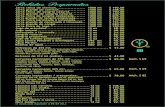
Quiz 5/13/04 Identify the quantities from the units: 1.100 K 2.15kPa 3.790 dm 3 4.22.3 mL 5.2.0 atm...
-
Upload
jason-atkins -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
5
Transcript of Quiz 5/13/04 Identify the quantities from the units: 1.100 K 2.15kPa 3.790 dm 3 4.22.3 mL 5.2.0 atm...

Quiz 5/13/04Quiz 5/13/04Identify the quantities from the units:Identify the quantities from the units:
1.1. 100 K100 K
2.2. 15kPa15kPa
3.3. 790 dm790 dm33
4.4. 22.3 mL22.3 mL
5.5. 2.0 atm2.0 atm
6.6. If If 5.0 ml5.0 ml of a gas at a of a gas at a constant temperature at constant temperature at 1.0 atm1.0 atm, expands to fill , expands to fill 7.5 ml7.5 ml, what is the , what is the new new pressurepressure? Identify V? Identify V11, V, V22, ,
and Pand P11 and P and P2 ( 4 pts)2 ( 4 pts)
1.1. temperaturetemperature
2.2. pressurepressure
3.3. volumevolume
4.4. volumevolume
5.5. PressurePressure
6.6. VV1 1 = 5.0 mL= 5.0 mL
7.7. VV2 2 = 7.5 mL= 7.5 mL
8.8. PP11 = 1 atm = 1 atm
9.9. PP2 2 = ?= ?
-1 = 89 %-2 = 78%-3 = 67%-4 = 56%-5 = 45 %-6 = 34 %-7 = 23%-8 = 12 %-9 = 1% turn in bonus

Chapter 18: GasesChapter 18: GasesChapter Homework:Chapter Homework:
HW 17: Definitions page 471HW 17: Definitions page 471
HW 18: Notes p 451-456; # 1-3 page 456; #30 HW 18: Notes p 451-456; # 1-3 page 456; #30 32, 34 page 32, 34 page 472472
HW 19: Notes page 457-459 #5,6 page 457-460; #26, 36HW 19: Notes page 457-459 #5,6 page 457-460; #26, 3638 38 p 471p 471
HW 20: notes page 460-461 Do #7HW 20: notes page 460-461 Do #713 page 461,213 page 461,2
HW 21: notes p 463; Do #15 page 464; #43HW 21: notes p 463; Do #15 page 464; #4346 page 47346 page 473
HW 22: notes page 464HW 22: notes page 464469 Do #21,22 page 469469 Do #21,22 page 469
HW 23 Do #48,50 page 473HW 23 Do #48,50 page 473
Turn in all Lab write-ups!Turn in all Lab write-ups!

Standard Temperature and Pressure:Standard Temperature and Pressure:STPSTP
Standard Temperature = the freezing point of Standard Temperature = the freezing point of water/ the melting point of water.water/ the melting point of water.
00oo C C 273 K273 K
Standard Pressure Standard Pressure = 1 atmosphere= 1 atmosphere = 101.3 kPa= 101.3 kPa = 760 mm Hg= 760 mm Hg = 760 torr= 760 torr
Molar Volume = 22.4 L = 1 mole of Molar Volume = 22.4 L = 1 mole of any any ideal gas ideal gas AT STPAT STP..

1-3 page 4561-3 page 456If 4.41 L of gas are collected at a pressureof 94.2 kPa, what volume will the same gas occupy at standard atmospheric pressure, assuming the temperatureremains the same? 101.3 kPa
V2 = (4.41 L) (94.2 kPa) (101.3 kPa)
V2 = 4.1 L
If some oxygen gas at 101 kPa and 25oCis allowed to expand from 5.0 L to 10.0 Lwithout changing the temperature, whatpressure will the oxygen gas exert?
P2 = (101 kPa) (5.0 L) (10.0L)
P2 = 50.5 kPa

#3 page 456 #3 page 456 Correct the following Correct the following volumes to standard pressure (101.3 kPa).volumes to standard pressure (101.3 kPa).
PP11 = 98.5 kPa = 98.5 kPa
VV1 1 = 844 cm= 844 cm33
PP2 2 = 101.3 kPa= 101.3 kPa
VV2 2 = ?= ?
PP11 = 59.4 kPa = 59.4 kPa
VV1 1 = 273 cm= 273 cm33
PP2 2 = 101.3 kPa= 101.3 kPa
VV2 2 = ?= ?
PP11 = 90.0 kPa = 90.0 kPa
VV1 1 = 116 m= 116 m33
PP2 2 = 101.3 kPa= 101.3 kPa
VV2 2 = ?= ?
V2 = 821 cm3
V2 = 160 cm3
= 103 m3

#30 Correct the following volumes of gas from the #30 Correct the following volumes of gas from the indicated pressures to standard atmospheric indicated pressures to standard atmospheric
pressure. Assume constant temperature.pressure. Assume constant temperature.
PP11 = 80.8 kPa = 80.8 kPa
VV11 = 817 cm = 817 cm33
PP2 2 = 101.3 kPa= 101.3 kPa
VV2 2 = ?= ?
Answers: No credit given unless you show your work!a. 652 cm3; b. 27.2 m3, 11.8 dm3, 589 cm3, 916 cm3
#31. Make the indicated corrections in the following gasvolumes. Assume constant temperature.
PP11 = 110 kPa = 110 kPa
VV1 1 = 0.600 m= 0.600 m33
PP2 2 = 62.4 kPa= 62.4 kPa
VV2 2 = ?= ?

VocabularyVocabulary
Correct the volume: Correct the volume: figure out the new volume.figure out the new volume. Cylinder: Cylinder: A container the shape of a can of soup.A container the shape of a can of soup. Compressed: Compressed: Smooshed, particles are packed Smooshed, particles are packed
tightly and at high pressure.tightly and at high pressure. Constant: Constant: The beginning and end are the same.The beginning and end are the same. piston: piston: A device used to push a gas or fluid (like in A device used to push a gas or fluid (like in
a car engine, or a syringe.a car engine, or a syringe. vapor pressure: vapor pressure: pressure caused by water pressure caused by water
molecules which have evaporated.molecules which have evaporated.

Boyle’s Law Lab: Page 197 of Lab Boyle’s Law Lab: Page 197 of Lab Book.Book.
Do the lab, follow each instruction one word Do the lab, follow each instruction one word at a time and answer the questions.at a time and answer the questions.

HW 19: Notes page 457-459 #5,6 HW 19: Notes page 457-459 #5,6 page 457-460; #26, 36page 457-460; #26, 3638 p 47138 p 471
Dalton’s Law of Partial Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures:Pressures:
Each gas molecule is Each gas molecule is totally independent of totally independent of other gas molecules, other gas molecules, – to find the total to find the total
pressure, pressure, we just add all the we just add all the
pressures of each pressures of each individual gas.individual gas.
– Water evaporates in air Water evaporates in air to create “vapor to create “vapor pressure”pressure”
boili
ng p
oint
boili
ng p
oint
Water Vapor Pressure Graph

Water Vapor PressureWater Vapor PressureWater vapor pressureincreases as we get closerto the boiling point. Solidsusually have a vapor pressureof approximately zero.
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/kinetic/watvap.html#c1This is a really nice link – for more information about boiling etc. The graphis from this link. Use this link for extra credit – explain how water vapor forms and how that is related to boiling.
http://wine1.sb.fsu.edu/chm1045/notes/Forces/Vapor/Forces05.htmAnother good link for more help understanding boiling.
http
://w
ww
.che
m.p
urdu
e.ed
u/gc
help
/liqu
ids/
vpre
ss.h
tml
link
from
whi
ch m
ovin
g pi
ctur
e w
as ta
ken.