Parkinson’S Disease
Transcript of Parkinson’S Disease

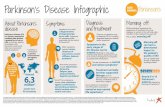
Parkinson’s Disease
NeuropathologyNeuropathology
ClassificationClassification
DiagnosisDiagnosis
ManagementManagement

NEUROPATHOLOGY

RAMESH DEBURRAMESH DEBUR
Neuropathology
Loss of pigmented dopaminergic neurons in
Substantia Nigra mostly in the ventral and
lateral areas (pars Compacta) Presence of lewy bodies

RAMESH DEBURRAMESH DEBUR
Neuropathology
Normal Parkinson’s

RAMESH DEBURRAMESH DEBUR
Neuropathology

CLASSIFICATION

RAMESH DEBURRAMESH DEBUR
Classification
CLASSIFICATIONCLASSIFICATION
Idiopathic
Secondary or ACCQUIRED
Parkinson’s plus syndromes

RAMESH DEBURRAMESH DEBUR
Idiopathic
Most common form.
1% of population over age 50 yrs., Incidence 40,000/yr.
Incidence increase with age, peak 60-80 yrs.
Male = female.
CLASSIFICATIONCLASSIFICATION

RAMESH DEBURRAMESH DEBUR
Secondary or Acquired
CLASSIFICATIONCLASSIFICATION
Drugs( neuroleptics, metoclopramide, reserpine )
- Toxics( manganese, carbon monoxide, carbon disulfide )
- Stroke, postencephalitis, head injury, boxer's brain

RAMESH DEBURRAMESH DEBUR
CLASSIFICATIONCLASSIFICATION
Parkinson’s PLUS
Progressive supranuclear palsy
Shy-Drager syndrome
Normal pressure hydrocephalus
Alzheimer disease
Wilson's disease

DIAGNOSIS

RAMESH DEBURRAMESH DEBUR
DIAGNOSISDIAGNOSIS
Diagnosis
Presence of at least three of bradykinesia
Rigidity
4-6 Hz resting tremor
Postural instability( primary visual, vestibular, cerebellar or proprioceptive dysfunction excluded )
Unilateral onset

RAMESH DEBURRAMESH DEBUR
DIAGNOSISDIAGNOSIS
Diagnosis
Persistent asymmetry Absence of clinical exclusion criteria Excellent response to l-Dopa Clinical course of 10 years or more

MANAGEMENT

RAMESH DEBURRAMESH DEBUR
Management
Medications Medical and nursing care Physical therapy Occupational therapy Speech therapy Psychological therapy
MANAGEMENTMANAGEMENT

MEDICATIONS

RAMESH DEBURRAMESH DEBUR
MANAGEMENTMANAGEMENT
Medications
Neurotransmitter replacement( l-dopa, carbidopa with l-dopa )
Anticholinergic( trihexyphenidyl, benztropine mesylate, procyclidrin )
Receptor agonist( amantadine, bromociptine, pergolide mesylate)
Other( selegiline )

SURGICAL

RAMESH DEBURRAMESH DEBUR
Surgical
Thalamotomy Pallidotomy Deep brain stimulation Striatal grafting of Dopaminergic fetal
tissue
MANAGEMENTMANAGEMENT

MEDICAL AND NURSING

RAMESH DEBURRAMESH DEBUR
Medical and Nursing
Firm bed
- Monitor for orthostatic hypotension
- Regular meal with low protein
- Measure vital capacity
- Bowel program for hypomobility
- Bladder evaluation and urodynamic study
- Artificial tears for lack of blinking
- anticholinergic for excessive drooling
- Administration of medications prior a mealtime
MANAGEMENTMANAGEMENT

PHYSIOTHERAPY

RAMESH DEBURRAMESH DEBUR
PHYSIOTHERAPY
Requires Prior Assessment:Can be based on Specific Scales Eg: UPDRSCan be Based on General Scales Eg: Barthel Index
TreatmentSymptomatic Problem Based ApproachHolistic

RAMESH DEBURRAMESH DEBUR
Physiotherapy
Relaxation technique to decrease rigidity
- Slow rhythmic rotational movement
- ROM exercise, stretching and preventing contracture, pectoralis stretching, hip extensor and quadriceps isometric exercise
- Back flexion-extension exercise and pelvic tilting
MANAGEMENTMANAGEMENT

RAMESH DEBURRAMESH DEBUR
Physiotherapy
- Proper sitting and postural control
- Mat activities
May be tilt table
- Functional mobility training, rocking chair or chair lift
- Stationary bicycling for reciprocal training MANAGEMENTMANAGEMENT

RAMESH DEBURRAMESH DEBUR
Physiotherapy
- PNF, NDT and biofeedback to facilitate the slow movement
- Auditory and rhythmic cueing in alternating movement
- Standing balance
- Progressive ambulation training, blocking, proper heel-toe gait, feet 12-15 in apart, arm swing
MANAGEMENTMANAGEMENT

RAMESH DEBURRAMESH DEBUR
Physiotherapy
- Use of assistive devices( weight walker or
wheel walker )
- Aerobic conditioning exercise( walking, swimming )
MANAGEMENTMANAGEMENT

RAMESH DEBURRAMESH DEBUR
Physiotherapy
- Frequent rest period
- Frenkel's exercise
- Family training and home program
MANAGEMENTMANAGEMENT

RAMESH DEBURRAMESH DEBUR
Occupational Therapy
ROM activities and stretching of upper extremity
- Fine motor coordination skills
- ADL training
- Hand cycling for reciprocal training
MANAGEMENTMANAGEMENT

RAMESH DEBURRAMESH DEBUR
Occupational Therapy
- Rocking chair for mobilization
- Handwriting skills
MANAGEMENTMANAGEMENT

RAMESH DEBURRAMESH DEBUR
Occupational Therapy
- Adaptive devices
- Position and posture training
- Family training and home program
MANAGEMENTMANAGEMENT

SPEECH THERAPY

RAMESH DEBURRAMESH DEBUR
Speech Therapy
Diaphragmatic breathing exercise and deep breathing before talking
- Swallowing training
- dysarthria training
- Facial, oral and lingual muscle exercise
MANAGEMENTMANAGEMENT

PSYCHOLOGY

RAMESH DEBURRAMESH DEBUR
Psychology
Psychological support
Patient and family counseling
Antidepressant as indicated
Cognitive remediation
Group therapy
MANAGEMENTMANAGEMENT

RAMESH DEBURRAMESH DEBUR
Bibliography
Required ReadingRehabilitation: O’SullivanTherapeutic Exercises: Kisner, Neurological Rehabilitation: Umphred Darcy
Further ReadingNeurological Rehabilitation: DobkinsNeurological Physiotherapy: Carr and Shepherd