Photosynthesis limiting factors - Bathwick · Activity 11 The effect of light intensity on the rate...
Transcript of Photosynthesis limiting factors - Bathwick · Activity 11 The effect of light intensity on the rate...

1
Photosynthesis — limiting factors
What you should know by the end of this unit:
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants make their own food.
Light energy is trapped by the green pigment chlorophyll.
Chlorophyll is found in structures called chloroplasts.
Green plants make sugar from carbon dioxide and water.
The energy to synthesise (make) the food is obtained from the sunlight absorbed by chlorophyll.
Oxygen is a by-product of photosynthesis.
The sugar made by plants during photosynthesis is a high-energy chemical
called a carbohydrate.
A plant uses this sugar as a source of energy to grow.
A plant can store sugar as starch.
Iodine solution turns blue-black when starch is present.
Light, chlorophyll and carbon dioxide are the three requirements for photosynthesis.
A limiting factor is an environmental factor which slows down the rate of
photosynthesis if it is in short supply.
Light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration and temperature limit the rate of photosynthesis if they are in short supply.
Skills that you should be able to carry out by the end of this unit:
Design a table with appropriate headings.
Draw a line graph from a table of results.
Interpret information presented as a line graph.
Work as part of a group and take responsibility to support the work of the group.
Write up experiments with an aim, method, results and conclusion.
Appreciate the importance of variables in an experiment and how to improve the reliability of results.

2
Photosynthesis copy this heading
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants make their own
food.
During photosynthesis green leaves convert light energy to chemical
energy which is contained in sugar.
The green plants make sugar from dioxide and water.
This process involves the trapping of light energy from the sun.
Light energy is trapped by the green pigment chlorophyll. Chlorophyll
is found in structures called chloroplasts.
Photosynthesis goes on mainly in the leaves, though any green part of
the plant can photosynthesise.
Oxygen is given off as a by-product.
Word equation for photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide + water sugar + oxygen
raw materials products
Essential requirements
Chlorophyll Light

3
Water and minerals are absorbed from the soil by the roots and
drawn up the stem through tubes to the leaves where the water is used
for photosynthesis.
Carbon dioxide is absorbed from the air through tiny pores mainly on
the underside of the leaf.
Activity 1 Collect the photosynthesis true/ false/ don’t know cards. Work in pairs and use the resources available to sort the cards.
roots
pores
Open Closed

4
Activity 2 Answer these questions in sentences
1. Name the process by which green plants make food.
2. Where does the green plant get the energy to synthesis food?
3. Name the pigment that traps this energy and where it can be found.
4. What energy change takes place during photosynthesis?
5. (a)Name the two raw materials green plants use to make
food. (b) Explain how these raw materials get into the plant.
6. (a)Name the products of photosynthesis.
(b) Which of these is the by-product?
Food storage in plants copy this heading
The food (sugar) made by plants during photosynthesis is a high-energy
chemical and is a type of carbohydrate. If a plant does not
immediately use this sugar as a source of energy to make new cells and
grow, the plant will store the sugar as starch.
This starch is the plant’s store of food and can be converted back to
sugar for energy when needed.
Some sugar will be stored as starch in the leaves and some will be
transported to other parts of the plant.
Cells in a leaf

5
Stored sugar
Fruit is an examples of a part of a plants containing stored sugar e.g.
grapes, plums, oranges.
Other examples of parts of plants containing stored starch are tubers
and seeds such as potatoes, beans, corn, wheat and rice.
Activity 3 copy and complete this note
The sugar made by plants during photosynthesis is a high energy
c______________.
The sugar can be used by the plant immediately as a source of energy
to make n____ c______ and g____ or the plant can store the sugar as
s______.
This starch can be c_______ back into sugar when the plant needs
e___________.
Starch can be stored in the leaves or in s______ or f________.

6
Testing leaves for starch copy this note
We can use the presence of starch in a leaf as proof that photosynthesis
has taken place. We test the leaf with iodine solution.
Iodine solution turns blue-black when starch is present.
It is important that the plants have no starch in them at the start of the
experiment. Potted plants are de-starched by leaving them in a dark
cupboard for two or three days
Activity 4
Collect this instruction sheet and stick it into your jotter
Procedure to test a leaf for starch:
1. Boil the leaf in a beaker of water for one minute (to
burst cell membranes).
2. Switch the Bunsen burner off.
3. Place the leaf into a boiling tube of
ethanol. Place the boiling tube into
the freshly boiled water. Leave until
all the chlorophyll is dissolved out.
3. Remove the leaf from the boiling
tube and rinse it in the beaker of
water. Spread the leaf out over a
white tile and test it for starch using
iodine solution.

7
Activity 5 Complete the starch test sort cards
Activity 6 Collect the results sheet shown below.
You are going to test a leaf from plant A and plant B for starch. Record your result and your conclusion on the sheet.
Is light necessary for photosynthesis?
Set up starch present? Conclusion
Tidy away all your equipment and get your teacher to check
your results and conclusion.
.
Clear plastic
bag
Green plant that has been destarched
Plant B
Green plant that has been destarched
Black plastic bag
Plant
A

8
Activity 7 Collect the results sheet shown below.
You are going to test a leaf from plant A and plant B for starch. Record your result and your conclusion on the sheet.
Is carbon dioxide necessary for photosynthesis?
Set up Result Conclusion
Tidy away all your equipment and get your teacher to check
your results and conclusion.
Clear plastic
bag
Sodium hydroxide
solution
Water
Plant B
Plant A
Green plant that has been destarched
Green plant that has been destarched
Clear plastic bag

9
Activity 8 Collect the results sheet shown below.
You are going to test a leaf from a variegated plant for starch.
Record your result and your conclusion on the sheet.
Tidy away all your equipment and get your teacher to check
your results and conclusion.
Is chlorophyll necessary?
Set up Result Conclusion
Green part contains chlorophyll White part does not contain chlorophyll
Clear plastic bag
Variegated plant that has been in the dark for 2 days to destarch
Green (chlorophyll) White (no chlorophyll)

10
Activity 9 Answer these questions in sentences
1. Name the chemical reagent used to test for starch.
2. Describe the colour change shown by this reagent if starch is
present.
3. Copy and complete
Photosynthesis will not take place in the absence of
c_________ d__________ l_____________
c__________________
Limiting factors copy this note
A limiting factor is an environmental factor which if in short supply slows down the rate at which a plant can carry out photosynthesis
Activity 10 Group activity
THINK/ PAIR/ SHARE
Can you think of an environmental factor which will affect the rate of photosynthesis? Share and discuss with your partner and the other groups in the class. Make a list in your jotter. Use the help cards if you find this difficult.

11
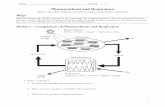
Activity 11 The effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis Look at the equipment shown in the diagram below.
This equipment can be used to find the effect of changing light
intensity on the rate of photosynthesis.
We can measure the rate of photosynthesis using aquatic plants like Elodea and Cabomba. During photosynthesis, these plants give off bubbles of oxygen. The rate of photosynthesis can be measured by counting the number of bubbles produced or by collecting the oxygen and measuring its volume.
Copy this heading

12
Discuss in your groups how you could change the light intensity
the plant is receiving.
Discuss what variables have to be kept the same in order to make it a fair experiment.
Think about how your group would measure the rate of
photosynthesis.
Use the information gathered during your group
discussion to Copy and complete this table.
What is the aim of this experiment?
What are you changing?
How are you changing it?
What will you keep the same?
How will you measure the rate of photosynthesis?

13
Use the webpage “water weed”
Set the carbon dioxide levels to 2.0
Set the light intensity to 1 and note the rate of photosynthesis in your jotter.
Repeat for a light intensity of 2 to a light intensity of 10, remember to note down your results.
Copy and complete the table below into your notes.
Light intensity
Rate of photosynthesis
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Collect graph paper and draw a line graph of your results.
Answer the following questions in sentences
1. What happens to the rate of photosynthesis as the light
intensity increases?
2. Why does the graph level off?
3. What could be limiting the rate of photosynthesis at this point?

14
Activity 12 The effect of carbon dioxide concentration
on the rate of photosynthesis
Look at the equipment shown in the diagram below.
This equipment can be used to find the effect of changing Carbon
dioxide concentration on the rate of photosynthesis.
Discuss in your groups how you could change the carbon dioxide
concentration the plant is receiving.
Discuss what variables have to be kept the same in order to make it a fair experiment.
Think about how your group would measure the rate of
photosynthesis.
Copy and complete this table
What is the aim of this
experiment?
What are you changing?
How are you changing it?
What will you keep the same?
How will you measure the rate of photosynthesis?
Copy this heading

15
Use the webpage “water weed”
Set the light intensity to 7
Set the carbon dioxide levels to 2.0 and note the rate of photosynthesis in your jotter.
Repeat for a carbon dioxide level of 2 to a level of 10; use the results to copy and complete the table below
Carbon dioxide concentration
Rate of photosynthesis
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Collect graph paper and draw a line graph of your results.
Answer the following questions in sentences
1. What happens to the rate of photosynthesis as the carbon dioxide
concentration increases?
2. Why does the graph level off?
3. What could be limiting the rate of photosynthesis at this point?

16
Activity 13 The effect of temperature on the rate of photosynthesis
Design an experiment to find the effect of changing temperature
on the rate of photosynthesis.
Discuss in your groups how you could change the temperature the
experiment is at.
Discuss what variables have to be kept the same in order to make it a fair experiment.
Think about how your group would measure the rate of
photosynthesis.
Copy and complete this table
What is the aim of this experiment?
What are you changing?
How are you changing it?
What will you keep the same?
How will you measure the rate of photosynthesis?
Activity 12 Copy this table of results into your notes.
Temperature (OC) Rate of photosynthesis
5 1
10 4
20 9
30 26
40 35
50 30
60 0
70 0
Collect graph paper and draw a line graph of these results.

17
Answer the following questions in sentences
1. What happens to the rate of photosynthesis as the temperature
increases?
2. What is the optimum temperature?
3. Why does the rate of photosynthesis fall above the optimum
temperature?