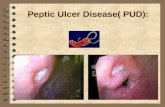
Peptic ulcer disease
description
Transcript of Peptic ulcer disease

Peptic ulcer disease

Factors influencing
• Aggressor– Acid– Pepsin– NSAIDs– H.Pylori
• Defense – Bicarbonate– Blood flow– Mucous– Cell junctions– Apical resistance
• Repair– Restitution– Proliferation– Mucous cap– Growth factors

H.Pylori
• Acid hypersecretion1. Inhibits antral D cells
• Decreased somatostatin• Increased gastrin• Increased acid
2. Local alkalization of the antrum• Increased gastrin• Increased acid
• Toxins – Cag A– Vac A
• Cytokines – IL-8
• These cause inflammation -> direct damage to epithelium

Other etiological factors
• NSAIDs• Gastrinoma (zollinger allison syndrome)• Smoking• Stress

The gastrinoma triangle

Clinical features
• Abdominal pain• Nausea• Bloating• Stool positive for occult
blood
• ALARM symptoms– Wt loss– Recurrent vomitting– Dysphagia– Bleeding– Anemia
• If any alarm symptom present, UGI endoscopy should be done

Upper GI series showing ulcer

Complications of peptic ulcer
• Intractability• Bleeding• Perforation• Obstruction

Perforation
• Acute abdomen – Sudden excruciating pain• Fluid sequestration into third space• Peritoneal signs– Guarding, tenderness, rebound tenderness
• Free air under domes of diaphragm

Ulcer perforation - xray

Closure of perforated DU with onlay patch

Gastric ulcer excision

Closure after excision

Intractability

Nonspecific vagotomy

Antrectomy

Completed vagotomy, antrectomy and gastroduodenostomy

Selective and highly selective Vagotomy

Laparoscopic HSV using clips or harmonic scalpel
Clips Harmonic shears

The criminal nerve of Grassi

Heineke-Mikulicz Pyloroplasty

Finney’s pyloroplasty

Biliroth I procedures

Biliroth II reconstruction

Roux en y gastrojejunostomy

Bleeding
• Melena/hematemesis• Nasogastric aspiration confirmatory• ShockNPO, acid supressionAggressive resuscitation with fluids and bloodUrgent endoscopyIf endoscopic Rx fails, or re-bleed, Surgery

Exosure of posterior bleeding DU

Figure of eight suture for bleeding control

Gastric resection

Separation of the greater omentum from the entire transverse colon

Mobilization of the left lobe of liver and GE junction

Mobilization of the greater curvature

Transection of the duodenum

D2 compartment lymphadencectomy

Division of the left gastric vessels

Transection of the esophagus

Roux en y reconstruction

Post operative complications of gastrectomy
• Short term:– Intra-abdominal bleeding– Subphrenic abscess– Anastomotic leak– Pancreatic fistula– Duodenal stump leak
• Long term:– Weight loss, decreasing nutritional status (reservoir capacity)– Diarrhea– Dumping syndrome– Alkaline reflux

Gastrojejunostomy

Complications of gastrojejunostomy
• Gastric hemorrhage• Anastomotic bleeding• Anastomotic leak• Obstruction (anastomotic or functional)• Anastomotic stenosis (long term)

Gastrostomy
Stamm Witzel

Janeway (permanent stapled gastrostomy

Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy

Laparoscopic gastrostomy

Pyloromyotomy