PEG & TPN
-
Upload
api-3722454 -
Category
Documents
-
view
143 -
download
1
Transcript of PEG & TPN

Percutaneous Percutaneous Endoscopic Endoscopic
Gastrostomy Gastrostomy
By: Jose Byron Dadulla-By: Jose Byron Dadulla-EvardoneEvardone

A A percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomypercutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy ((PEGPEG) is an ) is an endoscopicendoscopic procedure for placing a procedure for placing a tube into the tube into the stomachstomach through the through the abdominal wallabdominal wall. PEG tubes may also be extended into the . PEG tubes may also be extended into the small bowelsmall bowel..
The procedure is performed in order to place a The procedure is performed in order to place a gastric feeding tubegastric feeding tube as a long-term means of as a long-term means of providing nutrition to patients who cannot take providing nutrition to patients who cannot take food orally. Many food orally. Many strokestroke patients, for example, patients, for example, are at risk of are at risk of aspiration pneumoniaaspiration pneumonia due to poor due to poor control over the swallowing muscles; some will control over the swallowing muscles; some will benefit from a PEG performed to maintain benefit from a PEG performed to maintain nutrition.nutrition.

PEGs may also be inserted to PEGs may also be inserted to decompress the decompress the stomachstomach in cases of in cases of gastric gastric volvulusvolvulus..


Indications Indications
PEG should be considered for pediatric PEG should be considered for pediatric and adult patients who have an intact, and adult patients who have an intact, functional gastrointestinal tract but are functional gastrointestinal tract but are unable to consume sufficient calories unable to consume sufficient calories to meet metabolic needs. PEG is to meet metabolic needs. PEG is inappropriate in patients with rapidly inappropriate in patients with rapidly progressive and incurable disease, progressive and incurable disease, since nasoenteral feedings over a short since nasoenteral feedings over a short interval can provide the same result. interval can provide the same result.

The most common indications for The most common indications for PEG are neurologic conditions PEG are neurologic conditions associated with impaired swallowing associated with impaired swallowing and neoplasms of the oropharynx, and neoplasms of the oropharynx, larynx and esophagus. Other larynx and esophagus. Other indications include facial trauma and indications include facial trauma and the need for supplemental feedings the need for supplemental feedings in patients with miscellaneous in patients with miscellaneous catabolic conditions. catabolic conditions.

In patients with repeated aspiration In patients with repeated aspiration of nasogastric tube feedings or of nasogastric tube feedings or requiring prolonged gastric requiring prolonged gastric decompression, PEG can be modified decompression, PEG can be modified to percutaneous endoscopic to percutaneous endoscopic jejunostomy to provide both jejunal jejunostomy to provide both jejunal feeding and gastric decompression. feeding and gastric decompression.

Contraindications Contraindications
An absolute contraindication to PEG is An absolute contraindication to PEG is the inability to bring the anterior gastric the inability to bring the anterior gastric wall in apposition to the anterior wall in apposition to the anterior abdominal wall. Therefore, patients with abdominal wall. Therefore, patients with prior subtotal gastrectomy, ascites, or prior subtotal gastrectomy, ascites, or marked hepatomegaly require careful marked hepatomegaly require careful evaluation to be sure the stomach and evaluation to be sure the stomach and abdominal wall can be brought together abdominal wall can be brought together with gastric insufflation. with gastric insufflation.

Recognition of apposition may be Recognition of apposition may be difficult in patients with severe obesity. difficult in patients with severe obesity. PEG should not be used for nutritional PEG should not be used for nutritional support, when gastrointestinal tract support, when gastrointestinal tract obstruction is present. Relative obstruction is present. Relative contraindications to PEG include contraindications to PEG include proximal small bowel fistula, neoplastic proximal small bowel fistula, neoplastic and infiltrative diseases of the gastric and infiltrative diseases of the gastric wall, and obstructing esophageal lesions. wall, and obstructing esophageal lesions. Coagulation defects, if correctable, are Coagulation defects, if correctable, are not a contraindication to PEG not a contraindication to PEG

Technique Technique
The most widely used technique of PEG is the The most widely used technique of PEG is the "pull" method introduced by Gauderer and Ponsky "pull" method introduced by Gauderer and Ponsky in 1980. Modifications of the original technique in 1980. Modifications of the original technique have been reported. The gastrostomy tube can be have been reported. The gastrostomy tube can be pushed rather than pulled into place by a "push" pushed rather than pulled into place by a "push" method that has comparable results. In another method that has comparable results. In another modification, the "introducer method," the modification, the "introducer method," the stomach is directly punctured and a Foley Catheter stomach is directly punctured and a Foley Catheter placed over a guidewire. Finally, percutaneous placed over a guidewire. Finally, percutaneous gastrostomy has also been described without gastrostomy has also been described without endoscopy using a nasogastric tube or gastric endoscopy using a nasogastric tube or gastric insufflation, fluoroscopic monitoring, and a direct insufflation, fluoroscopic monitoring, and a direct percutaneous catheter insertion technique. percutaneous catheter insertion technique.

The basic elements common to all of The basic elements common to all of these techniques are: (1) gastric these techniques are: (1) gastric insufflation to bring the stomach into insufflation to bring the stomach into apposition to the abdominal wall; apposition to the abdominal wall;
(2) percutaneous placement of a (2) percutaneous placement of a tapered cannula into the stomach; tapered cannula into the stomach;
(3) passage of a suture or guidewire (3) passage of a suture or guidewire into the stomach; into the stomach;
(4) placement of the gastostomy (4) placement of the gastostomy tube; and verification of the proper tube; and verification of the proper position position

Complications Complications
Reported complications include a Reported complications include a wound infection, peritonitis, wound infection, peritonitis, septicemia, peristomal leakage, tube septicemia, peristomal leakage, tube dislodgement, aspiration, bowel dislodgement, aspiration, bowel perforation, and gastrocolic fistula. perforation, and gastrocolic fistula. Pneumoperitoneum is common after Pneumoperitoneum is common after PEG and of no significance, unless PEG and of no significance, unless accompanied by signs and symptoms accompanied by signs and symptoms of peritonitis . of peritonitis .

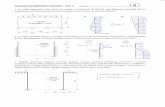
Position of PEG TubePosition of PEG Tube



TOTAL PARENTERAL TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITIONNUTRITION
By: Jose Byron Dadulla-By: Jose Byron Dadulla-EvardoneEvardone

Total parenteral nutritionTotal parenteral nutrition (TPN), (TPN), is the practice of feeding a person is the practice of feeding a person intravenouslyintravenously, bypassing the usual , bypassing the usual process of process of eatingeating and and digestiondigestion. The . The person receives nutritional formulas person receives nutritional formulas containing containing saltssalts, , glucoseglucose, , amino acidsamino acids, , lipidslipids and added and added vitaminsvitamins..

TPN is normally used following surgery, TPN is normally used following surgery, when feeding by mouth or using the when feeding by mouth or using the gutgut is is not possible, when a person's digestive not possible, when a person's digestive system cannot absorb nutrients due to system cannot absorb nutrients due to chronic diseasechronic disease, or, alternatively, if a , or, alternatively, if a person's nutrient requirement cannot be person's nutrient requirement cannot be met by met by enteralenteral feeding feeding (tube feeding) and (tube feeding) and supplementation. It has been used for supplementation. It has been used for comatosecomatose patients, although enteral feeding patients, although enteral feeding is usually preferable, and less prone to is usually preferable, and less prone to complications. complications.

Short-term TPN may be used if a Short-term TPN may be used if a person's digestive system has shut person's digestive system has shut down (for instance by down (for instance by PeritonitisPeritonitis), and ), and they are at a low enough weight to they are at a low enough weight to cause concerns about nutrition during cause concerns about nutrition during an extended hospital stay. Long-term an extended hospital stay. Long-term TPN is occasionally used to treat people TPN is occasionally used to treat people suffering the extended consequences suffering the extended consequences of an accident or surgery. of an accident or surgery.

The preferred method of delivering TPN is The preferred method of delivering TPN is with a medical with a medical infusion pumpinfusion pump. A . A sterilesterile bag of bag of nutrient solution, between 500 mL and 4 L is nutrient solution, between 500 mL and 4 L is provided. The pump infuses a small amount provided. The pump infuses a small amount (0.1 to 10 mL/hr) continuously in order to (0.1 to 10 mL/hr) continuously in order to keep the vein open. Feeding schedules vary, keep the vein open. Feeding schedules vary, but one common regimen ramps up the but one common regimen ramps up the nutrition over a few hours, levels off the rate nutrition over a few hours, levels off the rate for a few hours, and then ramps it down over for a few hours, and then ramps it down over a few more hours, in order to simulate a a few more hours, in order to simulate a normal set of meal times.normal set of meal times.

The nutrient solution consists of The nutrient solution consists of waterwater, , glucoseglucose, , saltssalts, , amino acidsamino acids, , vitaminsvitamins and (more and (more controversially) sometimes emulsified controversially) sometimes emulsified fatsfats. Long . Long term TPN patients sometimes suffer from lack of term TPN patients sometimes suffer from lack of trace nutrients or trace nutrients or electrolyteelectrolyte imbalances. imbalances. Because increased Because increased blood sugarblood sugar commonly occurs commonly occurs with TPN, with TPN, insulininsulin may also be added to the may also be added to the infusion. Occasionally, other drugs are added as infusion. Occasionally, other drugs are added as well.well.
Chronic TPN is performed through a Chronic TPN is performed through a Hickman lineHickman line or a or a Port-a-Port-a-CathCath (venous access systems). In (venous access systems). In infants, sometimes the umbilical artery is used.infants, sometimes the umbilical artery is used.

ComplicationsComplications
The most common complication of TPN use is The most common complication of TPN use is bacterial infection, usually due to the increased bacterial infection, usually due to the increased infection risk from having an indwelling central infection risk from having an indwelling central venous catheter. Liver failure may sometimes venous catheter. Liver failure may sometimes occur; a recent study at Children's Hospital occur; a recent study at Children's Hospital Boston on the cause suggests it is due to a large Boston on the cause suggests it is due to a large difference in omega-6 to omega-3 ratio. When difference in omega-6 to omega-3 ratio. When treated with a different fatty acid infusion (which treated with a different fatty acid infusion (which is not approved for use in the U.S.) two patients is not approved for use in the U.S.) two patients were able to recover from their condition.[1]were able to recover from their condition.[1]
Two related common complications of TPN are Two related common complications of TPN are venous thrombosis and priapism. Fat infusion venous thrombosis and priapism. Fat infusion during TPN is assumed to contribute to both.[during TPN is assumed to contribute to both.[