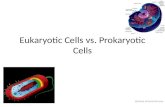
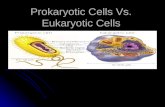
Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic cells. Cells of all living things are incredibly diverse.
-
Upload
suzanna-joleen-chase -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
1
Transcript of Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic cells. Cells of all living things are incredibly diverse.

Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic
cells

Cells of all living things are incredibly
diverse.

Currently, the cells of all living things can be divided into two
major categoriesProkaryotes Eukaryotes

Prokaryotic cells include all types of bacteria. Eukaryotic cells make up all
other organisms like protists, fungi, plants and animals..
Eukaryotic Cell
Prokaryotic Cells

What are the differences?
What are the similarities between
Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes?

Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes (all cells, really) have
several structures in common:
DNA
Ribosomes
PlasmaMembrane
Cytoplasm

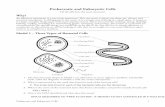
All cells have several structures in common:
1. DNA: nucleic acid, genetic material, instructions for making proteins.
2. Ribosomes: tiny structures that make proteins
3. Plasma membrane (aka cell membrane)
o Cell boundary, regulates what enters and leaves the cell
4. Cytoplasm: All contents inside cell except DNA/nucleus

However, they have many differences:
SizeComplexity
NucleusReproduction

The Theory of Endosymbiosis

Symbiosis is the close relationship between two
different species.
MutualismCommensalismParasitism

Before complex life existed, the bigger cells ate the smaller cells.

Instead of becoming food, the Theory of Endosymbiosis
explains that the smaller cells stayed inside and helped the
larger cells survive.

There are many factors that help to support this theory: Both
plasts have their own DNA and ribosomes

Both reproduce through binary fission (a type of prokaryotic
reproduction)

Both have double membranes; the inner membrane from the original
prokaryote, and the outer membrane from the ancient host cell.