportunities for Practice– Formative Assessment– Corrective instruction where required– Assessment of Student Knowledge and Skills using:
• Teacher Designed Assessments• District Assessments (where available)• DPI Assessment Prototypes (where appropriate)

Learning occurs best when there is:
• A purposeful process that aligns what is:– Written– Taught– Tested
• Attention to both:– Content– Cognitive Type

Content AlignmentThis is about the rows in RBT
“Does the teacher teach and test the topics listed in
the curriculum?”

Cognitive Type Alignment This is about the columns in RBT
“Do the students get to work and think at the level the curriculum prescribes?”

The key to mastery of a standard is the teacher’s clear understanding of the level of cognition required and how to support students in reaching that level.
Teaching for Higher Order Thinking

1. What is it we expect students to learn?2. How will we know when they have learned it?3. How will we respond when they don’t learn it?4. How will we respond when they already know
it?
DuFour Reference
RBT is most helpful here

Verbs: Evaluate
Start with the Nouns and the Verbs
Nouns: Lives• Individuals (past & present)• Families (past & present)
Learner Objective:The learner will evaluate how the lives of
individuals and families of the past are different from what they are today
Pull Sample fro
m
Essentia
l Standards

Determining the Cognitive Expectations
The Knowledge Dimension(nouns)
The Cognitive Process Dimension (verbs)1.
Remember2.
Understand3.
Apply4.
Analyze5.
Evaluate6.
Create
A.Factual X
Individual
B.Conceptual X
Family Life
C.Procedural
D.Meta- Cognitive
The learner will evaluate how the lives of individuals and families of the past are different from what they are today
Pull Sample fro
m
Essentia
l Standards

Describe the life of the mountain girl’s family.
The Knowledge Dimension
The Cognitive Process Dimension1.
Remember2.
Understand3.
Apply4.
Analyze5.
Evaluate6.
Create
A.Factual X
Individual
B.Conceptual X
Family Life
C.Procedural
D.Meta- Cognitive
X
Pull Sample fro
m
Essentia
l Standards

How was the life of the mountain girl’s family different from your
family?The Knowledge Dimension
The Cognitive Process Dimension1.
Remember2.
Understand3.
Apply4.
Analyze5.
Evaluate6.
Create
A.Factual X
Individual
B.Conceptual X
Family Life
C.Procedural
D.Meta- Cognitive
X
Pull Sample fro
m
Essentia
l Standards

Sometimes We Miss the Mark
• If the teaching sequence is designed to support student learning at the knowledge level, but the standard is actually at the analysis level, we have taught to the wrong target.

How might we get closer to the target?What are the distinct cognitive processes for
the category?
The Knowledge Dimension
The Cognitive Process Dimension1.
Remember2.
Understand3.
Apply4.
Analyze5.
Evaluate6.
Create
A.Factual B.Conceptual C.Procedural
D.Meta- Cognitive

Craft a question closer to the target:The learner will evaluate how the lives of individuals and families of the past
are different from what they are today
Evaluating allows one to: assess, choose, decide, judge, justify, prioritize,
rank, rate, select
This is a Kindergarten objective, so how do we say it in terms a five year old can understand?
Pull Sample fro
m
Essentia
l Standards

Student Work Sample
• Where does a Venn Diagram fit on the RBT

Using your example
• Where does it fit • What would you have students do?
– Think, “Cognitive processes and alternate names”
How might we get closer to the target?What are the distinct cognitive processes f or the
category?
The Knowledge Dimension
The Cognitive Process Dimension1.
Remember2.
Understand3.
Apply4.
Analyze5.
Evaluate6.
Create
A.Factual
B.Conceptual
C.Procedural
D.Meta-Cognitive
Provide link to chart, Table 5.1 from Taxonomy for Learning and Teaching

Well Worth Repeating! • Alignment is an even stronger predictor
of student achievement on standardized tests than are socioeconomic status, gender, race, and teacher effect.
(Elmore & Rothman, 1999: Mitchell, 1998; Wishnick,1989)