Usha Die Casting Industries (Inds Eqpt Div)., Surat, Ventilation Fans
Project On Ginza Industries Surat
-
Upload
ravi-singh -
Category
Documents
-
view
130 -
download
1
description
Transcript of Project On Ginza Industries Surat

Ginza Industries Ltd.
CH-1- INDUSTRY PROFILE.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 1

Ginza Industries Ltd.
1.1 INTRODUCTION:-
India’s Garment Industry is a well-organized enterprise and is
among the best in the world. It constitutes of designers, manufacturers,
exporters, suppliers, stockiest, and wholesalers. Indian Garment Industry
has carved out a niche in the global markets and earned a reputation for its
durability, quality and beauty. Today’s changing consumer preferences –
buying branded apparel and fashion accessories, major boom in retail
industry, people shopping at department and discount stores, shopping
malls, with rising disposable incomes, government policy focused on fast-
track textile export growth, and ambitious goals have created several
investment opportunities in India.
Government has even made effort to include benefits for Garment
Industry. The annual plan for 2007-08 formulated by Indian government to
promote the textile sector, includes schemes for attracting foreign direct
investments, brand promotion through public-private partnership (PPP) for
global acceptance of Indian brands, trade centres for facilitating business
and image building, fashion hubs as a stable marketplace for Indian
fashion, common compliance code for creating apparel standards for the
benefit of buyers, and training centres for developing human resources.
1.2 HISTORY:-
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 2

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Indian sub continent is the second largest manufacturer of garments
after China being the global leader in garment production. India is known
for its high quality garments for men and most of the garment
manufacturers are in the Small and Medium scale industry. Indian men's
clothing industry has been growing steadily over the past few years, this
has been possible owing to the Indian male becoming more fashion
conscious, and hence there is more consumption which has increased
global demand of men's garments by the rest of the world.
India Garment Industry has an advantage as it produces and exports stylish
garments for men at economical prices due to cheap labour rates. Today because of
technological advancement and use of sophisticated machinery it has enabled the
manufacturers to achieve better quality and well designed garments. India’s
Garment Industry has been rapidly growing in last few years. Exports have been
rising as there is an increase in orders from global buyers accompanied by a rise of
investments in the garment sector of the country. From all over the world the
Retailers are come to India traced by low production costs.
1.3 EVOLUTION:-
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 3

Ginza Industries Ltd.
In southern India’s Tripura town, young girls are lured to work
in the garment industry with a promise of ‘golden opportunity’ to earn
their own dowry at the end of a three-year apprentice period. Garment
industry of Tripura projects a turnover of Rs 10,000 core this year, down
from Rs 11,000 core in 2006-07.
The Indian Garment industry is today modernized via an
exclusive scheme, which has set aside $5bn for investment in
improvisation of machinery. International brands like the Levis, JC Penny,
Wal-Mart, Gap, Marks & Spencer and other industry giants are sourcing
more and more fabrics and garments from India.
According to a study China and India will be major gainers.
Where India could increase their share from present 3% to 8% in US
Garment market.
The garment industry in India faces stiff competition from
countries such as Bangladesh, China and Vietnam. There is a pressure on
the Indian garment industries to produce finished garments at lower costs
to survive the cut-throat competition.
Garment Industry in India is looking at achieving an export
target of $25 billion.
The industry today would need an additional 1.5 million
people.
An investment of Rs. 35000 core in terms of related
infrastructure is required.
1.3 MAJOR GLOBAL PLAYERS:-
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 4

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Carolina Herrera
Oscar de la Rental
Calvin Klein
Donna Karan
Liz Claiborne
Nicole Miller
1.4 MAJOR INDIAN PLAYERS:-
Pantaloon Retail India Ltd
Shopper’s Stop
Tata – Trent
Globus stores Pvt Ltd
Pirmayd Retail Ltd
Arvind Brands Ltd
Provogue India Ltd
The Raymond Group
1.5 CONTRIBUTION IN GDP :-
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 5

Ginza Industries Ltd.
The Indian Garment Industry has an overwhelming presence in the
economic life of the country. Apart from providing one of the basic
necessities of life, the Garment Industry also plays a pivotal role through
its contribution to industrial output, employment generation, and the
export earnings of the country. It contributes about 14 per cent to industrial
production, 4 per cent to the GDP, and 16.63 per cent to the country's
export earnings.
1.6 EMPLOYMENT GIVEN BY INDUSTRY:-
It would provide direct employment to over 35 million people by
2010, which includes a substantial number of people from less privileged
sections of society. The textiles sector is the second largest provider of
employment after agriculture.
In 2006, India’s Garment industry employed 35 million people
including women and backward classes.
1.7 FUTURE TREND:-
The world of clothing is always changing, as new cultural influences
meet technological innovations. Researchers in scientific labs have been
developing prototypes for fabrics that can serve functional purposes well
beyond their traditional roles, for example, clothes that can automatically
adjust their temperature, repel bullets, project images, and generate
electricity.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 6

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Company Profile.
2.1 INTRODUCTION:-
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 7

Ginza Industries Ltd.
The year 1986 marked the inception of GINZA, since then Ginza
have gone to become one of the most sought brand for fashion fabrics,
accessories and now having new focus on developing the same image in
garment field as well.
After nearly two decades of intense and committed efforts, with its
persistent belief in “Quality and innovation is the only guarantee of
customer’s satisfaction” It has various product ranges. Ginza’s all plants
are backed up by 24X7 uninterrupted power supplies. Time to time Ginza
revises its marketing strategies to become a successful player in the
market.
Ginza offers the biggest range of garment fashion accessories in
hundreds of hues and designs. Each line of product from Ginza is an
outcome of "Excellent Craftsmanship and innovation".
Equipped with latest machinery and expert technicians, Ginza has
managed to deliver quality products at competitive rates. It is this policy of
quality and innovation that has helped Ginza in building long term
relationships with best names in the industry as its customers.
Ginza has its own brand name Intense.
Ginza strike deep roots in the domestic branded garment market, and
its flag flies high in some of the most fashion and quality conscious
markets in the world: Europe, USA, Middle East. In each of these markets
Ginza have won the enduring confidence of buyers, leading to repeat
orders time to time.v
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 8

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Ginza has become perhaps the only company in the world, having
all the major activities of Ladies Undergarments in house, looking for a
major share in Indian Ladies Innerwear Exports in next 3 years.
2.2 BOARD OF DIRECTORS:-
Mr. Ashok Sethia Founder, CMD &
Marketing Department
Mr. Manoj Sethia Joint MD
Mr. Arvind Sethia Executive director
Mr. laxmipat banthia Whole time director
Mr. maganmal baid Whole time director
Mr. ajay agrawal Whole time director
2.3 INFRASTRUCTURE:-
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 9

Ginza Industries Ltd.
A state of art plant having machines from JUKI, SUNSTAR,
PEGASUS, and EASTMAN with customized molding, underwire,
lamination, embossing & eye and hook facilities. This unit has a
production capacity of around 1000 dozens per day and is being expanded
to about 2000 dozens before this year end. This unit is compatible to meet
all International Standards & 100% of the production is being exported to
the U.S market at present. This unit is spread over a total area of
approximately 80,000 sq. feet.
2.4 Goals of the Company:-
As Ginza is new in the Garment sector the main objective of Ginza
is to expand its roots in the global market and domestic market as well.
To provide good quality and designer garments to the customers and
exapand its turnover from approx 20 crore to 25-30 crores.
2.4 ACHIEVEMENTS:
Ginza believes that quality is a dynamic and has to be integrated into
each of their processes so that the outcome is perfect. Due to this Ginza
secured ISO 9000 certification in 2008.
Ginza also won the WRAP (Worldwide Responsible Accredited
Production) certification in December, 2009.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 10

Ginza Industries Ltd.
2.5 BANKERS.
Union Bank Of India
State Bank Od India
Bank Of India
The Saraswat Co.Op. Bank Ltd
The Hsbc Ltd
Standard Chartered Bank
Idbi Bank Ltd
Allahbad Bank.
2.6 PLANTS:-
Yarn & tape unit
Warp knitted fabric unit
Torch on lace unit
Garment unit
Value addition unit
Eye & hook unit
Garment unit
Raschel & warp knitted fabric unit
Embroidery unit
Process house
Warehousing facilities
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 11

Ginza Industries Ltd.
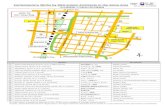
2.5 LOCATION :-
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 12
Head Office: Kimatrai Building, 2nd Floor,
77/79 Maharishi Karve
Road,
Marine Lines, Mumbai: 400
002
Email: [email protected]
Website:
www.ginzalimited.com
Surat
Branch:
Plot No. A-15, 16, 17
Sardar Patel Road No.2,
Udhana, Surat
Plant: Plot No. 61,
Road No. 4,
parel Park,
Sachin, Surat

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Organizational Chart.
Managing director
General Manager.
Human resource finance production marketing
Manager manager manager manager
Assistant manager assistant manager Department
In charge
HR officer Clerk
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 13

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Worker
Purchase sales officer advertisement import & export
officer manager manager
sales manager
Know the company:
An ISO 9001 : 2000 certified company engaged in offering Raschel and Warp Knitted
Fabrics and Laces, Cotton Braided Laces, Woven and Knitted Elastics, Embroidery Laces
and Fabrics, Textured and Twisted Yarns, Eye & Hook, and Women’s Fashion Wear, etc.
Catering to the requirements of garment, textile and home furnishing industries,
we, Ginza Industries Limited are offering distinct kind of Fabric, Garment and allied
products to our customers. Started in the year 1986, we are reckoned as a top
notch manufacturer, exporter and importer of Raschel and Warp Knitted Fabrics and
Laces, Cotton Braided Laces, Woven and Knitted Elastics, Embroidery Laces and
Fabrics, Textured and Twisted Yarns, Eye & Hook, and Women’s Fashion Wear,
etc. Manufactured using the best quality nylon and polyester, our collection is widely
known for its soft texture, smooth finish, colour fastness, exclusive design and several
more salient features. In addition, we also offer value added services On Net and Lace
Fabrics with Prints, Flocking, Embossing, Shading, Pleating Crushing, Paper / Foil
Printing and many more. Moreover, owing to our quality centric approach, innovative
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 14

Ginza Industries Ltd.
product features, we have acquired many clients like Wal Mart, Gel Mart, K-Mart and
others.
“Excellent Craftsmanship and innovation” has always been our motto. Hence, we have
appointed an expert team of craftsmen, creative designers, experienced technicians and
others, who have immense experience in the industry and hold relevant credentials. With
the help of our state-of-the-art machinery and sound production unit, they manufacturer
our range, which is confirmed as per International Quality Norms. Due to our team
support, innovative collection, we have established a strong foothold in the domestic as
well as international markets.
SUCCESS STORY
Ginza straddles the entire spectrum of feminine fashion with a range of fashion fabrics,
accessories and garments. Their success in these areas has led them on to the world of
their wide appeal brand.
Ginza began operations in 1990 in an industrial zone here in Surat, with Raschel and
Wrap Knit. Equipped with state of the art machinery, this plant today has a production
capacity of over 200 million meters per annum. This plant also hosts Ginza’s in-house
design studio. Brimming with creative energy, their young design team has helped Ginza
create fine fabrics that have won the acclaim of the biggest buying houses in Europe and
USA.
Catering to the finer aspects of design and craftsmanship, Ginza specializes in the
production of stretch lace and tricot fabrics across floral, printed and mesh varieties.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 15

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Today, Ginza enjoys the status of being India’s only producer of Jacquardtronic fabric, a
fabric that caters to the distinct needs of the Indian customer.
With the launch of an Embroidery unit at Sachin, Ginza marked its foray into
embellishment and detailing. Modern Swiss and Korean machines helped them to
introduce Schiffli embroidery, delicate sequencing and cording techniques into our
production efforts. The success of this unit helped us broaden our offering to include
motifs, patchwork, sarees, laces, gupier fabrics and collars among others.
Their quest for backward integration led to the establishment of two more specialized
units for the manufacture of elastic tape and yarn, as well as a unit that produces just lace
braiding.
As their products found wide overseas markets, they set up 100% Export oriented units
for the manufacture of wrap knitted fabric, and eyes for brassieres-which brings them to
one of Ginza’s ambitious ventures. A forward integration project for the manufacture of
high quality of ladies’ innerwear. Their inner wears are designed and produced to
international standards at apparel park, Surat, are being sold under major American labels
across stores in the USA since 2006.
This strong endorsement in overseas countries led them homewards to the vast Indian
market. Sold under the brand name of SOIE, this marks their successful entry into the
huge domestic market for branded under garments. The domestic launch of our inner
garment line was made all the easier because of the customer recognition already
established by their outer wear line which had been launched in 2008 under the
INTENSE brand.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 16

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Even as they strike deep roots in the domestic branded garment, their flag flies high in of
the most fashion and quality-conscious markets in the world: Europe, USA, and Middle
East. In each of these markets they have won the enduring confidence of knowledgeable
buyers, leading to repeat orders, time after time.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 17

Ginza Industries Ltd.
MARKETING DEPARTMENT.
ORGANITION OF MARKETING DEPARTMENT:
The marketing manager is responsible for coordinating & controlling of all the
activities of the department with the help of competent executives. A marketing manager
must be skilled in planning organization, coordinating & controlling all marketing
operation.
A marketing organization is like power station sending out energy which is
devoted to selling & distribution on particular lines & there is a tremendous gape between
the power-station & point where it reaches the consumer. Therefore there arises a great
necessity of planning, organizing & controlling all sales efforts through a sound
marketing organization to prevent wastage in distribution.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 18

Ginza Industries Ltd.
MARKETING MANAGER
The head office of the marketing department of GINZA industries is at Mumbai
as it is one of the main business center of India. This company doesn’t face any
marketing problem as it products on order basis. GINZA market is widely.
The organization follows line & staff type of organization system. The main
responsibility of this department is to determine the product to be produced to determine
the selling cost & produces etc…
MARKET SEGMENTATION & CONSUMER BEHAVIOR.
Model marketing is consumer oriented the primary object of marketing is to
satisfy only when the company concentrate on limited number of well define group of
consumer therefore primary task of marketing manager is to define & select target
market.
GINZA industries produce products on the order basis. GINZA has number of
major customers from which customer from which they get order so; its task is to
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 19
Purchase officer Sales officer Import export manger
Sales manager

Ginza Industries Ltd.
increase production with quality maintaining & consumer satisfaction. It has different
types of group of customer which wants different products for the manufacturing.
According to Webster “consumer behavior is all psychological, social & physical
behavior of potential customer as they become aware of evaluate purchase consume &
tell other people about products & service. ”
In GINZA have a fixed consumer which buy product from him. From these
consumers they satisfy than they tell other in favor of its product & GINZA also get a
new customer.
ii) Product Portfolio
The stunning range of fabrics and other products are highly acknowledged for their soft
texture, smooth finish, color fastness, exclusive design and many other traits. We offer an
attractive range that is as follows:
Product Range.
Warp Knitted Fabrics
100% Nylon Warp Knitted Fabrics
Nylon Spandex Stretch Fabrics
100% Polyester Printed Net Fabrics
100% Polyester Warp Knitted Fabrics
Nylon Spandex Power Nets
Raschel Fabrics
100% Nylon Allover Fabrics
Raschel Fabrics With Lurex Raschel Lurex Fabrics with Fall Plate Effects
Nylon/Spandex Fabrics 100% Nylon Raschel Fabrics with Fall Plate Effect
Raschel Jacquardtronic Fabrics
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 20

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Fascination Fabrics
100% Nylon Fascination Fabrics
Nylon/Spandex Fascination Fabrics
Nylon/Polyester Fascination Fabrics
Embroidery Fabrics
100% Cotton Embroidered Fabrics
Gupier Fabrics Embroidered Fabrics with Sequence and Cording effects
100% Nylon Net Embroidered Fabric
Nylon Net/Lurex Embroidery Fabrics
Embroidered Sarees with Sequence Work
Polyester/Cotton Embroidered Fabrics
SE 38
Computerized Talam Fabrics
Talam Strolls Talam 100% Nylon Allovers Talam Nylon/Polyester Allovers
Talam Suit Dupattas Talam Sarees Talam Dupattas
Talam Nylon/Spandex Fabrics
Torchan Lace 100% Polyester Allover Fabrics
Jacquard Fabrics
Jacquard Allover Fabrics Jacquard Furnishing Fabrics
In addition, we also offer following range of products:
Laces:
Nylon/Spandex Raschel Laces
100% Nylon Net Embroidered Laces
Jacquard Laces
Nylon/Lurex Raschel Laces
100% Cotton Embroidered Laces
Torchan Laces
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 21

Ginza Industries Ltd.
100% Nylon Raschel Laces
Gupier Laces
Cotton Crochet Laces
Value Added Fabrics:
Embossed Fabrics
TCF-288 Fabrics
Frilled Fabrics
Laminated Fabrics
Fancy Fabrics
Elastics:
Shoulder Elastic Tape Shoe Elastic
Frill Knitted Elastic
Folding Elastic & Garment Elastic
Knitted Elastic
Jacquard Elastic
Frill Elastic for Bra & Panties
Plain Knitted Elastic
Printed Elastic
Plain Woven Elastic (Basic Tape)
Undergarments:
Designer Bra & Panties
Sport Bra & Panties
Padded Bras
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 22

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Foam Padded Bras
Garments:
Ladies high fashion garments
Kurtis
Designer Tops
Skirts
Ladies Nightwear's
Ladies Beach wear
iii) PACKAGING.
“Packaging is the buyer’s first encounter with the product & is capable of turning the
buyer on or off”.
While packaging the fabrics, the company uses quality-packaging materials like
polythene sheets and others. This assists in ensuring the safely of the end products during
the transits period. Our entire packaging process is conducted under the supervision of
our experienced packaging personnel, Further; the company has association with various
transportation and logistic agents, which helps us in smooth and prompt delivery of the
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 23

Ginza Industries Ltd.
range to the final destinations. This ensures the timely delivery of our consignments to
the clients.
iv) PRICING STRATEGIES
“Pricing is just not a number on a tag or an item. It represents the product in
a very large way.”
Pricing policy of the company usually stable, it does not keep on fluctuating with time
and the price is decided after taking into consideration the price of its competitors.
According to the company the price of the finished product is decided on the basis of
the price of its raw material. Say for example if the demand of petroleum is increased or
decreased then it consequently affects the price of the raw material and also the price at
times depends on the demand of the product also
The price of the company changes, when the yarn market is in boon period the price
tend to be high and vice-versa.
The Ginza Company follows this pricing policy, which is show here.
PRICE=COST+MAGIN+BRAND EQUITY
This Criterion is called forward pricing. However, In Cutthroat Competition, Ginza has
Adopted Backward pricing, I.E. First of all, they determine the Price at which it can be
sold having deducted the required margin from the basis of which it achieves the cost.
Then it strives to reach the determined cost. It assists the company in Effective cost
control in reducing Wastage.
In GINZA industries pricing is fixed with great concentration & care. The
manufacturing cost is the main determinant for fixing price. First of all cost is decided by
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 24

Ginza Industries Ltd.
costing department then board of director decided the price of the product with adding a
profit. In deciding price of product they also consider discounts allowances.
.v) PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE
A company’s positioning and strategy must change as the product, market, and
competitors change over the product life cycle. To say that a product has a life cycle is to
assert four things.
1. Products have a limited life.
2. Product sales pass through distinct stages, each posing different challenges,
opportunities, and problems to the seller.
3. Profits rise and fall at different stages of the product life cycle.
Product requires different marketing, financial, manufacturing, purchasing, and
human recourse strategies in each life- cycle stage.
There are four stages of Product life cycle like:
1. Introduction Stage: the stage where company introduce itself in the market.
2. Growth Stage: In this stage, a product of rapid market acceptance and substantial
profit improvement.
3. Maturity Stage: In this stage, sales growth of product is slowdown, the product
has achieved acceptance by most potential buyers. Profits stabilize or Decline
because of increased competition.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 25

Ginza Industries Ltd.
4. Decline Stage: sales show a downward drift and profit erode.
Right now in Ginza Industries Ltd, their product with code “82004b”
is at it’s maturity stage.
VI) CHANNELS OF DISTRIBUTION AND INTEGRATED MARKETING CHANNELS
CHANNEL DISTRIBUTION:
According to Mc. Mc.Carthy, “any sequence of institution from the products to be
the customer including one or any number of middlemen is called channel distribution”
Channel of distribution may be defined as the set of marketing institutions. The
term channel of distribution is used to denote the middlemen engaged in moving goods
from the place to production to the place of consumption. In the field of marketing
channel of distribution initiate root or pathway through which goods flow producer to
customer.
The most common router used for bringing product in the market from producers
to customer are as under.
Manufacturer consumer
Manufacturer whole seller consumer
Manufacturer retailer consumer
Manufacturer whole seller retailer consumer
Manufacturer agent whole seller consumer
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 26

Ginza Industries Ltd.
GINZA producing on the order basis so, it does not take any help from the
middlemen or any selling or distribution agent. Hare, the product directly supplied to the
customer. Thus the company has a very short channel of distribution.
Marketing channels are independent organization; subsidiaries; and the
companies own sales employees in the market. These make the product available for the
end customers. Selection of the correct marketing channel or channels is a crucial
decision for a company, since the right channels can offer competitive advantage such as
cost effectiveness, and because it is neither easy inexpensive to change channels. Ginza
industries apply B2B marketing so large numbers of buyers are other organizations only.
Types of marketing Activities.
Marketing can be done in different levels depending on how the customers the company
wants to reach. The levels differ in factors like effectiveness, cost and have different
purposes.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 27
GINZA INDUSRIES
CUSTOMER & PARTY

Ginza Industries Ltd.
It includes following activities :
Local Marketing
Refers to marketing programs tailored to find the needs and wants of
Customers in a small and well-defined geographic region.
Individual customer marketing.
It is marketing done on a one to one basis where each individual
Customer‟s requirement are individually addressed”.
Marketing in different levels can be done with different methods. Examples of marketing methods are :
Personal discussions, telephone communication and Email.
Letters, Prospects, Pamphlets and catalogs.
Homepages
Sponsoring
Exhibitions
Direct marketing
Public relations
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 28

Ginza Industries Ltd.
There are four different types of marketing which the methods above can be sorted into.
Direct and personal marketing :
It is selling discussions between the salesman and the customer. It
Can also be service and advice from the selling company, oration and personnel selling.
Direct and impersonal marketing :
It is direct advertising with written information.
Indirect and personal marketing :
It is a link which is handled by actors between the
Manufacturer and customers.
Indirect and impersonal marketing :
It is the media advertising from news papers, articles,
Television and radio.
In Ginza Industries Direct and Personal marketing is done, as they won’t
advertise themselves at any public platform at large. They personally meet
the customer and share the details about the product.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 29

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Different Threats :
Threat of new entrants :
The entry of new competition into a market often leads to price pressure more intensive
competition and reduced profits for the other competitions in the market. The principal
impediments which tend to prevent new competitors attempting to enter the market.
Threats from segment competitions :
Common methods for improving ones position in the market are: Price, competition,
advertising, intensified, introduction of new products, improving customer service and
offering strong product warranties. The intensity of the competition depending on number
of competition; trademark identity; consumer demand variety of available products,
inflexible costs etc.
Threats of substitute products :
There are two ways treat the pressure from compensation products; develop a strategy
that stops for other products and accept the product like a factor on the market. The
threats from compensation products are that it costs to change supplier, the customers
unwilling to change supplier and price performance from the competitor.
At present there are no competitors for Ginza Industries, as they are maintaining the
monopoly in the market. But there are some companies that are going to start up with the
production work in near future that can threat monopoly of the company.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 30

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Different Factors.
Internal Factors :
Every business needs to evaluate its internal strengths and weaknesses. The company
does not need to eliminate all weakness, and a question that should be considered
whether is they should repair its weakness or consider those weaknesses might actually
be converted to advantages.
External Factors :
Opportunities refer to future possibilities in existing and potential new markets. For
examples, the company may create direct marketing opportunities by establishing a
presence on the Internet; do a better job of making information about its products and
services available to customers; introducing new precuts and services; for particular
markets or customers and improving the delivery time for its products and services.
Market Promotion:
In the word of Masson & Ruth. “Promotion consists of those activities that are
designed to bring a company goods & service to the favorable attention of customers”
It’s time gone when the customers were innocent & not so informed of products
availability. They were buying what they offered. However, today’s customer is not like
that, rather they are most intelligent & educated who know everything about the product.
They also have lot of choice.
Sales promotion is a new trend in business units. It covers all marketing activities
like advertising, publicity that stimulates consumer purchasing & dealer effectiveness. In
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 31

Ginza Industries Ltd.
short , sale promotion are bridge or a connecting link covering the gap between
advertising & personal salesmanship.
The main objectives of sale promotion are.
Providing information
Increase in sales
Reducing cost
GINZA industries produce products on order basis. By this way they increase the
quality of product. By increasing in quality or reasonable price they get a new orders
from new customers.
Advertising is nothing but a pair of non personnel presentation of idea, goods of
service by an sponsor. In the present day, advertising has become an inseparable part of
the business. However the form of advertisement may different from business to
business.
GINZA has need for the advertisement. GINZA has advertise their product in
magazine, news pepper, sales promotion, diaries etc…
They spend in advertisement is depended their net profit.
Marketing Research And Activity:
The marketing manager has to take various decisions regarding the different activities of
marketing. The correct decision can be the outcome of the analysis of the punctual data.
In modern marketing system management does not produce what it can the sell but it puts
the goods in the market whatever is desired or required by the consumer. Marketing
research by relevant facts can aid considerably to the executives to raise the level of
performance .
Marketing research may be defined as the application of scientific method to the
solution of marketing problem. Marketing research is any systematic attempt to get
information useful in moving market problems.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 32

Ginza Industries Ltd.
In , GINZA they also follow the marketing research procedure. marketing research
team visit all industry sectors & study the needs & desire. They try to introduce new
facility every time.
Production management.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 33

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Production management:
“ Production management is the deals with the production of goods &
service that people buy and use everyday this production management
function enables the organization management to achieve its good through
efficient acquisitions and utilization of resources like land , labor , capital,
raw material ,machine”
Production is one of the main stages of an enterprise without which a manufacturer can‟t
survive. It converts the raw material into semi-finished goods and then converts into
finished goods.
According to Buffa,” Production management deals with decision making regarding
production of goods & services at the minimum cost according to demand of customers
through the management process of planning, directing, and controlling.”
Production Planning:
Ginza is a company that produced textile products. Before producing product Company
plans a schedule on a yearly base, monthly bases & it goes very deeply by preparing a
weekly schedule.
For preparing this schedule they consider the following points.
The lead of the product.
The preparation time of the product.
The demand of the product in market.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 34

Ginza Industries Ltd.
According to these points they use to plan the schedule and give the order to
produce the product.
Responsibility of the production manager:
The responsibility of the production manager in to the Ginza Company is as follows.
To control the cost of the production.
To motivate workers for maximum efforts.
To fulfill demand of the customer.
To plan production schedule.
To avoid defective goods.
To maintain enough semis finish goods as well as finish goods.
To decide on way of handling and re handling.
Operation management:
“operation management refers to the planning , organizing, directing , and
controlling of input like land, labor etc into desired output to good and service so as
make the goals of the organization in accordance with they overall strategy ”
Production:
“Production means any activities process which adds to the GDP of nation
or economy here economy cover all three sectors namely mfg agriculture and service”
Introduction:
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 35

Ginza Industries Ltd.
“Production is a process of converting input into output” i.e. raw material is converts into
finish good. In relation to physical goods, production means manufacturing an object
using various input like raw material, power, labour. In relation to services, production
means discharge of any function which has got some utility.
Both knitting is a continuous process.
While it is continuous process the production in bulky size.
In dyeing house they have laboratory for checking the raw materials and fabric.
They also use bills of materials
In Ginza industry they produce the seasonal wise production like autumn winter, spring
summer, high summer they using fabric according their requirement or seasonal
production.
Raw Material House.:
It is available in large scale. It’s also near to fabric checking machine so , that the raw material testing can be easily. Our company have many type of fabric like georgette, chiffon, cotton, modal voile, modal satin, santoone, viscose twill, cotton lyena etc. materials are purches bye the company like mandhana cotton mill, arvind mill, wels pun, madhuva coats, vardhman.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 36

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Ring and slide:
Is also available in different size like 15mm, 12mm, 16mm, 8mm..
Eye and hook:
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 37

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Ginza's foray into the global markets demanded the establishment of an exclusive
unit to cater to export needs . this unit came into being as a result.
Our state of the art eye & hook unit , established in October 2007, has a
production capacity significantly.
With the commissioning of this plant the entire manufacturing process for ladies
brassieres is now completed in-house by Ginza.
Set up under the technical supervision of a renowned overseas domain expert, this
unit
provides quality that can be benchmarked to the world's best.
Is also available in different size like 18mm, 30mm and 40mm.
Lace:
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 38

Ginza Industries Ltd.
T ORCHON LACE BRAIDING UNIT
Our Torchon Lace Braiding Unit is located in palghar, on the out skirts of greater
Mumbai.
this facility has 13000 spindles and produces a wide range of Crochot, Torchon, Bobbin-
Laces & Fabrics
with capacity of 15million meters per annum.
This facility is built on area of 35000 sq feet and features top of the line
equipment from Takeda Mayer, Japan and Come.
Threads:
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 39

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Elastic:
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 40

Ginza Industries Ltd.
ELASTIC TAPE AND YARN UNIT
Located in the pictiresque sea-side town of Daman, the elasticape unit of Ginza
meets almost all of our in house requirements. We use state of the art machinery
from global leaders:
Comez, Omm, Britenbach,EPIS, KY, Jakob muller to produce a range of elastc tapeds -
knitted and woven, velvet ribbons and fancy crocheted fabrics. This uint has a production
capacity of 150 million meters per annum.o
Daman is also the location for our yarn unit. conceived as a backward integration
project that would give us enormous cost and quality leverage, this unit is
powered by machines from Barmeg lshikawa and Muratta machines of German &
japan make. This unit produces 3 million kgs. of nylon, polyester, crimped &
filament yarn per annum.
It’s also available in different type and different size and different color
Machine shope
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 41

Ginza Industries Ltd.
In machine shop the semi finished goods are given a finishing touch. In this department
small semi finishing goods like the cutting part of the fabric are given a finishing touch.
In this department used the different type of the machine according their requirement .
Fabric checking:
Cutting department:
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 42

Ginza Industries Ltd.
In this department cutting of raw material is done different size and shape so, as to
available the production unit their requirement of the raw material for the cutting purpose
cutter machine are used. a person is employed for this that cuts the fabric in different and
require shape. In cutting department total worker is 10.
Straight knife machine:
Band knife machine:
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 43

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Heating process:
Under this process the raw materials are heated to give a desire shape.
Band knife machine:
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 44

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Stitching department
In stitching department all worker are stitching the different part of the garment or undergarment. It is the target based for example one worker produce the 40 pcs per day. One worker gives only one operation. In stitching department in garment section total machine is 100 and worker are 78 other machine are extra when any machine is not work that time it using. In undergarment the total machine is 150 and worker are 130 and 20
machine is extra machine.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 45

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Single needle machine:
There are 74 machine .capacity is depends upon the machine, style and
ability of the worker.
Flat lock machine:
There are 2 machine are available.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 46

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Zig zag machine:
There are 2 machines.
Over lock machine:
There are 6 machines.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 47

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Chain stitch machine:
There are 2 machines.
Checking department
Here the all product are checking properly if any product are damage its going in wastage
section. All workers try to minimum waste of the material.
Finishing and packaging:
All products are complete then the finishing the product they using the different type of
machine like kaaj machine, button machine, steam iron mac hine, checking table and
then after finely the product is packing. In finishing department the total worker are 48
and checking table is 2 and worker is 4 who check the final product. Kaaj machine is 2
and stem iron machine is 3.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 48

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Checking table:
Dispatching:
Dispatching is actually authorizing or assigning the work to be done at different work
centers by listing all the job available to a work center in their priority sequence & giving
the due dates for each. It is done by issuing job orders, job cards and material issue to the
foreman. it is implementation of planning.
Function of dispatching:
1. Providing for movement of raw materials from stores to first operation machine &
between all different operation
2.collecting tools from the tools stores & issuing them to the worker or the machine.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 49

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Materials handling:
“Material handling can be defined as storage reservation & controlled movement of
different materials in any from (raw material, finish goods, stores & spares, supplies,
packing, wastage by product) from one place to another place starting from receiving
through storage production packing up to final shipment material handling utilizes proper
scientific method technique & equipment so that time & space utility is created at the
lowest possible cost”
Equipment is use for the material handling:
In Ginza industry use the equipment areas under
Elevators
Trolley
Industrial vehicles
Etc
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 50

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Materials receipt procedure:
Material receipt procedure of all industries will be different. All industries mean different
fields. Procedure of receipt will follow which is as under.
When material will come to the company, the deliveryman will come with invoice and
challan in which quality & quantity of material will have mentioned
The deliveryman will contact to the production manager.
The production manager will sign the challan and gives gate pass to deliveryman.
The supervisor will check the material quality, quantity and weight.
If quality, quantity and weight will have according to order, then it enters in,
If material will be accepted, the delivery challan, excise invoice, bill of material which
includes freight, sales tax, excise tax etc. will be signed by manager.
Material issue procedure:
Procedure of issue will be followed which is as under:
As soon as company that will be department head receives order , the supervisor will be informing to deliver the said order
Supervision will prepare challan in which name of customer, details of package no. weight, quantity etc.is given
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 51

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Plant layout:
Plant layout is the physical arrangement of machine, equipment and other facilities like receiving, shipping tool rooms, maintenance room, inspection, cabin, stators etc.
Type of plant layout
Product layout
“In this type of layout they machine & facility are arranged according the sequcance of production required by a particular product so for each product there will be separate line of machines or equipment”
Product layout
Raw materials
Checking department
Cutting department
Cut-part department
Stitching department
Checking department
Finishing department
Final checking
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 52

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Packing
Finish goods stores
Process layout:
In this layout all the machines or facilities performing similar type of
operation or function are group
Together in the same area or section or department thus all casting are
made at one place or section know as foundry turning is done in a turning
section where all lathe machine are group in one machine welding machine
will be there and drilling section all drilling machine will be there.
Process layout
Selection of fabric
Section of design
Prepare the sample
Garment presentation
Garment selection procedure
Lunching the garment
Promotion activity
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 53

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Oder feeding
Production process
Product Name:
Laces
Net fabric
Raschel fabric
Eye & hook
Elastics
Leggings
Trousers
Jackets
Casual shirt
Dress
Kurti
Tops
Tunics
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 54

Ginza Industries Ltd.
HUMAN RESOURCE DEPARTMENT.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 55

Ginza Industries Ltd.
“HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT is a management function that helps the
manager to recruit, select, train and develop member for an organization. HRM is
concerned with the people dimensions in the organization.”
Organization is not just bricks, motors, machines or inventories. They are people. It is the
people who staff and manage the organization.
“human resource management, in the sense of getting things done through people. It’s an
essential part of every manager’s responsibility, but many organizations find it
advantageous to establish a specialist division to provide an expert service dedicated to
ensure that the human resource function is performed efficiently.”
Human resource management is a management function that helps the managers’ recruit,
select, train and develops members for an organization. HRM is a concerned with the
people dimensions in an organization. It is also concerned with hiring, motivating and
maintaining people in an organization. It focuses on people in organization. A formal
definition of HRM is as follows:
“ HRM is the planning, organising, directing and controling of the procurement,
develpoment, compensation, integration, maintenance and separation of human resources
to the end that individual, organiztional and social objectives are accomplished.”
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 56

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Human resource department
Managing director
General Manager
Assistance manager
Senior executive
Executive officer
Accountant
Assistance
Staff
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 57

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Scope Of HRM.
The scope of HRM is indeed vast. All major activities in the working life of a worker-
from the time of his or her entry into an organization until he or she leaves- come under
the purview of HRM. Specifically, the activities included are:
Nature of HRM
Employee hiring
Prospects of HRM
Industrial relation
Employees maintenance
Employee motivation
Employee and excutive remuneration
Activities Of Personnel Department.
Human resource department is one of the very important part for any unit. Because it
maintains the relationsip between the workers and their owners and also helps it in
maintaining proper atmosphere in the company. The main aim of HRM is to recruit and
select themost eligible peson for a particular job. Once a person is selected then it does
not mean that the job of HRM is done, infect their job starts there itself. After the
selection of the employees for that particular job the human resource managers have to
give the best remuneration to the employees and also have to motivate to his employees
to work harder and also in an efficient way. The most important part of HR department is
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 58

Ginza Industries Ltd.
the maintenance of relationship. The relationship is being primary and the activities
involved in HR department is like recruitment abd selection, human resource planning,
trainning and dvelopment, promotion and transfer, giving performance appraisal,
formation of wages and salary structure, employee welfare schemes, maintenance of
human resource audit, hierarchy structure maintenance, maintaining Absenteesim rate
and employees turnover rate.
Recruitment And Selection.
Recruitment.
In a simple words recruitment can be defined and understood as the process of searching
for and obtaining applicant for the right jobs, from among whom the right people can be
selected.
k. Aswathappa defined recruitment as “it is the process of finding and
attracting capable applicants for employement”
recruitment is a process to disover the sources of man power to meet the requirements of
the staffing schedule and the employ effective measures for attracting that man power in
adequate numbers to facilitate effective selection of an efficient work in force.
Recruitment Of Lower Level Employees.
In this firm there is no formal recruitment process adopted for lower level of employees.
The only source of recruitment for them is on the gate and preseent employees. They tell
their present employees about the requirement and they inform their relatives and then
hire the employees . for some technical people, they inform the contractors and after that
they are responsible for the recruitment of the employees.
Recruitment Of Higher Level Employees.
For recruiting higher level of employees, a formal process is adopted. First of all a
recruitment planning is done. They decide about the number and type of people required.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 59

Ginza Industries Ltd.
They, then look for the sources from where they can get their propable employees. The
most important source of recruitment for the company is campus interview and
advertising. The other sources are personal contacts, employee’s reference, etc. then all
the application screened and qualified applications are selected for further processess.
Selection:
In a simple word selection can be defined and understood as the process of picking
individuals with requisite qualifications and competence to fill job in the organization.
k. Ashwathapa defined selection as “it is the process of differentiating between applicants
in order to identify those greater likelihood of succcess in a job.”
Selection means choosing an eligible candidate from all the applicants.
Selection oF Process In The Company.
After the recruitment had been completed the selection procedure starts. The first step in
recruitment process is interview.
Preliminary Interview. :
An interview is held after having been received the application of the candidates. In
addition to filling up the application blank, the candidate is also supposed to pass through
the color blindness test, color recognition test, remembrance of quality test.
Final Interview.:
The candidate is called for final interview after having passed the various tests. In the
interview, aptitude, intelligence, background and adaptabilityof the job is scrutinized
properly. Successful in the interview are sent for physical examination. A candidate
matched with physical criteria is placed on the job suited to him.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 60

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Educational Criteria For Employees.
For Labours:-
No educational background is required. They should have skills and experience for the
job wages is given in accordance with the daily wage system.
For Temporary Staff Of Supervisory level:-
The candidate should have minimum qualification to suit the requirement of the job.
Generally, science graduates or diploma in engineering field are recruited.
For Permanent Staff Of Managerial Level:-
Engineers possessing textile, mechanical or production degrees are employed to
respective jobs.
Human Resource Planning .
As in the Ginza Industries the nature of workers is very fluctuating and there is number
of job opportunities to the workers so there is very immediate changes in the position of
the workers in the industry so there is no need of maintaining Human Resource Planning.
Training And Development.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 61

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Successful candidates placed on the jobs need trainning to perform their duties
effectively. Every organization needs educated, experienced and trained personnel to
handle the activities. Trainning is a process of learning programmed behaviour. It is an
application of knowledge. It attempts to improve the behaviour of the people on the
current job. It gives people an awareness of the rules and procedure to guide their
behaviour.
“Training is any attempt to improve current or future employee performance by
increasing an employee’s ability to perform through learning.”
It is very necessaryfor the company to train their personnel or workers to perform the
activities. It simply means teaching the employee, the entire skill of performing that
particular job. The company adopts various methods for training their employees.
Ginza Industries selects those employees who have sufficient knowledge and/ or
experience for the position to which they are assigned. Thus they are not required to learn
the basic operation of production, but instead how those operations are carried out in
firm, in its own secular way. Thus the firm does not have to spend precious time and
resources for the training.
If training is required for a particular emploee, the head of the particular department
trains him. He is assigned work which can help him get used to environment. The
contractors handle the training of labourers. The contractors hand them over the
experienced man to tain the labour because it helps in reducing scrap and avoid accidents.
Training Programs.
The HR department organises training progamme for the employee within and outside the
company based on the performance of the individual. The department organizes training
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 62

Ginza Industries Ltd.
to over come the limitations. It organizes seminars at training centres at the learning skill
department.
Objectives:
To increase the productivity and creativity of an individual
To enable the employee to update their knowledge, increase the level of
performance.
To create an environment of “we feeling” and enhance the accountability of the
people.
Bring the desired change in the organizational culture and management processes
through in
Calculation of desired values, beliefs and mindsets in consonance with the
organizational needs.
Base on performance review and organizational studies conceptualize, design and
develop the existing competencies, professional’s skills and learning techniques
for higher level of proficiency and realization of their potential.
In Ginza Industries, training programmers is done throughout the year. Training is
provided for both internal and external employees. It is not only for employees it is also
providing for the fresher and to those who are not in the organization. For providing
training, companies hire faculty from inside as well as outside the organization. The
training should be important for all the employees at all the levels of the organization.
Job Description And Specification.
In job description, it includes about how the job is to be done. In this textile business the
job can easily being learn as the most of the work is done by the machine only the worker
has to learn that how the machine can be operated but, Ginza Industries is using
advanced technology so there are many different machines is there in the firm. Training
is given to the worker that how machine is operated.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 63

Ginza Industries Ltd.
JOB ANALYSIS = JOB DESCRIPTION+JOB SPECIFICATION
Promotion And Transfer.
Promotion:
If the employee benefits the firm with higher and better performance then he is promoted
to a better position in the organization hierarchy e.g. worker may be promoted to the post
of supervisor, which would not only increase his status but also authority and pay scale.
This helps the employees to work harder and perform better in order to get a promotion.
This keeps competition among the employees and in order to achieve their targets.
Transfer:
K. Ashwathapa defines transfer as “a transfer involves a change in the job of an employee
without a change in responsibility or remuneration.”
There are two types of transfers followed by the company:
(1) INTRA:
Under this transfers are done internally among the different businesses run by
Ginza Industries, such as from one unit to another.
(2) INTERNAL:
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 64

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Here, the transfers are done between its plants such as from quality supervisor to
material supervisor, etc.
Reasons Of Transfer.
Requirement:-
The company makes transfers if there is any requirement from one business to
another or one plant to another.
Employee’s Need:-
If the employee approaches, the management for transfer then they are shifted as per
the feasibility.
Performance Appraisal.
Aparty from given training, selection and promotion to the employees, it is required
that he should be evaluated for his performance.it is also described as a merit ranking
in which individual is ranked as better or worse in comparison to others. Performance
appraisal is the part of all other staffing process, like recruitment, selection placement
and induction. It is considered to be the most significanttool for an organization. It is
highly useful in making decisions regarding personal aspects such as promotions.
“Performance appraisal is the systematic evaluation of the individual with respects to
his or her performance on the job and his or her potential for development.”
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 65

Ginza Industries Ltd.
The company does not follow the process of preformance appraisal on a large scale,
but managers do have interactions with the employees regarding their performance in
the given time. These few interactions keep the employees motivated and help them
perform better.The performance of the employees are checked and noted, so that
difficulties are sorted out.
In Ginza Industries, performance appraisal is done yearly. So as to motivate employees and to guide them to put right amount of effort at the right place
Wages And Salary Structure.
Employee compensation is a vital part of human resource management. Wages,
salaries and other form of employee compensation constitute a very large component
of operating costs. One of the biggest factors affecting industrial relation is the salary
or wage the compensation an employee receives for a fair day’s of work. No
organization can expect to attract and retain qualified and motivated employees
unless it pays them a fair compensation. Employee compensation can be classified
into two categories:
1. Basic or primary compensation (basic pay)
2. Supplementary compensation (incentive and variable payment)
Methods of Wage Payment:
There are two types of wage system. They are as follows:
1. Time wage system
2. Piece wage system
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 66

Ginza Industries Ltd.
In Ginza Industries both methods are adopted. For paying the salary of lower level of
worker, time wage system is used. They are paid on daily wage basis according to
their attendence records. The minimum wage is rs 100/day for any worker in the
organization.
For the employees involved in collection of grey and dispatching of final goods to the
party, piece wage system is adopted. Their wage is calculated according to the metres
of grey they collect from the party and again dispatch the final goods.
For higher level of employees fixed salary is given at the end of the month or within
the first week of fore coming month.
It is to be said that for all the employees wages and salary is at the end of the month
only perspective of level or method of wage payment. But the calculation of wages
made on the basis of method of payment adopted.
Employee Relation And Welfare.
Lobour is the basic power to run a business. Without the help and mutual
understanding either of the management and labour cannot perform. In any
production unit, the labourersdo work and the management ensures that the labourers
are provided with the congenial atmosphere to work. It maintains healthy relationship
with its employees and the smployees are also made to understand that they are
working not for themselves but for the family. All the employees are treated like a
family member and the employees also keep aside their personal gains and work for
the betterment of the organization by devoting their mind fully towards the work that
they have been assigned.
The employees have essay access to the management and they are free to draw the
attention of the management towards any of their grievances.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 67

Ginza Industries Ltd.
In spite of all the precautions taken by the management to maintain healthy
relationships with the labourers there are few cases in which labourers arenegatively
motivated by trade union of the industries. These union leaders then approach the
company for settlement, etc.but these sorts of cases are rare.
Ginza Industries had given the welfare policy to the member of origination and their
workers. Welfare policy indicates welfare and gives benefit according to the situation.
It includes the INSURANCE POLICY ,leaving, mediclaim, bonus etc.
Insurance.:-
The company pays the insurance premium of 100000/- per year for whole staff
member.
Leaving:-
The company also permits 12 days leaves in a year to each worker and if the worker
have any difficulty then it will permit the extra leave. Otherwise the company will cut
the salary.
Mediclaim:-
The company takes the whole responsibility of paying medical expenses if the worker
is injured during working hours.
Bonus:-
The company declare bonus on DIWALI and the increment of salary is about 5%. It
declares bonus to the top management a full month salary as a bonus.
Abseentism Rate.
The quantitative data cannot be determined but the rate of absenteeism is very high in
this industry
Because the workers can get an easy job in any other industry and also at a marginal
difference in the salary so they have the power to choose the industry as per their
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 68

Ginza Industries Ltd.
convenience and they are also not abided by any law or contract so they are free to do
the job in any industry they like so we can’t measure any exact rate of absenteeism.
But the rate of supervisors is low as compared to workers.
Employee Turnover.
As in our company “Ginza Industries” these criteria cannot be fulfilled so
it is not included in our project report. This is authenticated by our
manager below.
Finance Department
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 69

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Analysis OF Financial Statement OF Ginza Industry
Ternd Analysis
The trend analysis is a technique of studying several financial statements over a series of
years. In this analysis the trend percentages are calculated for each item by taking the
figure of that item for the base year taken as
100. Generally the first year is taken as a base year. The analyst is able to see the trend of
figures, whether moving upward or downward.
In brief, the procedure for calculating trends is as:
– One year is taken as a base year which is generally is the first year or last year.
– Trend percentages are calculated in relation to base year .
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 70

Ginza Industries Ltd.
TREND PERCENTAGE ANALYSIS OF BALANCE SHEET
2008–2009
2009–2010
2010–2011
2009–
2010
(%)
2010–
2011
(%)Assets:-Current assets
Cash7,696,254
.6314,428,43
5.9623,256,85
1.15187.47
161.19
Debtors214,344,4
14.38257,999,2
05.38316,171,3
98.93120.37
122.55
Stock439,489,5
63444,238,7
25.00454,908,8
77.00101.08
102.4
Other current assets
27,037,576.41
39,412,726.84 −
145.77 −
Loans and
advances
5,946,615.49
9,110,522.79
123,569,898.88
153.20
135.63
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 71

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Total current assets
694,514,423.91
765,189,615.97
917,907,025.96
110.17
119.96
Fixed assets
1,589,068,317.84
1,626,997,281.76
1,827,875,475.94
102.39
112.35
−Depreciation
502,868,542.60
622,509,428.81
729,613,739.02
123.79
117.21
Net block
1,086,199,775.60
1,004,487,852.92
1,098,261,736.02
92.48
109.34
Total assets
1,780,714,199.51
1,769,677,468.92
2,016,168,761.98
99.38
113.93
Liabilities
Current liabilitie
s97,046,49
5.84121,470,9
06.47252,474,1
70.61125.17
207.85
Provisions
22,098,000
22,823,000.00
25,555,000.00
103.28
111.97
Total current
119,144,495.84
144,293,906.47
278,029,170.61
121.11
192.68
Liabilities
Long term
funds:-Equity share
capital88,831,06
088,831,06
0.0088,831,06
0.00100.00
100.00
Securities
premium
60,639,432.22
45,730,822.83
79,399,248.83
75.41
173.62
Reserves
375,151,517.30
418,571,378.96
544,461,975.09
111.57
130.08
Total524,622,0
09.52553,133,2
61.79712,692,2
83.92105.43
128.85
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 72

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Secured loans
1,136,947,694.15
1,064,750,300.66
962,992,414.45
93.64
90.44
Unsecured
loans 0.007,500,000
.0062,454,89
3.00Total
liabilities
1,780,714,199.51
1,769,677,468.92
2,016,168,761.98
99.38
113.93
Interpretation: After examining the above mentioned statement of trend
percentage the following items are made clear:
There is increase in current assets and current liabilities are also
increasing but more than current assets. The trend percent of current
assets was increased by 9.79 % from year 2010 to 2011.
The increase in fixed assets is financed by share capital. The fixed
assets were increased by 9.96 %. Thus the advantage of trading on
equity has been taken.
On increasing fixed assets depreciation also increasing.
Trend Percentage Analysis OF Profit And Loss.
YEAR 2008 - 2009 2009 - 2010 2010 - 20112010(
%)2011(
%)
Sales1,278,592,11
9.691,588,104,99
6.851,907,927,81
8.75124.2
0120.1
4gross profit 245,964,798
336,734,429.63
389,144,347.32 136.9
115.56
operating expenses
114,565,222.51
78,318,926.73
92,298,000.83 68.36
117.56
net operating
131,399,575.49
25,841,550.29
296,846,346.49
19.66 148.71
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 73

Ginza Industries Ltd.
profit(G.P - O.P)
(ADD)other
expenses 4,347,381.85 5,351,118.73 1,699,305.43123.0
9 31.76(MINUS)o
ther expenses
112,053,420.25
142,466,527.59
153,620,816.70
127.14
107.40
NPBT 23,693,537121,300,094.
04145,524,835.
22511.9
5119.9
7(MINUS)t
ax 1,125,000.00 1,725,000.00 7,383,122.00153.3
3428.0
1
NPAT22,568,537.0
9119,575,094.
04138,141,713.
22529.8
3115.5
2
Interpretation:
In this year there is increase in sales as well as profit.
The figure of 2005 when compared with 2004 reveals that the sales have come
down by 4.6 %. However, the gross profit has come down by 21.34 %.
The operating expenses was increased therefore net operating profit was also
increased.
Common Size Financial Statement .
Differences in firm size may confound cross sectional and time series analyses.
To overcome this problem, common size statements are used.
A common size balance sheet expresses each item on the balance sheet as a
percentage of total assets.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 74

Ginza Industries Ltd.
A common size income statement expresses each income statement category as a
percentage of total sales revenues
YEAR2008 - 2009
2008-
2009(%)
2009 - 2010
2009 -
2010(%)
2010 - 2011
2010 -
2011(%)
Sales1,278,592,
119.69 1001,588,104,
996.85 1001,907,927,
818.75 100
gross profit
245,964,798 19.23
336,734,429.63 21.2
389,144,347.32 20.39
operating expenses
114,565,222.51 8.96
78,318,926.73 4.93
92,298,000.83 4.83
net operating
profit131,399,57
5. 49 10.2725,841,550
.29 0.01296,846,34
6.49 15.55
(G.P - O.P)
(ADD)other
expenses4,347,381.
85 0.345,351,118.
73 0.331,699,305.
43 0.08
(MINUS)other
expenses112,053,42
0.25 8.76142,466,52
7.59 8.97153,620,81
6.70 8.05
NPBT 23,693,537 1.85121,300,09
4.04 7.63145,524,83
5.22 7.62
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 75

Ginza Industries Ltd.
(MINUS)tax
1,125,000.00 0.08
1,725,000.00 0.1
7,383,122.00 0.38
NPAT22,568,537
.09 1.76119,575,09
4.04 7.52138,141,71
3.22 7.24
Interpretation:
–The sale and gross profit have increased in comparative figures in
2009-2010 as compared to 2008-2009. But the percentage of gross
profit to sales has gone down in 2010-2011.
Operating expenses have gone down by 4.03% from 2008-2009 to 2009-
2010 and it almost remained same in 2010-2011 in percentage.
Net profit have increased from 2008-2009 to 2009-2010 by 5.67 % and
almost remained same in 2010-2011 in percentage.
COMMON SIZE STATEMENT OF BALANCE SHEET
2009 % 2010 % 2011 %
Assets:-Current assets
Cash7,696,254.6
30.43
14,428,435.96
0.81
23,256,851.15
1.15
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 76

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Debtors214,344,41
4.3812.04
257,999,205.38
14.57
316,171,398.93
15.68
Stock439,489,56
324.68
444,238,725.00
25.1
454,908,877.00
22.56
Other current assets
27,037,576.41
1.52
39,412,726.84
2.22 − −
Loans and
advances5,946,615.4
90.33
9,110,522.79
0.51
123,569,898.88
6.12
Total current assets
694,514,423.91 39
765,189,615.97
43.27
917,907,025.96
45.52
Fixed assets
1,589,068,317.84
89.24
1,626,997,281.76
91.93
1,827,875,475.94
90.66
−Depreciation
502,868,542.60
28.24
622,509,428.81
35.17
729,613,739.02
36.18
Net block1,086,199,7
75.6060.99
1,004,487,852.92
56.76
1,098,261,736.02
54.47
Total assets
1,780,714,199.51 100
1,769,677,468.92 100
2,016,168,761.98 100
Liabilities
Current liabilities
97,046,495.84
5.45
121,470,906.47
6.86
252,474,170.61
12.52
Provisions 22,098,000
1.24
22,823,000.00
1.28
25,555,000.00
1.26
Total current
liabilities119,144,49
5.846.69
144,293,906.47
8.15
278,029,170.61
13.78
Long term
funds:-Equity share
capital 88,831,060 3.488,831,060.
005.01
88,831,060.00 4.4
Securities Premium
60,639,432.22
4.99
45,730,822.83
2.58
79,399,248.83
3.93
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 77

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Reserves375,151,51
7.3021.06
418,571,378.96
23.65
544,461,975.09 27
Total524,622,00
9.5229.46
553,133,261.79
31.25
712,692,283.92
35.34
Secured loans
1,136,947,694.15
63.85
1,064,750,300.66
60.16
962,992,414.45
47.76
Unsecured loans 0.00 0
7,500,000.00
0.42
62,454,893.00
3.09
Total liabilities
1,780,714,199.51 100
1,769,677,468.92 100
2,016,168,761.98 100
Interpretation:
The company is not suffering from shortage of working capital. The
Percentage of current liabilities is less than the percentage of current assets.
A close look at the balance sheet shows that investments in fixed asset have been
increasing.
Share cap i ta l f igure remained cons tan t however the i r %age to
ne t wor th has increased from 3.4 % to 4.4 %. Some amount of the
secured loans has been paid off. Reserves of company was increased came
21.06 % to 27 % from the year 2009 to 2011.
Receivable management
MONITORING RECEIVABLES :
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 78

Ginza Industries Ltd.
a. Efficient billing system:
Billing is necessary. Billing represents a fundamental component of healthy customer
relations; it serves as a reminder to the customer of his or her responsibility and
obligation. Here India Motor Parts & Accessories Limited mailing invoices on a timely
basis promotes quicker payment. According to the company, Customers should be billed
at least once a month for their purchases. Bimonthly billing encourages even faster
payment. A detailed billing statement presented in a simple format provides the customer
with key information that can be easily understood. Include the following, if applicable,
on a billing statement: product purchased, quantity, color, description, date order
received, date order completed, billing date, billing rate, time spent on the job, job
specifications, prior balance, prior payments and amount due. An enclosed envelope is
customer friendly and prompts return payment.
b. Aging of receivables method:
The aging of accounts receivable directs management's attention to accounts that are
slow to pay. It is also useful in determining the balance amount needed in the account
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts.
The aging of accounts receivable report is typically generated by sorting unpaid sales
invoices in the subsidiary ledger—first by customer and then by the date of the sales
invoices. If a company sells merchandise (or provides services) and allows customers to
pay 60 days later, this report will indicate how much of its accounts receivable is past
due.
c. Objectives of maintaining receivables:
The main objectives of credit sales and maintaining receivables are as under:
1. To increase the sales: It is quite natural that the policy of credit sales attracts
more customers for purchasing. Those who do not have money at present for
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 79

Ginza Industries Ltd.
purchasing are also induced to purchase with the expectation of making payment
from its sales proceeds. In short, credit sales increases sales volume.
2. Competition: In order to survive in competition every enterprise has to adopt
the strategy of following the footsteps of competitors. If a company ignoring the
liberal credit policy of competitors insists on cash sales, it cannot survive long.
3. Increase in profit: The ultimate aim of credit sales is to increase profit by
increasing sales volume through proper credit policy. Profit can be optimized by
adopting optimum credit policy. Here credit sales are accepted as a marketing tool
to boost up sales and profit.
d. Terms of payments:
1. Cash terms : It means the condition of making payment against delivery of
goods or payment of price in advance. Generally cash payment is insisted upon
when the goods are to be manufactured as per order the doubtful credit worthiness
of particular customers also inspires the company for cash terms.
2. Open credit policy: It is also known as open account policy. In open credit
policy seller and the buyer come to agreement about credit period, cash discount,
period of cash discount, etc. According to these agreement goods is sold to the
buyer in required quantity as and when needed by the customers. Both parties are
expected to abide by the credit term.
3. Consignment : In some cases goods is sold through del credor. The owner of
the goods sends it to the del credor as consignment. The del credor does not
receives the ownership rights. When it is sold he pays a price after deducting his
commission. Unsold goods are returned to its real owner.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 80

Ginza Industries Ltd.
4. Bills of exchange : In this method the seller sells the goods, prepares bill of
exchange, the buyer accepts it and sends it back to the seller. For the seller it is
bills receivable and for the buyer it is bill payable.
The use of bill of exchange has the following three advantages:
A documentary proof of the debt of the buyer is created.
Cost of credit is reduced to some extent.
Negotiable instruments come into existence.
5. Letter of credit : In case of import from foreign country the exporter insists on
letter of credit issued by the banker of importer. Letter of credit is certificate
regarding the credit standing of the importer issued by its banker on the basis of
the certificate the exporter dispatches the goods to the importer. Documents of
title to goods are sent to the bank.
6.
Valuation and Pricing Of Stock.
The Company use FiFo (First In First Out) method for stock Valuation since the
company started and the company follows it regularly without changing the
method to LIFO. Company uses this method because of the products which the
company deals like fabrics
Introduction To Working Capital.
Working capital management is concerned with the problems arise in
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 81

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Attempting to manage the current assets, the current liabilities and the inter relationship
that exist between them. The term current assets refers to those
Assets which in ordinary course of business can be, or, will be, turned in to cash within
one year without undergoing a diminution in value and without disrupting the operation
of the firm. The major current assets are cash,
Marketable securities account receivable and inventory. Current liabilities ware those
liabilities which intended at there inception to be paid in ordinary course of business,
within a year, out of the current assets or earnings of the concern. The basic current
liabilities are account payable, bill payable, bank over-draft, and outstanding expenses.
The goal of working capital management is to manage the firm’s current assets and
current liabilities in such way that the satisfactory level of working capital is mentioned.
The current should be large enough to cover its current liabilities. in order to ensure a
reasonable margin of the safety.
Definition:-
1. According to Guttmann & Douglas-
“Excess of current assets over current liabilities”
2. According to Park & Glad son -
“The excess of current assets of a business (i.e. cash, accounts
Receivables, inventories) over current items owned to employees and others
(Such as salaries & wages payable, accounts payable, taxes owned to
Government)”
Need Of Working Capital Management.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 82

Ginza Industries Ltd.
The need for working capital gross or current assets cannot be over emphasized.
As already observed, the objective of financial decision making is to maximize the
shareholders wealth. To achieve this, it is necessary to generate sufficient
Profits can be earned will naturally depend upon the magnitude of the sales
Among other things but sales cannot convert into cash. There is a need for
Working capital in the form of current assets to deal with the problem arising
Out of lack of immediate realization of cash against goods sold. Therefore
Sufficient working capital is necessary to sustain sales activity.
Then the company has to spend some amount for labor and factory overhead to convert
the raw material in work in progress, and ultimately finished goods. These finished goods
convert in to sales on credit basis in the form of sundry debtors. Sundry debtors are
converting into cash after expiry of credit period. Thus some amount of cash is blocked in
raw materials, WIP, finished goods, and sundry debtors and day to day cash
requirements. However some part of current assets may be financed by the current
liabilities also. The amount required to be invested in this current assets is always higher
than the funds available from current liabilities. This is the precise reason why the needs
for working capital arise
Gross working capital and Net working capital
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 83

Ginza Industries Ltd.
There are two concepts of working capital management
1. Gross working capital
Gross working capital refers to the firm’s investment I current assets. Current assets are
the assets which can be convert in to cash within year includes cash, short term securities,
debtors, bills receivable and inventory.
2. Net working capital
Net working capital refers to the difference between current assets and current liabilities.
Current liabilities are those claims of outsiders which are expected to mature for payment
within an accounting year and include creditors, bills payable and outstanding expenses.
Net working capital can be positive or
Type of working capital
The operating cycle creates the need for current assets (working capital).
However the need does not come to an end after the cycle is completed to
Explain this continuing need of current assets a destination should be drawn Between
permanent and temporary working capital.
1) Permanent working capital
The need for current assets arises, as already observed, because of the cash Cycle. To
carry on business certain minimum level of working capital is
Necessary on continues and uninterrupted basis. For all practical purpose, this
Requirement will have to be met permanent as with other fixed assets. This
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 84

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Requirement refers to as permanent or fixed working capital
2) Temporary working capital
Any amount over and above the permanent level of working capital is Temporary,
fluctuating or variable, working capital. This portion of the required working capital is
needed to meet fluctuation in demand consequent upon changes in production and sales
as result of seasonal changes
(A)ESTIMATION OFCURRENT ASSETS:
2008-2009 2009-2010 2010-2011
(a)Cash and bank balance 7,696,254.63 14,428,435.96 23,256,851.15
(b)Inventories 439,489,563.00
444,238,725.00 454,908,877.00
(c)Sundry debtors 214,344,414.38
257,999,205.35 316,171,398.93
(d)Other current assets 27,037,576.41 39,412,726.84 _
(e)Loans and advances 5,946,615.49 9,110,522.79 123,569,898.88
Total current assets 694,514,423.91
765,189,615.97 917,907,025.96
(B)ESTIMATION OF CURRENT LIABILITIES:
_ _ _
(a)Current liabilities 97,046,495.84 121,470,906.47 252,474,170.61
(b)Provisions 22,098,000.00 22,823,000.00 25,555,000.00
Total current liabilities 119,144,495.84
144,293,906.47 278,029,170.61
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 85

Ginza Industries Ltd.
NET WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT(A-B)
575,369,928.07
6,208,95709.5 639,877,855.35
RATIO ANALYSIS
RATIO ANALYSIS-OVERVIEW
Ratios:
1. Provide a method of standardization
2. More important - provide a profile of firm’s economic characteristics and Competitive
strategies.
• Although extremely valuable as analytical tools, financial ratios also have Limitations.
They can serve as screening devices, indicate areas of
Potential strength or weakness, and reveal matters that need further Investigation.
• Should be used in combinations with other elements of financial Analysis.
• There is no one definitive set of key ratios; there is no uniform definition
For all ratios; and there is no standard that should be met for each ratio.
• There are no "rules of thumb" that apply to the interpretation of financial Ratios.
The main object of all the business concerns is to earn profit. Profit is the measurement of
the efficiency of the business. Equity shareholders of the company are mainly interested
in the profit ability of the company. Profitability ratios include the following:
1. Gross profit ratio.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 86

Ginza Industries Ltd.
2. Net profit ratio.
3. Operating ratio.
4. Expense ratio.
1. Gross profit ratio:
It is a ratio expressing relationship between gross profits earned to net sales.
Gross Profit
Gross Profit Ratio = ------------------- * 100
Net Sales
YEAR Gross profit ratio = Gross profit/ Net sales × 100
%
2009 245,964,798.80 ÷ 1,278,592,119.69 × 100 19.23
2010 336,734,429.63 ÷ 1,588,104,996.85 × 100 21.20
2011 389,144,347.32 ÷ 1,907,927,818.75 × 100 20.39
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 87

Ginza Industries Ltd.
2009 2010 201118
18.5
19
19.5
20
20.5
21
21.5
percentage
percentage
Interpretation: here we can see that the gross profit ratio in 2010 increased by 1.97%.
It shows the efficiency of the firm but in 2011 the gross profit ratio is decreased by 0.81%
so we can conclude that in this year the company lost its ability of controlling the cost of
its inventory and manufacturing products.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 88

Ginza Industries Ltd.
1. Net profit ratio:
The ratio is valuable for the purpose of ascertaining the overall profitability if business and shows the operating efficiency of the business.
Net Profit
Net Profit Ratio = ------------------- * 100
Net Sales
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 89

Ginza Industries Ltd.
200939%
20108%
201153%
Interpretation : In the year 2009, a company is having net loss a 5.69 % that means
company is unable to pay all the expenses of the firm but in the next year increasing trend
of net profit shows that it is able to pay all the expenses of the firm including taxes,
interest and depreciation.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 90
YEAR Net profit ratio = Net profit/ Net sales × 100 %
2009 (72,795,251.75) ÷ 1,278,592,119.69 × 100 (5.69)
2010 17,907,724.38 ÷ 1,588,104,996.85 × 100 1.13
2011 146,521,559.86 ÷ 1,907,927,818.75 × 100 7.68

Ginza Industries Ltd.
3. Operating ratio:
It is a ratio showing relationship between cost of goods sold plus operating expenses and
net sales. It shows the overall efficiency of the firm.
cost of good sold + Operating Expenses
Operating Ratio = ---------------------------------------------------- * 100
sales revenue
YEAR Operating ratio = COGS + Operating Expenses / Net sales × 100
%
2009 [{1,032,627,320.89 + 226,618,642.76} ÷ 1,278,592,119.69] × 100
98.48
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 91

Ginza Industries Ltd.
2010 [{1,251,370,567.22 + 188,074,685.52} ÷ 1,588,104,996] × 100
90.63
2009 201086
88
90
92
94
96
98
100
percentage
percentage
Interpretation: The operating ratio is decrease by 7.85 %. It shows that a company has
good overall operating efficiency incorporating all the expenses of ordinary daily
business activity so it is more profitable.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 92

Ginza Industries Ltd.
5. Expense ratio:
a. Administrative Expense Ratio
For the purpose of ascertaining relationship between operating expense and net
sales, expense ratio are computed.
YEAR Administrative Expense Ratio = Administrative Expenses / Net Sales × 100
%
2008 33,542,824.32 ÷ 1,097,348,091.96 × 100 3.06
2009 80,495,996.48 ÷ 1,278,592,119.69 × 100 62.95
2010 51,053,332.30 ÷ 1,588,104,996.85 × 100 3.21
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 93

Ginza Industries Ltd.
2008 2009 20100
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
percentage
percentage
b.Selling Expense Ratio.
YEAR Selling Expense Ratio = Selling Expenses / Net Sales × 100
%
2008 18,399,924.71 ÷ 1,097,348,091.96 × 100 1.67
2009 34,069,226.03 ÷ 1,278,592,119.69 × 100 2.65
2010 27,285,594.43 ÷ 1,588,104,996.85 × 100 1.71
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 94

Ginza Industries Ltd.
2008 2009 20100
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
percentage
percentage
c.Financial Expense Ratio .
YEAR Financial Expense Ratio = Financial Expenses / Net Sales × 100
%
2008 82,356,448.66 ÷ 1,097,348,096 × 100 7.50
2009 92,329,279.70 ÷ 1,278,592,119.69 × 100 7.22
2010 109,755,758.79 ÷ 1,588,104,996.85 × 100 6.91
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 95

Ginza Industries Ltd.
2011 92,298,000 ÷ 1,907,927,818.75 ×100 4.8
2008 2009 2010 20110
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
percentage
percentage
(B) Liquidity ratio:
1. Current ratio:
Creditors extending credit to its customer or making a short-term bank
loan are interested in more than a company’s leverage. They want to know
whether the customer will be able to lay its hand on the cash to repay.
The current ratio is a financial ratio that measures whether or not a firm has enough
resources to pay its debts over the next 12 months.
It is important to note that a very high ratio of current assets to current liabilities may be
indicative of slack management practices, as it might signal excessive inventories for the
current requirement & poor credit management in terms of overextended accounts
receivable. At the same time, the firm may not be making full use of its current
borrowing capacity.Although there is no hard & fast rule, conventionally, a current ratio
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 96

Ginza Industries Ltd.
of 2:1 isconsidered satisfactory. The logical underlying the conventional rule is that even
with a drop – out of 50% in the value of current assets, a firm can meet its obligations.
current assets
Current Ratio = --------------------------
curent liabilities
YEAR Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
2009 694,514,423.91 / 119,144,495.84 5.83
2010 765,189,615.97 / 144,293,906.47 5.30
2011 917,907,025.96 / 278,029,170.61 3.30
2009 2010 20110
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
percentage
percentage
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 97

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Interpretation: Current ratio indicates the working capital position. The
satisfactory ratio is 2:1 but company is showing good working capital position as
their current ratio in 2009 and 2010 approx. 5:1. In 2011 the ratio is 3.30:1
showing less ratio then previous 2 years company should take corrective action to
increase it.
2. Liquid ratio:
A variant of current ratio is the liquid ratio or quick ratio which is designed to
show the amount of cash available to meet the immediate payments. It indicates
the liquidity position of the firm
Liquidity Assets
Liquidity Ratio = ------------------------
Liquid Liabilities
YEAR Liquid Ratio = Liquid Assets / Liquid Liabilities %
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 98

Ginza Industries Ltd.
2009 255,024,860.91 / 119,144,495.84 2.14
2010 320950890.97 / 144,293,906.47 2.22
2011 462,998,148.96 / 278,029,170.61 1.67
2009 2010 20110
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
percentage
percentage
Interpretation: The satisfactory ratio is 1:1. According to this we can conclude
that GINZA industry is having very good liquidity position.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 99

Ginza Industries Ltd.
(1) Proprietary ratio:
This ratio shows the relationship between shareholder’s fund and total assets. The
result clearly shows the share of owners in the total assets of the company. When
the proprietary ratio is substracted from one, the resultant figure represents the
share of outsider’s claim on the assets of the company.
shareholder fund
Propritory Ratio = --------------------------
total assets
YEAR Proprietary Ratio = Proprietors Funds / Total Real Assets %
2009 463,982,577.30 ÷ 1,780,714,199.51 × 100 26.05
2010 507,402,438.96 ÷ 1769677468.92 × 100 28.67
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 100

Ginza Industries Ltd.
2011 633,293,035.09 ÷ 2,016,168,161.98 × 100 31.41
2009 2010 20110
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
percentage
percentage
Interpretation: The increasing rate of proprietary ratio shows that the financial
position of the GINZA industry is stronger, as it signifies that the proprietors have
provided larger funds to purchase the assets.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 101

Ginza Industries Ltd.
( 2) Debt-Equity ratios:
This ratio shows the proportion of external and internal equities i.e. proportion of
funds provides by long term creditors and that provided by share holders.
YEAR Debt-Equity Ratio = Long term Liabilities / Owners funds × 100 %
2009 ₋ ₋
2010 7,500,000 ÷ 507,402,438.96 × 100 1.48
2011 62,454,893 ÷ 633,293,035.09 × 100 9.86
2010 20110
2
4
6
8
10
12
percentage -
percentage -
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 102

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Interpretation: An increasing ratio indicates that outside creditors have a larger claim
than the owners of the business.
(2) Long term funds to fixed assets ratio :
Normally, the fixed assets f business must be purchased out of fixed capital
only, which includes share capital, reserves and long term liabilities. This
ratio, therefore, shows the relationship between fixed capital and fixed assets
the ratio must be 1:1 or more i.e. the fixed capital must be more than fixed
assets or must at least be equal to fixed assets.
YEAR Long term funds To Fixed Assets = Long Term funds / Fixed Assets × 100
%
2009 1,136,947,694.15 ÷ 1,589,068,317.84 × 100 71.50
2010 1,072,250,300.66 ÷ 1,626,997,281.76 × 100 65.90
2011 1,025,447,307.45 ÷ 1,827,875,475.94 × 100 56.10
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 103

Ginza Industries Ltd.
2009 2010 20110
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
percentage
percentage
Interpretation: A decreasing rate shows that fixed capital is also decreasing in
comparison to fixed assets. The reason behind this decrease rate is that company is using
short term forms in purchasing assets.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 104

Ginza Industries Ltd.
(4) Return on capital employed:
It is the index of the profitability if the business and its obtained by comparing net profit
with capital employed. The term employed includes share capital, reserves and long term
loans.
YEAR
Return On capital Employed = Net Profit(Before Interest and Tax) / Capital Employed × 100
%
2009 43,417,728.50 ÷ 463,982,577.30 × 100 9.36
2010 142,578,418.17 ÷ 507,402,438.96 × 100 28.09
2011 269,239,714.38 ÷ 633,293,035.09 × 100 42.51
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 105

Ginza Industries Ltd.
2009 2010 20110
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
percentage
percentage
(5)Return on shareholders’:
It shows what percent of profit is earned on the capital invested by ordinary shareholders.
This ratio is an indicator of the earning capicity of the capital employed in the
business. This ratio reflects the overall efficiency with which capital is used.
Return on Shareholders’ Funds = Net Profit / Shareholders’ Funds × 100
YEAR
Return On Shareholders’ Funds = Net Profit / Shareholders’ Funds × 100
%
2009 727,952,51.75 ÷ 463,982,577.30 × 100 15.68
2010 17,907,724.38 ÷ 507,402,438.96 × 100 3.52
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 106

Ginza Industries Ltd.
2011 146,521,559.86 ÷ 633,293,035.09 × 100 23.13
2009 2010 20110
5
10
15
20
25
15.68
3.52
23.13percentage
percentage
Interpretation: The profitability decreased from 2009 to 2010 by 11.56 % but in 2011 the
shareholders got more return in comparison to 2009.
(C) Activity (turnover):
Activity Ratio:-
These ratios are calculated on the basis of ‘cost of sales’ or ‘sales’, therefore, these ratios
are also called as ’Turnover Ratio’. These ratios indicate how efficiently the capital is
being used to obtain sales; how efficiently the fixed assets are being used to obtain sales;
and how efficiently the working capital and stock is being used to obtain sales.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 107

Ginza Industries Ltd.
(1) Inventory turnover ratio:
Inventory turnover ratio indicates the efficiency of the firm in producing and
Selling its products. It is calculated by dividing the cost of goods sold by average
Inventory:
The average inventory is the average of opening and closing balance of
Inventory in a manufacturing company like Ginza inventory of finished goods is
Used to calculate inventory turnover ratio.
Cost of goods sold
Stock Turnover Ratio = --------------------------
average inventory
YEAR Stock Turnover Ratio = Cost Of Goods Sold / Average Stock %
2009 245,964,798.80 ÷ 328,172,722.50 ×100 0.75
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 108

Ginza Industries Ltd.
2010 336,734,429.63 ÷ 344,971,204 × 100 0.98
2011 389,144,347.32 ÷ 322,260,351 × 100 1.20
2009 2010 20110
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
1.4
percentage
percentage
Interpretation:
A higher inventory turnover ratio is better than a lower inventory turnover ratio. A higher
ratio implies good inventory management and an indication of under investment lower
inventory turnover ratio indication of excessive inventory and over investment in
inventory.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 109

Ginza Industries Ltd.
(2)Total assets turnover ratio:
The amounts invested in business are invested in all assets jointly and sales are
affected through them to on profit
YEAR Total Assets Turnover = Sales / Total Assets %
2009 1,278,592,119.69 ÷1,780,714,199.51 × 100 71.80
2010 1,588,104,996.85 ÷ 1,769,677,468.92 × 100 89.73
2011 1,907,927,818.75 ÷ 2,016,168,761.98 × 100 94.63
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 110

Ginza Industries Ltd.
2009 2010 20110
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100percentage
percentage
Interpretation: The increasing rate of total assets turnover ratios shows that company has
a capacity to sell more and as such its profitability is more.
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 111

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Bibliography.
Books.
Marketing Management
Marketing Management By Philip Kotler.
Edition-
Page No’s.
3,298,315-334,471-495,471-484
Human Resource Management.
Human Resource Management text And Cases.
By- K. Aswathappa.
Edition-6th
Page No’s.
11-15,21-23,96-111,123-136,.144-148,170-183,
196-198, 220,247-262.
Site.
http://www.ginzalimited.com/products.htm
http://ginzalimited.tradeindia.com/company-profile.html
http://ginzalimited.tradeindia.com/
http://www.cim.co.uk/resources/understandingmarket/definitionmkting.aspx
Other.
Magazines, Pamphlets, Notes..
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 112

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Annexure.
4.1 Profit & Loss Account
1-Apr-2009 to 31-Mar-2010
Year ended year ended
31.03.2010 31.03.2009
(Rs.) (Rs.)
Income
Sales 1,588,104,996.85 1,278,592,199.69
Increase\decrease in stock (16,771,656.oo)50,368,619.00
Other income 5,351,118.734,347,381,.85
TOTAL 1.576,684,459.58
1,333,308,120.54
EXPENDITURE
Raw materials 971,430,120.97857,758,010.
Store & spares 16,067,461.86 16,575,045.78
Payments to and provisions for employees 142,466,527.59 109,481,564.47
Power & fuel 82,585,265.1077,578,399.28
Processing , colouring ,& hand printing & cutting charges 22,049,535.70 21,602,870.10
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 113

Ginza Industries Ltd.
Administrative & other expenses 51,053,332.3055,976,781.74
Selling and distribution expenses 27,265,594.4334,069,226.03
Interest 109,755,758.79112,053,420.25
Depreciation 121,188,203.4692,329.279.70
TOTAL 1,543,861,800.20
1,377,424,597.55
Less: deferred revenue expenditure 4,159,560.004,159,560.00
Profit before taxation & exceptional item 28,663,099.38(48,276,037.01)
Less: exceptional item 10,755,375.0024,591,214.74
Profit before taxation 17,907,724,38(72,795,251.75)
Less: provision for current taxation 725,000.00
Less: provision for fringe benefit tax1,125,000.oo
Less: provision for deferred tax liability (24,363,425.39) (19,690,427.07)
Profit after taxation 41,546,149.77 (54,229,427.68)
Add: items 1,873,711.89
Balance b\f from previous year 312,846,517.30367,076,341.98
Less: income tax payment
Balance carried to balance sheet 356,266,517.30312,846,517.30Basic and diluted earnings per share 4.68
(6.10)
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 114

Ginza Industries Ltd.
4.2 BALANCE SHEET
1-Apr-2009 to 31-Mar-2010
Sources of funds 31.03.2010 31.03.2009
1.shareholders funds
a)share capital 88,831,060.00 88,831,0 60.00
b)reserves & surplus 418,571,378.96 507,402,438.96 375,151,517.30 463,982,577.30
2.loan funds
a)secured loans 1,064,750,300.66 1,136,947,694.15
b)unsecured loans 7.500,000.00 1,O72,250,300.66 0.00 1,136,947,694.15
3.deferred tax liabilities 57,452,988.5481,816,413.93
TOTAL 1,637,105,728.16 1,682,746,685.30
Application of funds
1.fixed assets
a) gross block 1,626,997,281.76 1,589,068,317.84
b) less: depreciation 622,509,428.81 502,868,542.24
c)net block 1,004,487,852,.95 1,086,199,775.60
d)capital work in progress 2,575,744.00 1,007,063,596.951,086,199,775.60
2. investments 827,300.008,698,300.00
3. current assets , loans
& advances
a)inventories 444,238,725.00 439,489,563.00
b)sundry debtors 257,999,205.38 214,344,414.38
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 115

Ginza Industries Ltd.
c)cash current assets 14,428,435.96 7,696,254.63
d)other current assets 39,412,726.84 27,638,724.98
e)loans and advances 9,110,522.79 5,345,448.92
765,189,615.97 694,514,423.91
less: current liabilities
& provisions
Current liabilities 121,470,906.47 97,046,495.84
Provisions 22,823,000.00 22,098,000.00
144,293,906.47 119,144,495.84
Net current assets 620,895,709.50575,369,928.07
4. Miscellaneous
expenditure
(to the extent not
Written Off or adjusted)
Deferred revenue expenditure 8,319,121.7112,478,681.71
TOTAL 1,637,105,728.16 1,682,746,685.38
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 116

Ginza Industries Ltd.
4.3 Profit & Loss Account
1-Apr-2010 to 31-Mar-2011
Year ended year ended
31.03.2011 31.03.2010
(Rs.) (Rs.)
Income
Sales 1,90,79,27,818.75 1,33,22,35,082.85
Increase\decrease in stock (2,86,50,050.00)(1,67,71,656.00)
Other income 16,99,305.4353,51,118.73
TOTAL 1,880,977,074.18
1,32,08,14,545.58
EXPENDITURE
Raw materials 1,05,49,15,820.2371,55,60,206.97
Manufacturing & other expenses 43,52,17,600.45 34,56,47,276.98
Interest 9,22,98,000.8310,97,55,758.79
Depreciation 12,16,03,939.1212,11,88,203.46
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 117

Ginza Industries Ltd.
TOTAL 1,70,40,35,360.63
1,29,21,51,446.20
Profit before taxation & exceptional item 17,69,41,713.552,86,63,099.38
Less: exceptional item 4,51,61,168.691,07,55,375.00
Add: excess dep provided in earlier years written back 1,44,76,014.00 15,47,316.90
Add: prior period items 2,65,001.00 3,26,394.99
Profit before taxation 14,65,21,559.861,97,81,436.27
Less: provision for taxation 2,37,05,000.007,25,000.00
Less: provision for deferred tax liability 2,73,83,122.00 (2,43,63,425.39)
: income tax for earlier years 10,35,213,73 0.00
Add: MAT credit entitlement 3,14,92,372.00 0.00
Profit after taxation 12,58,90,596.13 4,34,19,861.66
Balance b\f from previous year 35,62,66,378.96 31,28,46,378,96
Balance carried to balance sheet 48,21,56,975,0935,62,66,378.96
Basic and diluted earnings per share 14.17 4.89
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 118

Ginza Industries Ltd.
4.4 BALANCE SHEET
1-Apr-2010 to 31-Mar-2011
Sources of funds 31.03.2011 31.03.2010
1.shareholders funds
a)share capital 88,831,060.00 88,831,0 60.00
b)reserves & surplus 54,44,61,975.09 63,32,93,035.09 41,85,71,378.96 50,74,02,438.96
2.loan funds
a)secured loans 96,29,92,414.45 1,06,47,50,300.66
b)unsecured loans 6,24,54,893.00 1,02,54,47,307.45 75,00,000.00 1,07,22,50,300.66
3.deferred tax liabilities 8,48,36,110.545,74,52,988.54
TOTAL 1,74,35,76,453.08 1,63,71,05,728.16
Application of funds
1.fixed assets
a) gross block 1,82,78,75,475.94 1,62,69,97,281.76
b) less: depreciation 72,96,13,739.92 62,25,09,428.81
c) net block 1,09,82,61,736.02 1,00,44,87,852.95
d)capital work in progress 4,50,000.00 1,09,87,11,736.02 25,75,744.001,00,70,63,596.95
2. investments 8,27,300.008,27,300.00
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 119

Ginza Industries Ltd.
3. current assets , loans
& advances
a) Inventories 45, 49, 08,877.00 44,42,38,725.00
b) Sundry debtors 31, 61, 71,398.93 25,79,99,205.38
c) Cash & bank balance 2,32,56,851.15 1,44,28,435,96
d) loans and advances 12,35,69,898.88 4,85,23,249.63
91,79,07,025.96 76,51,89,615.97
Less: current liabilities
& provisions
Current liabilities 252,474,170.61 12,14,70,906.47
Provisions 25,555,000.00 2,28,23,000.00
27,80,29,170.61 14,42,93,906.97
Net current assets 63,98,77,855.3562,08,95,709.50
4. Miscellaneous
expenditure
(to the extent not
Written Off or adjusted)
Deferred revenue expenditure 41,59,561,7183,19,121.71
TOTAL 1,74,35,76,435.08 1,63,71,05,728.16
Navnirman Institute Of Management.Page 120