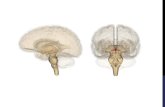
Pineal Gland Alyson Yun, David Seco, Brianna McCarthy, Jack Kahvejian Period 1.
-
Upload
tracy-wiggins -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
0
Transcript of Pineal Gland Alyson Yun, David Seco, Brianna McCarthy, Jack Kahvejian Period 1.
Hormones Associated With the Pineal Gland
Melatonin Regulates other hormones Maintains the Circadian Rhythm
This is your body’s 24hr clock that regulates when you wake up and go to sleep
Click here
Hormones con’t
Serotonin 80-90% is found in your gastrointestinal tract
It affects: Mood/ social behavior Appetite/ digestion Sleep Memory Sexual desire/ function
Click here
Depression and
Anxiety
Serotonin is a neurotransmitter, meaning it helps neurons send information to each other.
It signals brain cells that an individual feels relaxed and happy or sad and depressed.
Low levels of serotonin often lead to depression, anxiety, obsessive-compulsive disorder, insomnia, and addiction.
Some causes could come from being alone or being mistreated by their parents or other people.
Click here
Symptoms
Persistent sad or in an "empty" mood Feelings of hopelessness, pessimism Feelings of guilt, worthlessness, helplessness
Seasonal Affective Disorder
(SAD)
SAD is a melatonin deficiency disorder, low levels of melatonin can results in anxiety, stress and seasonal affective disorder
Abnormalities with melatonin have been quickly linked to a variety of mood and disorders
Some causes for the changes are the different types of seasons, this also plays a role in sleep patterns
Some symptoms are insomnia, feeling depressed, low energy, suicidal thoughts
The Pancreas
Gland
The pancreas gland is located behind your stomach
It is 6 inches long The pancreas is an exocrine gland as well as an endocrine
Insulin
Insulin helps control blood glucose levels
This happens by signaling the liver, muscle, and fat cells to take in glucose from the blood
Insulin helps cells to take in glucose to be used for energy
If the body has enough energy, insulin signals the liver to take up glucose and store it as glycogen
Click here
Glucagon
The pancreas releases glucagon when concentration of glucose in the bloodstream falls too low
Glucagon causes the liver to convert stored glycogen into glucose, which is released into the bloodstream
High blood glucose levels stimulate the release of insulin
Glucagon and Insulin are interdependent
Click here
Diabetes
Diabetes is a disease that affects how your body uses blood sugar (glucose)
Glucose is a vital to your health because it supplies the cells with energy
Diabetes means you have too much glucose in your blood
The pancreas doesn’t always produce enough insulin, which results in type 2 diabetes
Some possible causes of diabetes are genetic risk factors and environmental factors
Click here
Symptoms
Excessive thirst
Increased urination
Fatigue
Weight loss
Blurred vision
Swollen gums
Tingling hands and feet
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is when your level of blood sugar gets too low
The body doesn’t have enough energy to use as fuel
Some causes of hypoglycemia are your diet, some medication conditions, and exercise
Some symptoms are confusion, dizziness, feeling shaky, and hunger
Fun Facts
Baking Soda is produced by the pancreas, since one of its unique functions is it creates bicarbonate, which is basically standard baking soda
It has its own version of taste buds similar to what the tongue has. The receptors “taste” how sweet the food that is being eaten is and will release the appropriate amount of insulin as a result
Up until 1902, people thought it was the brain and not the pancreas that released substances
When you sleep or die, your pineal gland releases a drug called DMT, which is an illegal hallucinogenic that is naturally produced by the body. Some researchers believe that accounts of people dying and "going to heaven" are caused by the release of DMT
Concept Check
Questions
1. How might seasonal depression and melatonin levels be related to each other?
In humans, low levels of melatonin contributes to feelings of depression. This explains why people tend to feel unhappy during seasons when daylight is scarce due to cloudy skies or shorter winter days.
2. How does glucagon affect the body's metabolism? Glucagon has the opposite role as insulin, and
encourages the metabolism of fats as a way pf preserving existing glucose until blood sugar levels return to normal.
3.) What is the role of the insulin receptor? When it is activated by insulin, the insulin receptor
causes an increase in glucose absorption by all body cells.
Bibliography
Hendrickson, Kirstin. "Diseases Associated with Serotonin." Live Strong. N.p., 2 Sept. 2010. Web. 13 Mar. 2015. <http://www.livestrong.com/article/220756- diseases-associated-with-serotonin/>.
Mayo Clinic Staff. "Diseases and Conditions Diabetes." Mayo Clinic. Mayo Clinic Staff, 31 July 2014. Web. 13 Mar. 2015. <http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetes/basics/definition/con-20033091>.
Shmaefsky, Brian. Applied Anatomy & Physiology: A Case Study Approach. St. Paul, MN: EMC/Paradigm, 2007. Print.