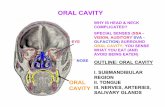
Oral Cavity
-
Upload
kalyan-polavarapu -
Category
Documents
-
view
20 -
download
1
description
Transcript of Oral Cavity

04/17/2023 1
EXAMINATION OF ORAL CAVITY

04/17/2023
WHY????
• Many diseases (systemic or local) have signs that appear on the face, head & neck or intra-orally.
• Making a complete examination can help you create a differential diagnosis in cases of abnormalities and make treatment recommendations based on accurate assessment of the signs & symptoms of disease
2

04/17/2023
Scope of examination
• Diseases of the head & neck
• Diseases of the supporting hard & soft tissues
• Diseases of the lips, tongue, salivary glands, oral mucosa
• Diseases of the oral tissues which are a component of systemic disease
3

04/17/2023 4

04/17/2023 5

04/17/2023 6
HISTORY

04/17/2023 7
AGE
AGE• Congenital
• Vitamin deficiency and malnutrition
• Carcinoma of buccal mucosa, lips, tongue

04/17/2023 8
• OCCUPATION– COUNTRY MANS LIP
• RESIDENCE– Australia– Caucasians– Negroes
OCCUPATION

04/17/2023 9
SYMPTOMS

04/17/2023 10
• Mode of onset
• Duration
• Progress
SWELLING / ULCER

04/17/2023 11
• PAINLESS LESIONS – Leukoplakia, mucous retention cysts, early carcinomas.
• PAINFUL LESIONS – Apthous ulcers, dental ulcers, abscess.
• Localized / radiating to ear
PAIN

04/17/2023 12
• Excessive Salivation
• Painful lesions
• Mass lesions – irritation
• Inability/difficulty to swallow due to ankyloglossia
SIALORIA

04/17/2023 13
• Ankyloglossia
• Tongue Tie
• Dysarthria
• Hoarseness of voice
• Cough with expectoration
HISTORY

04/17/2023 14
• Trismus• Ear pain• Eye pain• Dysphagia• Hearing loss• History of leukoplakia / erythroplakia
HISTORY

04/17/2023 15
MOKINGPIRITEPSISUPERFICIAL GLOSSITISYPHILISPICESHARP TOOTH

04/17/2023 16
• SMOKING– Type– Pack Years– Mode Of Smoking
• ALCOHOL INTAKE
• TOBACCO CHEWING
PERSONAL HISTORY

04/17/2023 17
• Build and Nourishment• Pallor
GENERAL EXAMINATION

04/17/2023 18
LOCAL EXAMINATION

04/17/2023 19
INSPECTION
• REQUIREMENTS

04/17/2023 20
LIPS
• Exterior surface of lips
• Cleft lip
• Pigmentation
• Swelling / ulcer

04/17/2023 21
LIPS
• Evert the lip and examine the tissue.
• Observe frenulum attachment.

04/17/2023 22
LIPS
• Clear mucous filled pockets may be seen on the inner side of the lip (mucocele).
• This is a frequent, non-pathologic entity which represents a blocked minor salivary gland

04/17/2023 23
• To examine the gums lip must be everted fully.
• Healthy gums are bright pink in colour.
GUMS

GINGIVA
• Note color, tone, texture, architecture & mucogingival relationships
2404/17/2023
GUMS

GINGIVA
• How would you describe the gingiva?– Marginal vs. generalized?– Erythematous vs. fibrous
• Drug reactions: Anti-epileptic, calcium channel blockers, immunosuppressant
2504/17/2023
GUMS

04/17/2023 26
GUMS
• Cancrum oris is infective ulceration affecting alveolous and progresses to produce orocutaneous fistula.

04/17/2023 27
BUCCAL MUCOSA
• Observe color, character of the mucosa
• Stenson’s duct

04/17/2023 28
• LEUKOPLAKIA / ERYTHROPLAKIA
BUCCAL MUCOSA

04/17/2023
Lesions – white, red
Lichen Planus, Submucous fibrosis
29
BUCCAL MUCOSA

04/17/2023 30
• Congenital cleft• Perforation• Ulceration• swelling
PALATE

04/17/2023 31
TONGUE
VOLUME• Macroglossia
COLOUR• White – • Red glazed tongue• Blue• black

04/17/2023 32
ULCER• Tuberculous – tip and lateral borders
• Gummatous – dorsum
• Carcinomatous – anywhere
• Dental – lateral borders and ventral surface
TONGUE

04/17/2023 33
Lingual thyroid – • swelling at foramen caecum
Mobility of tongueAnkyloglossia
TONGUE

04/17/2023
TONGUE
• The tongue and the floor of the mouth are the most common places for oral cancer to occur.
• It can occur other places; so visualize all areas
• You may observe:– Circumvallate papillae, epiglottis
34

04/17/2023
• Wrap the tongue in a dry gauze and gently pull it from side to side to observe the lateral borders
35
TONGUE

• You may observe lingual varicosities
36
TONGUE
04/17/2023

Exam: Tongue
• geographic tongue (erythema migrans)
37
TONGUE
04/17/2023

Exam: Tongue
• You may observe drug reaction
38
TONGUE
04/17/2023

• Observe signs of nutritional deficiencies, immune dysfunction
39
TONGUE
04/17/2023

• Ulceration, proliferative growth
40
TONGUE
04/17/2023

04/17/2023 41
• Frenulum
• Ranula
• Sublingual dermoid
FLOOR OF MOUTH

04/17/2023 42
PALPATION

04/17/2023 43
LIP
• Any lesion of lip should be palpated
• Benign neoplasms are firm & lobulated
• Carcinoma – hard

04/17/2023 44
• Apthous ulcers – small discrete shallow tender ulcers with a rim of inflammation

04/17/2023 45
LIP
• Hunterian chancre - in primary syphilis is rubbery hard

04/17/2023 46
LIP
Carcinoma of lip • hard in consistency
• restricted mobility
• fixity

04/17/2023 47
TONGUE
• Method of palpation

04/17/2023 48
• Dental ulcers are very tender with no induration of edge / base.
• Carcinomatous ulcers show induration of base and edge.
TONGUE

04/17/2023 49
PALATE
• Hard irregular swelling on hard palate with normal appearing overlying mucosa – minor salivary gland tumor
• Malignant lesions of hard palate are hard fixed ulcerative or proliferative lesions

04/17/2023 50
ALVEOLUS AND GINGIVA

04/17/2023 51
ALVEOLUS AND GINGIVA
• GINGIVITIS
• GINGIVAL HYPERTROPHY
• EPULIS
• ALVEOLAR CARCINOMA

04/17/2023 52
FLOOR OF MOUTH
• UNIDIGITAL PALPATION
• BIDIGITAL PALPATION
• RANULA

04/17/2023 53
RANULA

04/17/2023 54
BUCCAL MUCOSA

04/17/2023 55
MANDIBLE
• Bidigital palpation of mandible
• Temporo mandibular joint
• Movements at TMJ

04/17/2023 56

04/17/2023 57
PALPATION OF LYMPH NODES

04/17/2023 58

04/17/2023 59

04/17/2023 60

04/17/2023 61
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF ULCERS ONN TONGUE
• Apthous ulcers• Dental ulcers• Carcinomatous• Syphilis• Tuberculous

04/17/2023 62
INVESTIGATIONS
• HAEMOGRAM• WEDGE BIOPSY FROM EDGE OF ULCER• FNAC OF LYMPH NODES• CECT OF NECK• ORTHOPANTOMOGRAM

04/17/2023 63
ORTHOPANTOMOGRAM

04/17/2023 64

04/17/2023 65