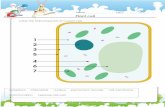
Plant Structure and Function. Types of Plant Cells Parenchyma Thin flexible cell walls. 2 main...
-
Upload
russell-douglas -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
0
Transcript of Plant Structure and Function. Types of Plant Cells Parenchyma Thin flexible cell walls. 2 main...

Plant Structure and Function

Types of Plant CellsParenchyma
Thin flexible cell walls.
2 main functions – storage and food production.– Large vacuole
stores water, starch and oils.
– Can contain many chloroplasts.

Types of Plant CellsCollenchyma
Typically long cells. Unevenly thickened
cell walls.– Thin parts can
stretch and grow. Provide support for
surrounding tissue. ie. – tough strands
in celery.

Types of Plant CellsSclerenchyma
Thick and rigid. Used for support Two types: fibers and
stone cells.– Fibers – long thin
strands, support, strength, vascular tissue.
– Stone cells – circular cells
Gritty texture of pears Fruit pits

Plant TissuesDermal or Epidermis
Flattened parenchyma cells cover and protect plant like skin
Produce a waxy cuticle – prevents water loss.

Plant TissuesDermal or Epidermis
Contain stomata: openings that control gas exchange.– Guard cells control
opening and closing.

Plant TissuesDermal or Epidermis
Root hairs: extensions of cell that help absorb water and minerals.

Plant TissuesDermal or Epidermis
Trichomes: hair like – give fuzzy texture– Reduce
evaporation.– Some protect by
secreting toxic substances.

Plant TissuesVascular Tissues
Transport food minerals and water through the plant.
Two types:– Xylem – Moves water and minerals from
roots to rest of plant.– Phloem – Transport sugars and organic
compounds from leaves to rest of plant.

Plant TissuesXylem
Two types Tracheids: In conifers.
– Tubular, tapered ends, dead at maturity.
– Cell walls have pits for water flow across cells.
Vessel elements: In Anthopytes.– Wider and shorter.– Openings in end walls for
water flow through cells.

Plant TissuesXylem

Plant TissuePhloem
Transport sugars and organic compounds.
Living, tubular cells. Phloem cells are called
sieve tube members. Have cytoplasm but no
nucleus or ribosomes. Companion cells – next
to each sieve tube member. Help manage transport.

Plant TissuesGround Tissue
All other tissues Mostly parenchyma Functions: photosynthesis, storage,
support.– In stems and roots: have large vacuoles
to store starch and water.

Plant TissuesMeristematic Tissues
Region of actively dividing cells. Small, round, with large nuclei. Apical meristems:
– At tips of roots and stems.– Increase length.
Lateral meristems:– Cylinders of dividing cells in roots and stems.– Increase diameter.– Vascular cambium: produce xylem and phloem.– Cork cambium: produces tough covering for root
and stems.

Meristems

Roots Anchor, absorb water and minerals from soil. Some used for food storage (carrots) Two types
– Taproots: central fleshy with small branch roots. (carrots, beets)
– Fibrous roots: numerous branches from central point.

Root Variations Adventitious
roots:– Prop roots above
ground to support tall plants.
Aerial roots:– Cling to objects
to provide support.

Root Structure
Epidermis: outer layer.– Root hair: extension of single epidermal cell.– Absorbs water, oxygen and minerals.

Root Structure
Cortex: next layer.– Transports water and ions into vascular core.– Made of parenchyma cells
sometimes used for storage

Root Structure
Endodermis: forms waterproof seal around vascular tissue.– All water and minerals must pass through
endodermis cells.

Root Structure
Pericycle: just within endodermis.– Gives rise to lateral roots (offshoots of older
roots).

Root Structure
Xylem and phloem: center of root.– Transport of water, minerals and organic
materials through plant.

Dicot vs. Monocot Root

Dicot vs. Monocot Root

Root Growth Apical meristem
– Lengthens root Vascular cambium
– Increase diameter– Found between
xylem and phloem Root cap
– Layer of cells at root tip.
– Protection

Stems Transport, support and
storage. Some are Underground
– Corm: short, thick, surrounded by leaf scales. (gladiolus)
– Tuber: swollen underground stem with buds that sprout new plants. (potato)
– Rhizomes: (iris)

Stem: Internal Structure Vascular tissue arranged in bundles.
Dicot Monocot

Woody Stems Secondary
Growth: thickness from vascular cambium.– Xylem: wood –
causes growth rings.
– Bark: old phloem and cork cambium.

Stems – Material Transport Xylem: transports water from roots to leaves. Phloem: transports sugars, minerals, and
hormones.– Source: photosynthetic tissue – mostly leaves.– Sink: storage area (cortex of roots)– Translocation: movement from source to sink.

Leaf Variation Simple: blade no
divided Compound: divided
into leaflets Alternate: only one
leaf from a single point on stem
Opposite: leaves in pairs along stem
Whorled: three or more leaves occurring at same place on stem

Leaf Structure Vascular tissue in veins. Epidermis: outer layer of cells. Two layers of Mesophyll.
– Palisade mesophyll: Most photosynthesis.
– Spongy mesophyll: Loosely packed with irregular shaped cells. Air spaces for gas exchange: O2, CO2, H2O. Gases move in and out of stomata.


Transpiration Loss of water vapor through the stomata.

Leaf Venation Patterns Parallel – monocots Netlike – dicots

Leaf Modifications Cactus spines: leaves that reduce
water loss and protect plant. Bulb: short stem covered by large
fleshy leaves, modified for food storage.
Pitcher plant: modified to trap insects. Aloe vera: adapted to store water.



Plant Responses
Hormones
Tropisms
Nastic Responses

Plant Hormones Chemicals produced in one part of an
organism and transported to another to cause a change in growth or development.

Auxins: Hormone Promote cell elongation. (IAA) Indoleacetic acid.
– Produced in apical meristem.– Increases cell division and promotes cell
elongation. Weakens connections between cellulose
fibers in the cell wall allowing cells to stretch.

Auxin Auxins produced in apical meristem
inhibits growth of side branches. Remove stem tip – branches form

Gibberellins: Hormone Growth hormone. Stimulates cell
elongation. Also increases
rate of seed germination and bud development.

Cytokinins: Hormone Stimulate cell division or cytokinesis. Stimulate production of proteins
needed for mitosis. Produced in meristem of roots and
travel up xylem to rest of plant.

Ethylene: Hormone
A gas that speeds ripening of fruits.

Tropism Response to an external stimulus from
a particular direction.– Positive tropism: plant grows toward
stimulus.– Negative tropism: plant grows away from
stimulus.

Types of Tropism Phototropism: growth toward light.
– More auxin on side of stem away from light.
– Cell elongation on one side – dark side. Gravitropism: direction of plant growth
in response to gravity.– Stems up and roots down.
Thigmotropism: response to touch.– Tendrils of vine coil around objects.

Nastic Responses Response movement that is not dependent
on direction of stimulus. Mimosa Venus Flytrap