Reproductive System Male Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 28.
-
Upload
junior-evans -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
0
Transcript of Reproductive System Male Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 28.

Reproductive System
Male Anatomy & Physiology
Chapter 28

Basic Vocabulary• Gametes = sex cells (sperm & eggs), produced by
meiosis• Gonads = reproductive organs that produce gametes
(testes & ovaries) • Fertilization = process during which egg and sperm
unite• Zygote = fertilized egg• Gynecology = branch of medicine concerned with
treatment of female reproductive system• Urology = studies urinary system & disorders of male
reproductive system

Egg1n
Haploidnucleus
Fertilization Results In A Diploid Zygote
Sperm1nHaploid
nucleus

Sperm1n
Fertilization Results In A Diploid Zygote
Egg1n
Haploidnucleus
Haploidnucleus

Sperm1n
Fertilization Results In A Diploid Zygote
Egg1n
Haploidnucleus
Haploidnucleus

Sperm1n
Fertilization Results In A Diploid Zygote
Egg1n
Haploidnucleus
Haploidnucleus

Sperm1n
Fertilization Results In A Diploid Zygote
Egg1n
Haploidnucleus
Haploidnucleus

From Zygote to Embryo
Zygote2n
Zygote
2n

Cleavage
From Zygote to Embryo

Cleavage
From Zygote to Embryo

Cleavage
From Zygote to Embryo

Cleavage
From Zygote to Embryo

Morula
From Zygote to Embryo

• Puberty = process of physical changes by which a child’s body becomes an adult body capable of reproduction
• Puberty is initiated by production of FSH and LH which cause the development of secondary sexual characteristics
Secondary sexual characteristics

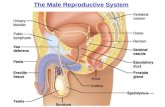
I. MALE ANATOMY• Scrotum = sac containing the testes; sperm develop
in the testes• Normal sperm production requires a temperature
about 2-3 degrees C below body T• Testes develop near kidneys and start descending
during the 7th month of fetal development

• Epididymis = site of sperm maturation• Vas deferens (or ductus deferens) = duct that
transports sperm from the epididymis towards the urethra
• Urethra = transports both semen & urine• Semen = sperm + the fluids secreted by accessory sex
glands

Accessory Sex Glands:• Seminal vesicles = glands that secrete alkaline
fructose rich fluid; used to neutralize acidic environment of male urethra & vagina; fructose is used for ATP production of sperm cells
• Seminal vesicles make 60% of the volume of semen

• Prostate gland = secretes slightly acidic fluid that contributes to sperm motility and viability
• Prostate gland makes up 25% of the volume of semen• Bulbourethral glands (Cowper’s glands) = secrete
an alkaline fluid into the urethra that protects the sperm by neutralizing acids from urethra
Bulbourethral gland




![Male Reproductive Physiology[1]](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/55cf8e9d550346703b93f717/male-reproductive-physiology1.jpg)