Physical basis of the Greenhouse Effect -The “wavelength shift”- 1.Solar insolation calculation...
-
Upload
june-atkinson -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
0
Transcript of Physical basis of the Greenhouse Effect -The “wavelength shift”- 1.Solar insolation calculation...

Physical basis of the Greenhouse Effect
-The “wavelength shift”-
1. Solar insolation calculation (doc file)
2. Blackbody radiation, 3. Absorption spectra4. Conservation of energy
Energy & Environment 263
Online at: http://www.umich.edu/~twod/energy/resources/greenhouse_lecture

2
Black body radiation
• Continuous spectra
400 500 600 700 Wavelength [nm, nanometers]
ColorScience.htm

3
Black body radiation
• Continuous spectra – we see as white light
400 500 600 700 Wavelength [nm, nanometers]
ColorScience.htm

4
Black body radiation
• Continuous spectra & human cones, rods
400 500 600 700 Wavelength [nm, nanometers]
ColorScience.htm
Warning:shows range
of three types of cones,
but notrelative
sensitivities(green
has ~ 10xsensitivity
of red).

5
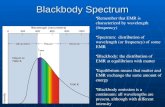
Black body radiation
• Continuous visible spectra – higher temp.
400 500 600 700 Wavelength [nm, nanometers]
ColorScience.htm

6
Black body radiation
• Continuous visible spectra -- lower temperature
400 500 600 700 Wavelength [nm, nanometers]
ColorScience.htm
Note peak shift And flatter shapewith lower Temperature

7
Black body radiation
• Continuous visible spectra -- lower temperature
400 500 600 700 Wavelength [nm, nanometers]
ColorScience.htm
-- Wavelength vs. temp is Stephan-Boltzmann law
-- Peak is Wein’s law
-- Shape or ‘distribution’ of intensity with frequency is Plank’s Readiation Law … A big deal in Quantum Mechanics’ history (Einstein, Plank, et al)
-More on this & math later

8
Black body vs. atomic line spectra
• Continuous spectra – from bulk solids with complex modes
• Atomic line spectra – discrete energy levels
400 500 600 700 Wavelength [nm, nanometers]
ColorScience.htm
Hydrogen EMISSION line spectra

9
Solar black body radiation
• Solar spectra … ~5800 K at surface • Yellow-green at middle. Combo ~ white.
But, some parts missing …
400 500 600 700 Wavelength [nm, nanometers]
ColorScience.htm

10
Blackbody radiation
400 500 600 700 Wavelength [nm, nanometers]
ColorScience.htm
Hydrogen ABSORPTION spectra
But, what we actually get from the sun is:

11
400 500 600 700
ColorScience.htm
Hydrogen EMISSION line spectra
Hydrogen ABSORPTION spectra
Hydrogen emits/absorbs same energies.
electron
neutron
proton
Atomic physics:ATOMISTICand QUANTUMview of micro-world
Larger jumpmore energy bluer color

12
400 500 600 700
ColorScience.htm
Hydrogen EMISSION line spectra
Hydrogen ABSORPTION spectra
Hydrogen emits/absorbs same energies.
electron
neutron
proton
Atomic physics:ATOMISTICand QUANTUMview of micro-world

13
Greenhouse: Black body radiation
Three concepts crucial to understand greenhouse effect:
1) Blackbody radiation is E&M radiation a) Continuous spectrab) Shifts with temperature
• Physics of radiant energy

14
Greenhouse: Black body radiation
Three concepts crucial to understand greenhouse effect:
1) Blackbody radiation is E&M radiation a) Continuous spectrab) Shifts with temperature
2) Line Spectra of atoms (or bands of molecules)a) Discrete lines (bands)b) Emission and absorption at same energies
• Physics of radiant energy

15
Greenhouse: Black body radiation
Three concepts crucial to understand greenhouse effect:
1) Blackbody radiation is E&M radiation a) Continuous spectrab) Shifts with temperature
2) Line Spectra of atoms (or bands of molecules)a) Discrete lines (bands)b) Emission and absorption at same energies
3) Equilibrium temperature reached when earth’s emission = earth’s absorption.- Slight change in either -> colder or hotter earth

16
Greenhouse: and “Wavelength shift”
• Fourth issue: CO2 emissions and H2O already in atmosphere
• Look in detail now Physics of radiant energy …
• We’ll need couple students with calculators … (And remember Sun = 6000 K, earth = 288 K, sigma = 5.67 x 10-8 Watts m-2)
Later: solar-earth spectra compared

17
• Fourth issue: CO2 emissions, and H2O already in atmosphere
Source: http://www.lenntech.com/The-greenhouse-effect.htm

18
• Fourth issue: CO2 emissions, and H2O already in atmosphere
Source: http://www.lenntech.com/The-greenhouse-effect.htm

19
• Fourth issue: CO2 emissions, and H2O already in atmosphere
Source: http://www.lenntech.com/The-greenhouse-effect.htm
Earthshine

20
• Fourth issue: CO2 emissions, and H2O already in atmosphere
Source: http://www.lenntech.com/The-greenhouse-effect.htm
Earthshine
WATER VAPOR “Water molecules, always abundant I air, absorb thermal IR light due to the H-O-H bending vibration, the peak in the spectrum for this absorption occurs at about 6.3 µm. Thus almost all the relatively small amount of outgoing IR in the 5.5-7.5 µm regions is intercepted by water vapor. There are other water vibrations the remove thermal infrared light of wavelength 12 µm and longer. In fact the water is the most important greenhouse gas in the earth’s atmosphere, though on a per molecule basis it is a less efficient absorber than is CO2. ““The equilibrium vapor pressure of liquid water, and consequently the maximum concentration of water vapor in air, increases exponentially with temperature. Thus the amount of thermal IR redirected by water vapor will rise as a result of any global warming induced by the other greenhouse gases and will amplify the temperature increase. Since it comes about as an indirect effect of increasing the levels of other gases. Consequently, water is not usually listed explicity among gases whose increasing concentrations are enhancing the greenhouse effect. Water in the liquid form droplets in clouds also absorbs thermal IR. “

21
Greenhouse: and
“Wavelength shift”